Abstract
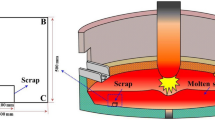
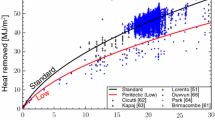
The melting rate of steel bars with various sizes, shapes, and initial temperatures in a 70 kg liquid steel bath (1650 °C) was measured to investigate the kinetics involved in steel scrap melting. Our measurements revealed that a solidified shell was formed around the original bar immediately after it was immersed into the liquid steel. This shell and an associated interfacial gap generated between it and the original bar were found to be critical to the melting kinetics. We also found that the total melting time decreased linearly with increasing initial bar temperature. The melting process was simulated using a two-dimensional phase-field model that considered heat convection with a constant heat-transfer coefficient. Our simulations were in good agreement with our experiments and showed that the heat conduction associated with the interfacial gap was one of the most important physical aspects controlling the melting of steel scrap.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Making, Shaping, and Treating of Steel: Steelmaking and Refining Volume, 11th ed., R.J. Fruehan, ed., AISE Steel Foundation, Pittsburgh, PA, 1998, pp. 525–48.
R.I.L. Guthrie and L. Gourtsoyannis: Can. Met. Q., 1971, vol. 10, pp. 37–46.
J. Szekely, Y.K. Chuang, and J.W. Hlinka: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 2825–33.
D.D. Burdakov and A.P. Varshavskii: Stal, 1968, No. 8, pp. 647–53 (in English).
Eckehard Specht and Rudolf Jeschar: Steel Res., 1993, vol. 64, pp. 28–34.
J.K. Wright: Metall. Trans. B, 1989, vol. 20B, pp. 363–74.
H. Gaye, P. Destannes, J.L. Roth, and M. Guyon: Proc. 6th Int. Iron and Steel Congr., ISIJ, Nagoya, Japan, 1990, pp. 11–17.
Q. Jiao and N.J. Themelis: Can. Met. Q., 1993, vol. 32, pp. 75–83.
Metals Handbook, vol. 1, Properties and Selections: Iron and Steel, 10th ed., S.R. Lampman et al., eds., ASM, Materials Park, OH, 1990, pp. 140–95.
B. Collins and H. Levine: Phys. Rev. B, 1985, vol. 31, pp. 6119–22.
A. Karma and W.J. Rappel: Phys. Rev. E, 1998, vol. 57, pp. 4323–29.
N. Provatas, J. Dantzig, and N. Goldenfeld: Phys. Rev. Lett., 1998, vol. 8, pp. 3308–11.
N. Provatas and J. Dantzig: The Encyclopedia of Material Science and Technology, World Scientific, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2001, pp. 2052–59.
B. Grossmann, K. Elder, M. Grant, and J.M. Kosterlitz: Phys. Rev. Lett., 1993, vol. 20, pp. 3323–26.
K.R. Elder, M. Grant, N. Provatas, and J.M. Kosterlitz: Phys. Rev. E, 2001, vol. 64, pp. 1604–21.
M. Chaikin and T.C. Lubensky: Principles of Condensed matter Physics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1995, p. 467.
Jun-Ho Jeong, N. Goldenfield, and J. Dantzig: Phys. Rev. E, 2001, vol. 64, pp. 041602(1–14).
H. Landau and M.J. Paez: Computational Physics: Problem Solving with Computers, Wiley, New York, NY, 1997, pp. 343–62.
Guowei Li and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 509–25.
J. Ni and C. Beckermann: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22B, pp. 349–61.
W.D. Bennon and F.P. Incropera: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1987, vol. 30, pp. 2161–70.
W.D. Bennon and F.P. Incropera: Num. Heat Transfer, 1988, vol. 13, pp. 277–96.
R.I.L. Guthrie: Engineering in Process Metallurg, Oxford Science Publications, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1993, p. 483.
Handbook of Physico-Chemical Properties at High Temperatures, Yasuji Kawai and Yutake Shiraishi, eds., ISIJ, Tokyo, 1988, pp. 2–257.
Introduction to Heat Transfer, Junqin Zhou, ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1999, p. 163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Provatas, N. & Brooks, G. Kinetics of scrap melting in liquid steel. Metall Mater Trans B 36, 293–302 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-005-0031-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-005-0031-2