Abstract
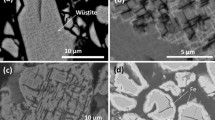
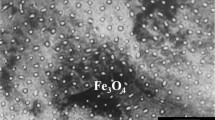
In order to understand the microreaction mechanism of the reduction of magnetite to wustite, hydrogen ions were implanted into magnetite at room temperature by an ion accelerator. The crystalloid transformation during the reduction process was investigated by using selected-area electron diffraction patterns. The experimental results showed that {220} planes on the surface of magnetite were changed first because the concentration of oxygen ions on the {220} planes is higher than other planes to follow the reaction of oxygen ions with hydrogen ions, leaving the {220} planes and resulting in rearrangement of ions. On the other hand, oxygen ions migrate more difficulty than iron ions in magnetite; therefore, {220} planes in the bulk are more stable than other planes. Based on the experimental facts, two kinds of microreaction mechanisms in reduction of magnetite to wustite are suggested. It was found that (1) wustite with [001] direction was formed on the magnetite with [001] direction, (2) (220) and (200) planes of wustite were parallel with (220) and (400) planes of magnetite, respectively, in crystal structure between parent phase and new phase, (3) some {220} planes were formed earlier than other ones in wustite during the reduction process. These results can be considered as due to the similar geometric distribution of oxygen ions between magnetite and wustite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.T. Turkdogan and J.V. Vinters: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1561–74.
J.W. Evans and K. Haase: High Temp. Sci., 1976, vol. 8, pp. 167–77.
J.O. Edstrom: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, vol. 175, pp. 289–304.
J.O. Edstrom and G. Bitsianes: AIME Trans., 1955, vol. 203, pp. 760–65.
S.K. El-Rahaiby and Y.K. Rao: Metall. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 257–69.
C.H. Koo and J.W. Evans: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1980, vol. 19, pp. 95–101.
Y.K. Rao and M. Moinpour: Metall. Trans. B, 1983, vol. 14B, pp. 711–23.
M.M. Al-Kahtany and Y.K. Rao: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1980, vol. 7, pp. 49–58.
S.K. El-Rahaiby and Y.K. Rao: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1980, vol. 20, pp. 287–91.
D.H. St. John and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Trans. B, 1982, vol. 13B, pp. 117–24.
D.H. St. John, S.P. Matthew, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 709–17.
W. Pluschkell and H. Yoshikoshi: Arch. Eisenhuttenwes., 1970, vol. 41, pp. 715–21.
Y.K. Rao: Metall. Trans. B, 1979, vol. 10B, pp. 243–55.
P.R. Swann and N.J. Tighe: Metall. Trans. B, 1977, vol. 8B, pp. 479–87.
J.R. Porter and P.R. Swann: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1977, vol. 5, pp. 300–07.
Mann-Fu Rau, David Rieck, and James W. Evans: Metall. Trans. B, 1987, vol. 18B, pp. 257–78.
M. Katsumi, Y. Tamura, Y. Kashiwaya, and K. Ishii: 6th Int. Iron and Steel Congr., Nagoya, Japan, 1990, vol. 1, pp. 50–57.
Y. Watanabe, S. Takemura, Y. Kashiwaya, and K. Ishii, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 1996, vol. 29, pp. 8–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Sasaki, Y., Kashiwaya, Y. et al. Microreaction mechanism in reduction of magnetite to wustite. Metall Mater Trans B 35, 517–522 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-004-0052-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-004-0052-2