Abstract
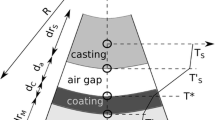
Accurate thermal modeling of the direct-chill casting process relies nowadays on increasingly complex boundary conditions for the secondary cooling zone. A two-dimensional axisymmetric finite-element model of the direct-chill casting process was developed to quantify the importance of secondary cooling at the surface compared with internal heat conduction within the billet. Boiling water heat transfer at the surface was found to dominate and be the governing factor only when stable film boiling or water film ejection take place; all other cases were dominated by internal heat conduction. The influence of various parameters (casting speed, cooling water flow rate, and thermophysical properties of the cast material) on the occurrence of water film ejection was analyzed. An exponential relationship was found between the cooling water flow rate and the minimum casting speed at which water film ejection takes place.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Grandfield and L. Wang: Light Metals 2004, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 685–90.
W. Roth: Aluminium, 1943, vol. 25, pp. 283-91.
D.C. Weckman and P. Niessen: Metall. Trans. B, 1982, vol. 13B, pp. 593-602.
H. Klein: Giesserei, 1953, vol. 10, pp. 441-54.
R. Siegel: Int. J. Heat Mass Trans., 1978, vol. 21, pp. 1421-30.
D.J.P. Adenis, K.H. Coats, and D.V. Ragone: J. Inst. Met., 1962–63, vol. 91, pp. 395–403.
D.A. Peel and A.E. Pengelly: Iron Steel Inst., 1969, vol. 23, pp. 186-96.
D.C. Weckman, R.J. Pick, and P. Niessen: Z. Metallkunde, 1979, vol. 70, no. 11, pp. 750-57.
J. Du, B.S.J. Kang, K.M. Chang, and J. Harris: Light Metals 1998, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1998, pp. 1025–30.
G.P. Grealy, J.L. Davis, E.K. Jensen, P.A. Tøndel, and J. Moritz: Light Metals 2001, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2001, pp. 813–21.
J.G. Collier and J.R. Thome: Convective Boiling and Condensation, 4th ed., Oxford University Press, New York, NY, 1996, pp. 148-69.
E. Caron: Ph.D. Dissertation, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Cananda, 2008.
J. Sengupta, S.L. Cockcroft, D.M. Maijer, M.A. Wells, and A. Larouche: J. Light Met., 2002, vol. 2, pp. 137-48.
J. Sengupta, S.L. Cockcroft, D.M. Maijer, M.A. Wells, and A. Larouche: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 532-39.
A. Håkonsen and O.R. Myhr: Cast Met., 1995, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 147-57.
L. Maenner, B. Magning, and Y. Caratini: Light Metals 1997, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 701–07.
J.F. Grandfield, A. Hoadley, and S. Instone: Light Metals 1997, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 1081–90.
H. Hao, D.M. Maijer, M.A. Wells, S.L. Cockcroft, D. Sediako, and S. Hibbins: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 3842-54.
E. Caron and M.A. Wells: in Aluminium Alloys: Their Physical and Mechanical Properties, J. Hirsch, B. Skrotzki, and G. Gottstein, eds., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2008, vol. 1, pp. 400–06.
E. Caron and M.A. Wells: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 585-95.
D.R. Poirier and E.J. Poirier: J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc., 1992, pp. 41–44.
H. Yu: Light Metals 2005, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005, pp. 983–87.
A. Larouche, Y. Caron, and D. Kocaefe: Light Metals 1998, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1998, pp. 1059–64.
J.F. Grandfield, A. Hoadley, and S. Instone: Light Metals 1997, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 691–99.
J. Langlais, T. Bourgeois, Y. Caron, G. Beland, and D. Bernard: Light Metals 1995, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1995, pp. 979–86.
H. Yu: Light Metals 1980, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1980, pp. 613–28.
R.F.T. Wilkins: Light Metals 1983, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1983, pp. 907–20.
R.E. Greene and J.L. Kirby: Light Metals 1989, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989, pp. 859–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 30, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caron, E., Wells, M.A. Film Boiling and Water Film Ejection in the Secondary Cooling Zone of the Direct-Chill Casting Process. Metall Mater Trans B 43, 155–162 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9579-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9579-1