Abstract
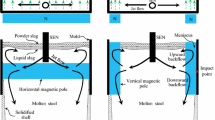
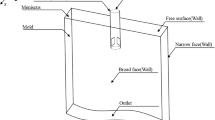
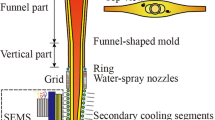
In the present work, a new type of magnet specially designed for the thin slab casting funnel shape mold is developed. The unique feature of the new type of magnet lies in the fact that, the inner surfaces of the new magnet facing the mold are irregular to fit the complex funnel shape, while the inner surfaces of the convential magnet are planar. Magnetic fields produced by both the new type and the conventional magnets are computed under the same number of ampere turns for comparison. Keeping the position of the magnet relative to the mold fixed, numerical simulations of the influence of the new and conventional type magnets on the flow field in the mold are made. The commercial software FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of electrically conducting fluid flow under the influence of static magnetic fields. For the computation of magnetic fields, the finite element method (FEM) is adopted, while for fluid flow, the finite volume method (FVM) based on structured body fitted coordinate grids is used. The results show that the new type of magnet can produce larger magnetic flux density in the mold region than the conventional one does with the same current intensity. For the funnel shape mold, the electromagnetic brake (EMBr) due to the new magnet can provide a more uniform downstream velocity profile than that due to the conventional magnet, and almost 40 pct reduction in ampere turns; this fact implies that a lot of electrical energy could be saved.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
magnetic flux density (T)
- C1, C2, C μ :
-
turbulence model constants
- E :
-
electric field intensity (Vm−1)
- F em :
-
Lorentz force (Nm−3)
- J :
-
current density (Am−2)
- k :
-
turbulent kinetic energy (m2 s−2)
- L :
-
characteristic length (m)
- p :
-
pressure (Pa)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- v :
-
velocity (ms−1)
- V :
-
velocity vector
- x :
-
coordinate (m)
- ε :
-
turbulence dissipation rate (m2 s−3)
- κ :
-
von Karman constant
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity (kgm−1 s−1)
- ρ :
-
density (kgm−3)
- σ k , σ ε :
-
turbulence model constants
- φ :
-
electric potential (Vm−1)
- σ :
-
electromagnetic conductivity (Sm−1)
- eff:
-
effective
- i, j :
-
component index
- inlet:
-
value at inlet entry
- l :
-
laminar
- t :
-
turbulent
References
Y.S. Hwang, P.R. Cha, H.S. Nam, K.H. Moon, and J.K. Yoon: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37 (7), pp. 659–67.
H. Tozawa, H. Kitaoka, K.I. Sorimachi, H. Ishizuka, M. Ohnishi, and S. Kakihara: Proc. 6th Int. Iron and Steel Congr., ISIJ, Tokyo, 1990, pp. 438–45.
Z.D. Qian, Y.L. Wu, B.W. Li, and J.C. He: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42 (11), pp. 1259–65.
D.S. Kim, W.S. Kim, and K.H. Cho: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40 (7), pp. 670–76.
T. Honeyands and J. Herbertson: Steel Res., 1995, vol. 66 (7), pp. 287–93.
B.W. Li, X.Y. Tian, E.G. Wang, and J.C. He: Acta Metall. Sinica (Eng. Lett.), 2007, vol. 20 (3), pp. 15–26.
H. Nam, H.S. Park, and J.K. Yoon: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40 (9), pp. 886–92.
H.S. Park, H. Nam, and J.K. Yoon: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41 (9), pp. 974–80.
Z.D. Qian, B.W. Li, G.L. Jia, and J.C. He: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41 (7), pp. 683–88.
B.K. Li and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46 (12), pp. 1833–38.
B.G. Thomas, Q. Yuan, and S. Sivaramakrishnan, T.B. Shi, S.P. Vanka, and M.B. Assar: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41 (10), pp. 1262–71.
Z.D. Qian and Y.L. Wu: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44 (1), pp. 100–07.
R. Hirayama, K Fujisaki, and T. Yamada: IEEE Trans. Magn., 2004, vol. 40 (4), pp. 2095–97.
W.P. Jones and B.E. Launder: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1972, vol. 15, pp. 301–14.
W.P. Jones and B.E. Launder: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1973, vol. 16, pp. 1119–30.
C.K.G. Lam and K. Bremhorst: J. Fluid Eng., 1981, vol. 103, pp. 456–60.
M.R. Aboutalebi, M. Hasan, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Numer. Heat Transfer, 1995, vol. 28A, pp. 279–99.
S.H. Seyedein and M. Hasan: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1997, vol. 40 (18), pp. 4405–23.
ANSYS Users Manual, ANSYS, Inc., 2003.
S.K. Choudhary and D. Mazumd: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34 (6), pp. 581–59.
C.P. Hong, S.Y. Lee, and K. Song: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41 (9), pp. 999–1005.
S.V. Patankar: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Hemisphere Publishers, New York, NY, 1980.
W.Q. Tao: Numerical Heat Transfer, 2nd ed., Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, Xi’an, 2001.
A.F. Lenhman, G.R. Tallblck, and H.R. Hackl: Proc. Int. Symp. on Electromagnetic Processing of Materials, ISIJ, Nagoya, 1994, pp. 372–77.
B.K. Li and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 844-849.
M.J. Cho: Numer. Heat Transfer, 2006, vol. 49B (6), pp. 599–15.
R. Moreau: Magnetohydrodynamics, Kluwer Academic Pub. Co, Norwell, MA, 1990.
M.J. Cho, I.C. Kim, S.J. Kim, and J.K. Kim: Trans. KSME, 1999, vol. 23B (13), pp. 1491–1502.
K. Cukierski and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 94–107.
FLUENT Manual, Fluent, Inc., Lebanon, NH, 2005.
Acknowledgment
This research was financially sponsored by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Contract No. 10772044.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 13, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, XY., Li, BW. & He, JC. Electromagnetic Brake Effects on the Funnel Shape Mold of a Thin Slab Caster Based on a New Type Magnet. Metall Mater Trans B 40, 596–604 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-009-9246-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-009-9246-y