Abstract
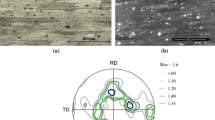
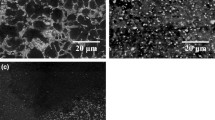
The main aim of the current study is the analysis of friction stir processing (FSP) of Mg-based alloys as a possible tool for nanocomposites production. The study reports microstructural changes taking place in a Mg-based alloy (AE42) subjected to FSP under different cooling conditions. The FSP process was carried out with single as well as multipass options. The friction stir processed samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), focused ion beam (FIB)-scanning ion microscopy (SIM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). It was observed that FSP tends to fragment the elongated precipitates and produces near homogeneous distribution of fine particles. The smallest particle size was observed to be produced by double-pass FSP supplemented by rapid cooling, thereby generating in situ nanocomposites. Vickers microhardness testing was done along the thickness (transverse direction) of the specimen to study and understand the variation of hardness with thickness. Nearly a two-times increase in the microhardness of AE42 was observed in the case of double-pass, FSP AE42 with cooling at temperature of approximately 253 K (–20 °C). To confirm these observations, another magnesium alloy AM50 was also friction stir processed under similar conditions. The fine submicron grain structure produced in AE42 alloy contributed immensely toward grain boundary strengthening and Orowan strengthening had only marginal influence. Subgrain boundary pinning by in situ nanoparticles contributed significantly in the strengthening process.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Friedrich and S. Schumann: J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 2001, vol. 117, pp. 276-81.
S.F. Hassan and M. Gupta: J. Alloy Comp., 2006, vol. 419, pp. 84-90.
Y. Morisada, H. Fujji, T. Nagaoka, and M. Fukusumi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 433, pp. 50-54.
B. Darras, M. Khraisheh, F. Abufarha, and M. Omar: J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 2007, vol. 191, pp. 77-81.
W. Woo, H. Choo, M. Prime, Z. Feng, and B. Clausen: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 1701-11.
Y. Morisada, H. Fujji, T. Nagaoka, and M. Fukusumi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 419, pp. 344-48.
C.I Chang, Y.N. Wang, H.R. Pei, C.J. Lee, C.H. Du, and J.C. Huang: Key Eng. Mater. Comp. Mater., 2007, vol. 351, pp.114-19.
C.I. Chang, Y.N. Wang, H.R. Pei, C.J. Lee, and J.C. Huang: Mater. Trans., 2006, vol. 47, pp. 2942-49.
P. Cavaliere and P.P. DeMarco: Mater. Proc. Tech., 2007, vol. 184, pp. 77-83.
P. Cavaliere and P.P. DeMarco: Mater. Charact., 2007, vol. 58, pp. 226-32.
S.K. Thakur, B.K. Dhindaw, N. Hort, and K.U. Kainer: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 1167-76.
S. Ugandhar, M. Gupta, and S.K. Sinha: Compos. Struct., 2006, vol. 72, pp. 256-72.
D.U. X. Hao and W.U. BaoLin: Sci. China Ser. E-Tech. Sci., 2009, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 1751-55.
H. Somekawa and T. Mukai: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 633-38.
V.N. Chuvildeev, T.G. Nieh, and M.Y. Gryaznov: Scripta Mater., 2004, vol. 50, pp. 861-65.
A. Yamashita, Z. Horita, and T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vol. 300A, pp. 142-47.
R.S. Mishra and M.W. Mahoney: Mater. Sci. Forum., 2001, vol. 357, no. 3, pp. 507-02.
R.S. Mishra, M.W. Mahoney, and S.X. McFadden: Scripta Mater., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 163-68.
S. Benavides, Y. Li, and L.E. Murr: Proc. Ultrafined Grained Materials Conf., 2000, pp. 155–68.
N. Saito, I. Shigematsu, and T. Komaya: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2001, vol. 20, pp. 1913-15.
Y.J. Kwon, N. Saito, and I. Shigematsu: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2002, vol. 21, pp. 1473-76.
T.A. Freeney and R.S. Mishra: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 73-84.
D.R. Ni, D. Wang, A.H. Feng, G. Yao, and Z.Y. Ma: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 61, pp. 568-71.
P. Cavaliere and P.P. DeMarco: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, vol. 184, pp. 77-83.
C.J. Hsu, C.Y. Chang, P.W. Kao, N.J. Ho, and C.P. Chang: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 5241-49.
C.J. Hsu, P.W. Kao, and N.J. Ho: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 3, pp. 341-45.
Q. Zhang, B.L. Xiao, Q.Z. Wang, and Z.Y. Ma: Mater. Lett., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 2070-72.
P. Asadi, G. Faraji, and M.K. Besharati: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 247-60.
E.R.I. Mahmouda, M. Takahashi, T. Shibayanagi, and K. Ikeuchi: Wear, 2010, vol. 268, pp. 1111-21.
C.J. Lee, J.C. Huang, and P.J. Hsieh: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1415-20.
P. Asadi, G. Faraji, A. Masoumi, and M.K. Besharati Givi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 2820–32.
A. Yazdipoura, A. ShafieiMc, and K. Dehghani: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 527, pp. 192-97.
X.Du. Hao and W.U. BaoLin: Sci. China Ser E-Tech. Sci., 2009, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 1751-55.
R.P. Dobriyal, B.K. Dhindaw, S. Muthukumaran, and S.K. Mukherjee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 477, pp. 243-49.
M.M. Avedesian and H. Baker: Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys ASM Specialty Handbook, 2nd ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1999.
L.Y. Wei, G.L. Dunlop, and H. Westengen: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1996, vol. 12, pp. 741-50.
M.J. Russell and H.R. Shercliff: Proc. First Int. Symposium on Friction Stir Welding, Thousand Oaks, CA, 1999.
Y. Morisada, H. Fujii, T. Nagaoka, and M. Fukusumi: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 55, pp. 1067-70.
C.J. Lee, J.C. Huang, and P.J. Hsieh: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1415-20.
C.J Lee and J.C. Huang: Mater. Trans., 2006, vol. 47, p. 2773.
C.I. Chang, X.U. Du, and J.C Huang: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 209-12.
C.I. Chang, X.U. Du, and J.C Huang: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 356-59.
X. Du. Hao and W.U. BaoLin: Sci. China Ser E-Tech. Sci., 2009, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 1751-55.
T.R. McNelley, S. Swaminathan, and J.Q. Su: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 349-54.
J.Q. Su, T.W. Nelson, and C.J. Sterling: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 405, p. 277.
S. Ganashanan, L.G. Hector Jr., and Z.K. Liu: Comp. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 301-07.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby: Deformation Mechanism Maps, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1982, p. 44.
W.D. Callister: Material Science and Engineering—An Introduction, 6th ed., Wiley, New York, NY, 2004, p. 118.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill Book Co., Columbus, OH, 1988, p. 711.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the help extended by Dr. David S. McPhail, Dr. S. Barbara and Mr. Richard J. Chater, Materials Department, Imperial College London, UK for TEM and FIB-SIMS analysis of the FSP specimens.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 5, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, H.S., Singh, H. & Dhindaw, B.K. Some Observations on Microstructural Changes in a Mg-Based AE42 Alloy Subjected to Friction Stir Processing. Metall Mater Trans B 43, 92–108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9573-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9573-7