Abstract
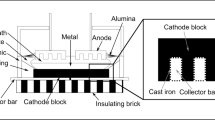
The study shows examples of the distribution of melt components in spent carbon cathodes from 16 industrial aluminum electrolysis cells shut down after 10 to 2534 days. The concentration of the phases was determined by quantitative X-ray diffraction (XRD), and the distribution was found by analyzing series of samples from several vertical cores from each cathode. The results show that the analysis is useful for characterizing phases in spent potlining, and the detailed distribution graphs are suitable for comparing different parts of a cathode, or different cathodes. The composition of the melt in the 16 cathodes changed systematically over time, and the stages in the evolution, the effect of the cathode material type, and the effect of the melt on the lining are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Brilloit, L.P. Lossius, and H.A. Øye: Metall. Trans. B, 1993, vol. 24B, pp. 75–89.
P. Brilloit, L.P. Lossius, and H.A. Øye: Light Met., 1994, pp. 1237–46. This is a corrected version of Light Met., 1993, pp. 321–30.
L.P. Lossius and H.A. Øye: Light Met., 1993, pp. 331–40.
R. Shamsili and H.A. Øye: Light Met., 1994, pp. 731–38.
R. Shamsili: Melt Penetration and Chemical Reactions in Carbon Cathodes during Aluminium Electrolysis, Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, 1996.
K.R. Kvam and L.P. Lossius: Int. Harald A. Øye Symp., M. Sørlie, T. Østvold, and R. Huglen, eds., Norwegian Institute of Technology, Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Trondheim, 1995, pp. 203–11.
M. Sørlie and H. A. Øye: Cathodes in Aluminium Electrolysis, 2nd ed., Aluminium-Verlag GmbH, Düsseldorf, 1994.
H. Schreiner and H.A. Øye: Light Met., 1995, pp. 463–72.
X. Liao and H.A. Øye: Light Met., 1998, pp. 659–66.
“ChemSage Application Software for Thermodynamical Calculations with SGTE Pure Substance Databases SOR94G02 (Organic) and SPS94T02 (Inorganic), ChemSage Handbook,” Version 3.0.1, GTT Technologies, Herzogenrath, 1994.
M. Sørlie, H. Gran, and H.A. Øye: Light Met., 1995, pp. 497–506.
“Unscrambler for PC Win 3.1/95/NT Ver. 7.0, A Program for Design of Experiments and Chemometric Analysis of Data,” Camo ASA, Trondheim, 1998.
K. Grjotheim, C. Krohn, M. Malinovsky, K. Matiasovsky, and J. Thonstad: Aluminium Electrolysis, 2nd ed., Aluminium-Verlag, Duesseldorf, 1982.
J.L. Holm: Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, University of Trondheim NTH, Trondheim, 1971.
Y. Mikhalev and H.A. Øye: Carbon, 1995, pp. 37–41.
J. Thonstad and S. Rolseth: Electrochemica Acta, 1978, vol. 23, pp. 233–41.
M.B. Dell: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 277–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lossius, L.P., Øye, H.A. Melt penetration and chemical reactions in 16 industrial aluminum carbon cathodes. Metall Mater Trans B 31, 1213–1224 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-000-0008-0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-000-0008-0