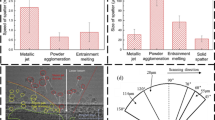
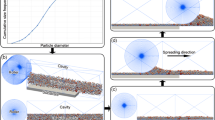
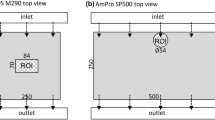
Abstract
Powder bed fusion using a laser beam (PBF-LB) is rapidly developing toward high laser power, high scanning speed, and multiple lasers; however, spatter has become one of the major bottlenecks limiting PBF-LB to form large metal parts. In this paper, the Eulerian–Lagrangian numerical simulation study was carried out for the spatter formation and spatter-protective gas flow coupling behavior. Among them, the Eulerian model considered the effect of particles on the gas-phase flow, and the Lagrangian model took into account the fluid drag force, gravity, buoyancy, non-uniform pressure distribution, additional mass force, and particle–particle collisions. For the effect of metal vapor on spatter and powder bed denudation, it was found that the larger the metal vapor jet speed or jet area, the faster the spatter speed and the larger the width of the powder bed denudation zone; the larger the lateral dimension of the metal vapor action zone (the scanning direction is longitudinal), the larger the number of spatters. For the effect of protective gas flow velocity on spatter movement, it was found that the longitudinal movement distance of spatter was significantly larger for larger protective gas flow velocity, and almost all spatters fell on the powder bed or substrate for smaller protective gas flow velocity. This paper is expected to provide scientific guidance for regulating PBF-LB spatter.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.M. Sefene: Manuf. Syst., 2022, vol. 63, pp. 250–74.
M.T. Andani, R. Dehghani, M.R. Karamooz-Ravari, R. Mirzaeifar, and J. Ni: Mater. Design, 2017, vol. 131, pp. 460–69.
Y. Liu, Y.Q. Yang, S.Z. Mai, D. Wang, and C.H. Song: Mater. Design, 2015, vol. 87, pp. 797–806.
S. Ly, A.M. Rubenchik, S.A. Khairallah, G. Guss, and M.J. Matthews: Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, p. 4085.
M.J. Matthews, G. Guss, S.A. Khairallah, A.M. Rubenchik, P.J. Depond, and W.E. King: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 114, pp. 33–42.
D. Wang, W.H. Dou, Y.H. Ou, Y.Q. Yang, C.L. Tan, and Y.J. Zhang: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, vol. 12, pp. 1051–64.
L.I. Escano, N.D. Parab, L.H. Xiong, Q.L. Guo, C. Zhao, T. Sun, and L.Y. Chen: Synchrotron Radiation News, 2019, vol. 32, pp. 9–13.
S.Y. Luo, X.Q. Ma, J. Xu, M.L. Li, and L.C. Cao: Sensors, 2021, vol. 21, p. 7179.
M. Slodczyk, A. Ilin, T. Kiedrowski, T. Bareth, and V. Ploshikhin: Mater. Design, 2021, vol. 212, p. 110206.
W.H. Zhang, H.L. Ma, Q. Zhang, and S.Q. Fan: Mater. Design, 2022, vol. 213, p. 110301.
C. Pauzon, B. Hoppe, T. Pichler, S.D.-L. Goff, P. Forêt, T. Nguyen, and E. Hryha: CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol., 2021, vol. 35, pp. 371–78.
Z.A. Young, Q.L. Guo, N.D. Parab, C. Zhao, M.L. Qu, L.I. Escano, K. Fezzaa, W. Everhart, T. Sun, and L.Y. Chen: Addit. Manuf., 2020, vol. 36, 101438.
T. Tran-Le, J. X. Wang, M. Byron, S. Lynch, R. Kunz: Proceedings of the ASME 2021, 2021, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/IMECE2021-69550.
M.L. Qu, Q.L. Guo, L.I. Escano, A. Nabaa, S.M.H. Hojjatzadeh, Z.A. Young, and L.Y. Chen: Nat. Commun., 2022, vol. 13, p. 1079.
R. Kasper, J. Turnow, and N. Kornev: Int. J. Heat Fluid Fl., 2019, vol. 79, p. 108462.
H. Chen, Y.J. Zhang, A. Giam, and W.T. Yan: Addit. Manuf., 2022, vol. 52, p. 102645.
H. Chen and W.Y. Yan: Acta Mater., 2020, vol. 196, pp. 154–67.
C.-Y. Chien, T.-N. Le, Z.-H. Lin, and Y.-L. Lo: Mater. Design, 2021, vol. 210, p. 110107.
T. Yu and J.D. Zhao: Comput. Method. Appl. Mater., 2021, vol. 377, p. 113707.
X.B. Zhang, B. Cheng, and C. Tuffile: Addit. Manuf., 2020, vol. 32, p. 101049.
A.B. Anwar, I.H. Ibrahim, and Q.-C. Pham: Powder Technol., 2019, vol. 352, pp. 103–16.
J. Jakumeit, G.Y. Zheng, R. Laqua, S.J. Clark, J. Zielinski, J.H. Schleifenbaum, and P.D. Lee: Addit. Manuf., 2021, vol. 47, p. 102332.
R. Kasper, J. Turnow, and N. Kornev: Int. J. Heat Mass Tran., 2017, vol. 115, pp. 932–45.
L. Cao: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech., 2019, vol. 105, pp. 2253–69.
L. Cao and W. Guan: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2021, vol. 114, pp. 2141–57.
C. Kloss, C. Goniva, A. Hager, S. Amberger, and S. Pirker: Prog. Comput. Fluid Dyn., 2012, vol. 12, pp. 140–52.
C. Zhao, Q.L. Guo, X.X. Li, N. Parab, K. Fezzaa, W.D. Tan, L.Y. Chen, and T. Sun: Phys. Rev. X, 2019, vol. 9, 021052.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic and Applied Basic Research Project of Guangzhou Basic Research Program (no. 202102020724), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (no. 2019A1515012040), and the Fast Support Project (No. 80923010304).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, L., Meng, RF., Zhang, QD. et al. Eulerian–Lagrangian Numerical Simulation of Powder Bed Denudation and Spatter Behavior During Powder Bed Fusion Process. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 2771–2790 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07055-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07055-3