Abstract
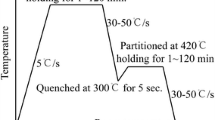
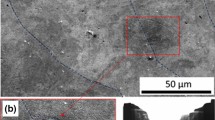
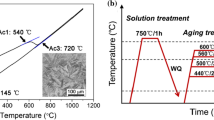
MLX19 stainless maraging steel grade exhibits a mechanical strength/fracture toughness balance within the required range for landing gear applications. However, the microstructure after the heat treatment still needs to be precisely controlled to obtain a better repeatability of the mechanical properties. This work shows that austenitizing is a critical stage. The influence of austenitization treatment parameters on the microstructure obtained after quenching was thus precisely quantified. It was first revealed that, after a standard austenitization at 850 °C and for specific heating rates and holding times, undissolved β-NiAl precipitates, reaching sizes up to 500 nm, still remain in the as-quenched state, in addition to a high retained austenite fraction. It was also found that large amounts of retained austenite are the result of local heterogeneities in the chemical composition of the austenitic phase prior to quenching, while the undissolved precipitates change the overall chemical composition of the austenitic matrix. New austenitization conditions were thus proposed, leading to a better homogeneity of the chemical composition of the martensitic matrix after quenching.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Floreen: Metall. Rev., 1968, vol. 13, pp. 115–28.
W. Sha and Z. Guo: Maraging Steels. Modelling of Microstructure, Properties and Applications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Oxford, 2009.
W. Sha, H. Leitner, Z. Guo, and W. Xu: Phase Transformations in Steels—Volume 2: Diffusionless Transformations, High strength Steels, Modelling and Advanced Analytical Techniques. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Oxford, 2012, pp. 332–262.
F. Roch: Trait. Therm., 2008, vol. 390, pp. 51–8.
R. Schnitzer, R. Radis, M. Nöhrer, M. Schober, R. Hochfellner, S. Zinner, E. Povoden-Karadeniz, E. Kozeschnik, and H. Leitner: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2010, vol. 122, pp. 138–45.
C.H. Beraldo, J.W. Calderón-Hernández, R. Magnabosco, and N. Alonso-Falleiros: Mater. Res., 2019, vol. 22, pp. 1–9.
S. Ifergane, M. Pinkas, Z. Barkay, E. Brosh, V. Ezersky, O. Beeri, and N. Eliaz: Mater. Charact., 2017, vol. 127, pp. 129–36.
C. Le Nué: Étude de la relation microstructure/ténacité d'aciers maraging inoxydables. PhD Thesis. Université de Toulouse, 2017.
C. Le Nué, J.M. Cloué, M.H. Mathon, S. Puech, D. Béchet, and D. Delagnes: Mater. Sci. Forum., 2016, vol. 879, pp. 413–8.
H. Nakagawa and T. Miyazaki: J. Mater. Sci., 1999, vol. 34, pp. 3901–8.
U.K. Viswanathan, T.R.G. Kutty, and C. Ganguly: Metall. Trans. A., 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 2653–6.
M.K. El-Fawkhry, M. Eissa, A. Fathy, and T. Mattar: in Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 2, Elsevier, 2015, pp. S711–14.
D. Boussaid: Université de Lorraine, 2018.
R. Bhambroo, S. Roychowdhury, V. Kain, and V.S. Raja: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2013, vol. 568, pp. 127–33.
H. Leitner, M. Schober, and R. Schnitzer: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 1261–9.
H. Leitner, R. Schnitzer, M. Schober, and S. Zinner: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, pp. 5012–22.
S.D. Erlach, H. Leitner, M. Bischof, H. Clemens, F. Danoix, D. Lemarchand, and I. Siller: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2006, vol. 429, pp. 96–106.
T.H. Simm, L. Sun, D.R. Galvin, E.P. Gilbert, D. Alba Venero, Y. Li, T.L. Martin, P.A.J. Bagot, M.P. Moody, P. Hill, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, S. Birosca, M.J. Rawson, and K.M. Perkins: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2017, vol. 702, pp. 414–24.
L. Sun, T.H. Simm, T.L. Martin, S. McAdam, D.R. Galvin, K.M. Perkins, P.A.J. Bagot, M.P. Moody, S.W. Ooi, P. Hill, M.J. Rawson, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Acta Mater., 2018, vol. 149, pp. 285–301.
M. Thuvander, M. Andersson, and K. Stiller: Ultramicroscopy., 2013, vol. 132, pp. 265–70.
E. Pereloma and D. Edmonds: Phase Transformations in Steels—Volume 1: Fundamentals and Diffusion-Controlled Transformations. Woodhead Publishing, Oxford, 2012.
W. Sha, H. Leitner, Z. Guo, and W. Xu: Phase Transformations in Steels—Volume 2: Diffusionless Transformations, High Strength Steels, Modelling and Advanced Analytical Techniques. Woodhead Publishing, Oxford, 2012.
L.T. Shiang and C.M. Wayman: Metallography., 1988, vol. 21, pp. 399–423.
L.T. Shiang and C.M. Wayman: Metallography., 1988, vol. 21, pp. 425–51.
J. Bridge and G. Maniar: in Metallography as a Quality Control Tool, J.L. McCall and P.M. French, eds., Plenum Press, New York, 1980, pp. 279–95.
J.M. Cloué, B. Viguier, and E. Andrieu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 2633–9.
R. Schnitzer, S. Zinner, and H. Leitner: Scr. Mater., 2010, vol. 62, pp. 286–9.
A. Mondelin, M. Coret, E. Feulvarch, and J. Rech: in 20ème Congrès Français de Mécanique, 2011, pp. 1–6.
R. Kapoor and I.S. Batra: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2004, vol. 371, pp. 324–34.
L.G. de Carvalho, M.S. Andrade, R.L. Plaut, F.M. Souza, and A.F. Padilha: Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 16, pp. 740–4.
R. Cozar: Trait. Therm., 1982, (165), pp. 63–71.
S. Floreen and R.F. Decker: Trans. ASM., 1962, vol. 55, p. 519.
H. Hou, H. Li, Y. Jin, X. Wang, and Z. Wen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2014, vol. 601, pp. 1–6.
H.M. Rietveld: J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1969, vol. 2, pp. 65–71.
A. Bénéteau: Université de Lorraine, 2018.
W.J. Kaluba, T. Kaluba, and R. Taillard: Scr. Mater., 1999, vol. 41, pp. 1289–93.
F. Christien, M.T.F. Telling, and K.S. Knight: Mater. Charact., 2013, vol. 82, pp. 50–7.
C.R. Hubbard and R.L. Snyder: Powder Diffract., 1988, vol. 3, pp. 74–7.
M. Durand-Charre: La Microstructure Des Aciers et Des Fontes: Genèse et Interprétation. Edp Sciences, Les Ulis, 2012.
S. da Silva de Souza, P.S. Moreira, and G.L. de Faria: Mater. Res., 2020, vol. 23, pp. 1–9.
S.A. Khan and H.K.D. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1990, vol. 129, pp. 257–72.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge DESY (Hamburg, Germany), a member of the Helmholtz Association HGF, for the provision of experimental facilities. Parts of this research were carried out at PETRA III and we would like to thank Andreas Stark and Norbert Schell for assistance in using P07 beamline. The research leading to this result has been supported by the project CALIPSOplus under the Grant Agreement 730872 from the EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation HORIZON 2020. Some of the microstructural observations presented in this paper were conducted at the CEMES laboratory and the EBSD analyses were performed at the Centre de microcaractérisation Raimond Castaing, in Toulouse (France). The authors would like to thank Cécile Marcelot for her precious help in the realization of STEM experiments and Arnaud Proietti and Mehdi Salem for their support in the realization of EBSD experiments. Within the Institut Clément Ader laboratory, the authors would also like to thank Sabine Le Roux for her help in the realization of image analysis and Karine Vieillevigne and Serge Tovar for the chemical etchings and the SEM observations.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted January 29, 2021; accepted July 25, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ancey-Rocchi, S., Vidal, V., Poulain, T. et al. Influence of Austenitization Parameters on the Precipitation Sequence and the Chemical Homogenization of Austenite in a High-Performance Fe–Ni–Cr–Al–Ti–Mo Stainless Maraging Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 52, 4623–4635 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-021-06415-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-021-06415-1