Abstract
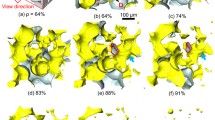
During coarsening of high-volume-fraction solid-liquid mixtures, a solid skeleton is formed. Electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) analysis of Sn particles in a liquid Pb-Sn eutectic is employed to yield quantitative evidence for the mechanisms that are operative during skeletal formation. We find that the grain boundaries (GBs) play a substantial role in setting the skeletal structure; however, they do not alter the mechanisms for skeletal coarsening. Particles do not rotate into low-energy configurations to minimize the GB energy in the solid-liquid mixture. Thus, there is no particle rotation-induced coalescence. We find that coalescence is not prevalent; Ostwald ripening is the primary mechanism for coarsening in this system. Our data suggest a model for skeletal formation and the origin of the skeletal stability. This model indicates that the primary factor in determining skeletal stability is the number of GB contacts. We recommend two methods to tailor the number of GBs and to engineer the properties of these solid-liquid mixtures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Masuda and R. Watanabe: Sintering Processes, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1980, pp. 3–22.
A. Niemi and T. Courtney: J. Mater. Sci., 1981, vol. 16, p. 226.
W. Kaysser, S. Takajo, and G. Petzow: Z. Metallkd., 1982, vol. 73, p. 579.
R.M. German, A. Bose, and S.S. Mani: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 211–19.
S. Kang and D. Yoon: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1405–11.
S.B. Brown and M.C. Flemings: Adv. Mater. Processes, 1993, vol. 143, p. 36.
R.M. German: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 909–14.
W.A. Kaysser, S. Takajo, and G. Petzow: Mod. Rev. Powder Metall., 1981, vol. 12, p. 473.
P.W. Voorhees: Technical Report, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, 1989.
S.C. Hardy and P.W. Voorhees: Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2713–21.
T.L. Wolfsdorf-Brenner, H. Wong, and P.W. Voorhees: 1997, unpublished research.
Orientation Imaging Microscopy, TexSEM Laboratories, Inc., Provo, UT, 84604.
G. Petzow: Metallographic Etching, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1978, pp. 79–85.
J.D. Gibbons: Nonparamatric Methods for Quantitative Analysis, American Sciences Press, Inc., Columbus, OH, 1971, pp. 241–72,
J. Sutliff: General Electric Corporate Research and Development, Schenectedy, NY, personal communication, 1996.
P.W. Voorhees, G.B. McFadden, R.F. Boisvert, and D.I. Meiron: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, p. 207.
P. Haasen: Metall. Trans. A., 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 1001–15.
T.L. Wolfsdorf, W.H. Bender, and P.W. Voorhees: Acta Mater., vol. 45, 1997, p. 2279.
H. Grimmer: Scripta Metall., 1979, vol. 13, p. 161.
A. Garbacz and M.W. Grabski: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, p. 469.
A. Garbacz and M.W. Grabski: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, p. 475.
I.V. Alexandrov, A.P. Zhilyaev, V.Y. Gertsman, and A.I. Pshenichnyuk: Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 1995, vol. 3, p. 149.
S.I. Wright and D. Field: Proc.: Microscopy and Microanalysis, G.W. Bailey et al., eds., Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1997.
A. Singh and A.H. King: Acta Cryst., 1993, vol. 49, p. 266.
S.S. Kim and D.N. Yoon: Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31, p. 1151.
D.N. Yoon and W.J. Huppman: Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, p. 973.
G. Herrmann, H. Gleiter, and G. Baro: Acta Metall., 1976, vol. 24, p. 353.
R. Balluffi: Scripta Metall., 1988, vol. 22, p. 709.
P.G. Shewmon: Recrystallization, Grain Growth and Textures, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1966, p. 165.
G. Gessinger, F.V. Lenel, and G.S. Ansell: Scripta Metall., 1968, vol. 2, p. 547.
K.P. Wieters, I.J. Boiko, and W. Schatt: Crystal Res. Technol., 1984, vol. 19, p. 1195.
S.M. Allameh, S.A. Dregia, and P.G. Shewmon: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, p. 2887.
G. Martin: Phys. Status Solidi (b), 1992, vol. 172, p. 121.
M.T. Lyttle and J.A. Wert: Advances in Hot Deformation Textures and Microstructures, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 373–83.
T.H. Courtney: Scripta Mater., 1996, vol. 35, p. 567.
S.-W. Chan: Ph.D. Thesis, MIT, Cambridge, MA, 1985.
A. Upadhyaya and R.M. German: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, p. 2631.
A.N. Niemi, L.E. Baxa, J.K. Lee, and T.H. Courtney: Mod. Rev. Powder Metall., 1981, vol. 12, p. 483.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolfsdorf-Brenner, T.L., Voorhees, P.W. & Sutliff, J. Texture evolution and the role of grain boundaries in skeletal formation during coarsening in solid-liquid mixtures. Metall Mater Trans A 30, 1955–1969 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0006-z
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0006-z