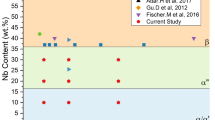
Abstract
Commercial load-bearing implant applications have detrimental stress-shielding effects. In this study, the molybdenum equivalence (Moeq) and molecular orbital methods were used in the composition design of low modulus Ti–35Nb–15Zr (at. pct) alloys. Based on Taguchi’s experimental design, the relationship between the process parameters (laser power, scanning speed, hatch spacing) and the performance (surface quality, porosity, and mechanical properties) of the sample fabricated by LPBF with a small spot diameter (30 μm) was studied. The use of EL is more effective in determining the process window. A surface roughness below 3 µm, porosity of less than 1 pct, and hardness of up to 391 HV of the samples were obtained at a laser power of 250 to 300 W, scanning speed of 400 to 600 mm/s, and hatch spacing of 35 µm. Ti–35Nb–15Zr (at. pct) alloys with Young’s modulus of 72.82 ± 0.77 GPa and yield strength of 1185.18 ± 41.79 MPa were obtained at a laser power of 250 W, and the values of both increased with the increasing laser power. The intensity of the β texture was also revealed to be related to the hatch spacing. As the hatch spacing increases, the intensity of β-texture decreases from 4.87 to 1.83 times from H35 to H60. Additionally, the correlations between process parameters and resultant properties were defined in study. The scan speed showed the highest correlation with surface roughness, porosity, and hardness, while the hatch spacing mainly affected surface roughness and hardness. Laser power had decreasing effects on porosity, surface roughness, and hardness in that order.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Azgomi, F. Tetteh, and S. Boakye-Yiadom: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2022, vol. 53A, pp. 1069–84.
B. Moretti, V. Pesce, G. Maccagnano, G. Vicenti, P. Lovreglio, L. Soleo, and P. Apostoli: The Lancet, 2012, vol. 379, p. 1676.
A. Mirza, A. King, C. Troakes, and C. Exley: J. Trace Elem. Med Biol., 2017, vol. 40, pp. 30–36.
M. Geetha, A.K. Singh, R. Asokamani, and A.K. Gogia: Prog. Mater Sci., 2009, vol. 54, pp. 397–425.
C.-W. Kang and F.-Z. Fang: Adv. Manuf., 2018, vol. 6, pp. 20–40.
S. Ozan, J. Lin, Y. Li, R. Ipek, and C. Wen: Acta Biomater., 2015, vol. 20, pp. 176–87.
J.C. Wang, Y.J. Liu, P. Qin, S.X. Liang, T.B. Sercombe, and L.C. Zhang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, vol. 760, pp. 214–24.
Z. X. Wenhui Yu, X. Zhang, Y. Sun, P. Xue, S. Tan, Y. Wu, H. Zheng: Mater. Sci. Addit. Manuf. (2022).
L.M. Elias, S.G. Schneider, S. Schneider, H.M. Silva, and F. Malvisi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 432, pp. 108–12.
M.H.C. Tan, A.D. Baghi, R. Ghomashchi, W. Xiao, and R.H. Oskouei: J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2019, vol. 99, pp. 78–85.
H.-C. Hsu, S.-C. Wu, S.-K. Hsu, J.-Y. Syu, and W.-F. Ho: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 568, pp. 1–7.
D. Doraiswamy and S. Ankem: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 1607–19.
Y.L. Hao, S.J. Li, S.Y. Sun, and R. Yang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 441, pp. 112–18.
M. Abdel-Hady, K. Hinoshita, and M. Morinaga: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 55, pp. 477–80.
S.-J. Dai, Y. Wang, F. Chen, X.-Q. Yu, and Y.-F. Zhang: Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China, 2013, vol. 23, pp. 3027–32.
R. Karre and S.R. Dey: Encyclopedia of Smart Materials, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019, pp. 512–27.
S.L. Sing, S. Huang, G.D. Goh, G.L. Goh, C.F. Tey, J.H.K. Tan, and W.Y. Yeong: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2021, vol. 119, 100795.
Y.J. Liu, S.J. Li, L.C. Zhang, Y.L. Hao, and T.B. Sercombe: Scripta Mater., 2018, vol. 153, pp. 99–103.
D.B. Witkin, R.W. Hayes, T.D. McLouth, and G.E. Bean: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, vol. 50A, pp. 3458–65.
R. Tosi, E. Muzangaza, X.P. Tan, D. Wimpenny, and M.M. Attallah: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2022, vol. 53A, pp. 927–41.
T.C. Niemeyer, C.R. Grandini, L.M.C. Pinto, A.C.D. Angelo, and S.G. Schneider: J. Alloy Compd., 2009, vol. 476, pp. 172–75.
H. Azizi, H. Zurob, B. Bose, S.R. Ghiaasiaan, X. Wang, S. Coulson, V. Duz, and A.B. Phillion: Addit. Manuf., 2018, vol. 21, pp. 529–35.
B. Zhang, S. Zhang, H. Yang, D. Peng, Y. Wang, and H. Zhu: J. Manuf. Process., 2022, vol. 84, pp. 1150–61.
C. Schwerz, F. Schulz, E. Natesan, and L. Nyborg: J. Manuf. Process., 2022, vol. 78, pp. 231–41.
S. Pilz, T. Gustmann, F. Günther, M. Zimmermann, U. Kühn, and A. Gebert: Mater. Des., 2022, vol. 216, 110516.
H. Zhang, C. Zhou, and C. Wei: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, vol. 254, pp. 1–12.
R. Li, M. Wang, T. Yuan, B. Song, C. Chen, K. Zhou, and P. Cao: Powder Technol., 2017, vol. 319, pp. 117–28.
X. Li, Y. Liu, and Z. Zhou: J. Manuf. Process., 2022, vol. 81, pp. 78–91.
W. Shao, B. He, C. Qiu, and Z. Li: Opt. Laser Technol., 2022, vol. 156, 108609.
S. Qu, J. Ding, J. Fu, M. Fu, B. Zhang, and X. Song: Addit. Manuf., 2021, vol. 48, 102417.
G.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liang, B. Kim, and P.E.J. Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, vol. 756, pp. 156–60.
M.-W. Wu and P.-H. Lai: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, vol. 658, pp. 429–38.
C. Panwisawas, C.L. Qiu, Y. Sovani, J.W. Brooks, M.M. Attallah, and H.C. Basoalto: Scripta Mater., 2015, vol. 105, pp. 14–17.
B. Feng, C. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Ren, L. Cui, Q. Yang, and S. Hao: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2022, vol. 840, 142965.
X.P. Song, L. You, B. Zhang, and A. Song: Mater. Technol., 2012, vol. 27, pp. 55–57.
R. Duan, S. Li, B. Cai, W. Zhu, F. Ren, and M.M. Attallah: Addit. Manuf., 2021, vol. 37, 101708.
S.H. Lee, M. Todai, M. Tane, K. Hagihara, H. Nakajima, and T. Nakano: J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2012, vol. 14, pp. 48–54.
Q. Wei, L. Wang, Y. Fu, J. Qin, W. Lu, and D. Zhang: Mater. Des., 2011, vol. 32, pp. 2934–39.
F.N. Depboylu, E. Yasa, Ö. Poyraz, J. Minguella-Canela, F. Korkusuz, and M.A. De los Santos López: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, vol. 17, pp. 1408–26.
M. Shahedi Asl, S.A. Delbari, M. Azadbeh, A. Sabahi Namini, M. Mehrabian, V.-H. Nguyen, Q.V. Le, M. Shokouhimehr, and M. Mohammadi: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 9, pp. 10647–58.
Y. Chen, P. Han, A. Dehghan-Manshadi, D. Kent, S. Ehtemam-Haghighi, C. Jowers, M. Bermingham, T. Li, J. Cooper-White, and M.S. Dargusch: J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2020, vol. 104, 103691.
D. Cai, X. Zhao, L. Yang, R. Wang, G. Qin, D.-F. Chen, and E. Zhang: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, vol. 81, pp. 13–25.
T. Lee, Y.-U. Heo, and C.S. Lee: Scripta Mater., 2013, vol. 69, pp. 785–88.
R. Ummethala, P.S. Karamched, S. Rathinavelu, N. Singh, A. Aggarwal, K. Sun, E. Ivanov, L. Kollo, I. Okulov, J. Eckert, and K.G. Prashanth: Materialia, 2020, vol. 14, 100941.
E. Chlebus, B. Kuźnicka, T. Kurzynowski, and B. Dybała: Mater. Charact., 2011, vol. 62, pp. 488–95.
H. Schwab, K.G. Prashanth, L. Lober, U. Kuhn, and J. Eckert: Metals, 2015, vol. 5, pp. 686–94.
Q. Wang, C.J. Han, T. Choma, Q.S. Wei, C.Z. Yan, B. Song, and Y.S. Shi: Mater. Des., 2017, vol. 126, pp. 268–77.
J.M. Walker, C. Haberland, M.T. Andani, H.E. Karaca, D. Dean, and M. Elahinia: J. Intel. Mater. Syst. Str., 2016, vol. 27, pp. 2653–60.
C. Haberland, M. Elahinia, J.M. Walker, H. Meier, and J. Frenzel: Smart Mater. Struct., 2014, vol. 23, p. 104002.
Z. Zhao, C. Wang, Q. Yu, L. Song, G. Yang, and J. Zhang: Mater. Charact., 2022, vol. 189, 111917.
L. You and X. Song: Scripta Mater., 2012, vol. 67, pp. 57–60.
N. Sakaguch, M. Niinomi, and T. Akahori: Mater. Trans., 2004, vol. 45, pp. 1113–19.
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by the Open Fund (No. 202101) of Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology, Ministry of Education, P.R. China, and the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (Grant No. JGY2021001). Yurong Wang acknowledged Dr. Liang for the discussion during the revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ contributed to conceptualization, writing—review & editing. YW contributed to writing—original draft, writing—review & editing, investigation, and validation. GZ contributed to data curation. LH contributed to supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Zhi, G. et al. A Novel Biomedical Ti–35Nb–15Zr (At. Pct) Alloy In Situ Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion: Processing Window, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 4356–4371 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07170-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07170-1