Abstract
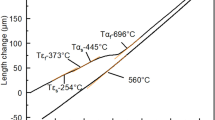
The martensite reversion behavior of a cold-rolled high Mn transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel was investigated through an elaborate continuous annealing procedure. The dilatometry analysis was employed to ensure a precise heating rate (50 °C/s) control during annealing along with acquiring the critical temperature range of the martensite reversion. The magnetic measurement was used for \( \alpha^{\prime} \)-martensite quantification through annealing, and electron channeling contrast imaging (ECCI) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses were also performed to characterize the microstructure. The dilatometry results revealed the dual temperature ranges for the \( \alpha^{\prime} \)-martensite reversion in the experimental TRIP steel; the reversion occurred in two separate temperature regions of 540 °C to 730 °C and 730 °C to 850 °C. Although the inhomogeneity in the morphology of \( \alpha^{\prime} \)-martensite (lath type and dislocation cell type), which was detected in the ECCI image of the cold-rolled structure, might be responsible for the reversion temperature range broadening, the discontinuity of the reversion was mainly attributed to the partitioning of Mn from \( \alpha^{\prime} \)-martensite to austenite through annealing. The microstructural characterizations indicated that the duality would also exist in the case of the martensite reversion mechanism. Accordingly, the reversion of lath-type martensite appeared to occur merely through an athermal mechanism, while the dislocation cell-type martensite might be reversed to austenite via both shear and diffusional mechanisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
References
M.C. Somani, P. Juntunen, L.P. Karjalainen, R.D.K. Misra, and A. Kyröläinen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 729–44.
S.J. Lee, Y.M. Park, and Y.K. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 515, pp. 32–37.
Y.S. Jung and Y.K. Lee: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 47–50.
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, and Y. Tokunaga: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31, pp. 1431–37.
R. Kapoor, L. Kumar, and I. Batra: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 352, pp. 318–24.
S. Takaki, K. Tomimura, and S. Ueda: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 522–27.
O. Grässel, L. Krüger, G. Frommeyer, and L.W. Meyer: Int. J. Plast., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 1391–1409.
M. Eskandari, A. Zarei-hanzaki, M.A. Mohtadi-bonab, Y. Onuki, R. Basu, and A. Asghari: 2016, vol. 674, pp. 514–28.
G. Frommeyer, U. Brüx, and P. Neumann: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 438–46.
H.E. Sabzi, A. Hanzaki, H.R. Abedi, R. Soltani, A. Mateo, and J.J. Roa: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 678, 23–32.
N. Eftekhari, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, A. Shamsolhodaei, A.L. Helbert, and T. Baudin: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, vol. 1700928, pp. 1–12.
A. Barabi, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H. Abedi, A. Anoushe, and J.-H. Cho: Steel Res. Int., 2018, 89, art. no. 1800245.
P. Dastur, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, M.H. Pishbin, M. Moallemi, and H.R. Abedi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 696, pp. 511–19.
C. Herrera, D. Ponge, and D. Raabe: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, pp. 4653–64.
P. Dastur, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, R. Rahimi, V. Klemm, B.C. De Cooman, and J. Mola: Philos. Mag. Lett., 2018, vol. 98, pp. 55–63.
A. Asghari, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and M. Eskandari: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 579, pp. 150–56.
S. Lee and B.C. De Cooman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 3263–70.
K.H. Lo, C.H. Shek, and J.K.L. Lai: Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep., 2009, vol. 65, pp. 39–104.
B. Kumar and S. Sharma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45A, 6027–38.
A. Kisko, A.S. Hamada, J. Talonen, D. Porter, and L.P. Karjalainen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, vol. 657, pp. 359–70.
S. Sabooni, F. Karimzadeh, M.H. Enayati, and A.H.W. Ngan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 636, pp. 221–30.
D.L. Johannsen, A. Kyrolainen, and P.J. Ferreira: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 2325–38.
S. Lee, S.-J. Lee, and B.C. De Cooman: Scripta Mater., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 225–28.
B.C. De Cooman, P. Gibbs, S. Lee, and D.K. Matlock: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 2563–72.
R.D.K. Misra, V.S.A. Challa, P.K.C. Venkatsurya, Y.F. Shen, M.C. Somani, and L.P. Karjalainen: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 84, pp. 339–48.
D.-S. Leem, Y.-D. Lee, J.-H. Jun, and C.-S. Choi: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 767–72.
C. Celada-Casero, B.M. Huang, M.M. Aranda, J.R. Yang, and D.S. Martin: Mater. Charact., 2016, vol. 118, pp. 129–41.
N. Nakada, R. Fukagawa, T. Tsuchiyama, S. Takaki, D. Ponge, and D. Raabe: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 1286–88.
R.D.K. Misra, S. Nayak, P.K.C. Venkatasurya, V. Ramuni, M.C. Somani, and L.P. Karjalainen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 2162–74.
R.D.K. Misra, Z. Zhang, P.K.C. Venkatasurya, M.C. Somani, and L.P. Karjalainen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 7779–92.
T. Furuhara and T. Maki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vol. 312, pp. 145–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted December 2, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dastur, P., Zarei-Hanzaki, A., Rahimi, R. et al. Martensite Reversion Duality Behavior in a Cold-Rolled High Mn Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 4550–4560 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05385-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05385-9