Abstract
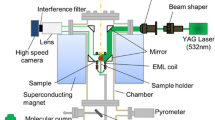
A combination of an electromagnetic levitation technique with a static magnetic field and laser modulation calorimetry was used to measure the thermal conductivity of Fe-Ni melts between 1673 K and 1904 K, including the supercooled temperature region. The static magnetic field suppressed convection, translational motion, and surface oscillation of the levitated droplet to reduce the experimental uncertainty in the measurements. High-purity Fe (99.9985 mass pct) and Ni (99.9960 mass pct) were used for the sample of the measurements. For all melt compositions, the thermal conductivity had a positive temperature dependence, except for a sample with a 0.4 mole fraction of Fe. The measured thermal conductivity values of Fe-Ni were larger than those evaluated from the electric conductivity assuming the Wiedemann–Franz law for all composition ranges. It implies that atomic thermal vibration contributes to the thermal conductivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Xu, W. Zhang, P. D. Lee, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33A(2002) 1805-1815.
P. Nie, O. A Ojo, Z. Li, Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 77, 85-95.
T. M. Pollock, A. Tin, J. Prop. Power, 2006, vol.22, 361-374.
X. Yuwen, L. Chen, Y. Han, Energy Proc., 2012, vol.17, 1864-1871.
H. Fukuyama, H. Kobatake, K. Takahashi, I. Minato, T. Tsukada, S. Awaji, Meas. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol.18, 2059-2066.
H. Kobatake, H. Fukuyama, I. Minato, T. Tsukada, S. Awaji, J. Appl. Phys., 2008, vol.104, 054901-1-8.
T. Tsukada, H. Fukuyama, H. Kobatake, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, vol.50, 3054-3061.
K. Sugie, H. Kobatake, M. Uchikoshi, M. Isshiki, K. Sugioka, T. Tsukada, H. Fukuyama, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 50, 1-6.
M. Watanabe, M. Adachi, H. Fukuyama, J. Mater. Sci., 2016, vol.51, 3303-3310.
M. Watanabe, M. Adachi, H. Fukuyama, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, vol.52, 9850-9858.
M. Uchikoshi, J. Imaizumi, H. Shibuya, T. Kékesi, K. Miura, M. Isshiki, Thin solid films, 2004, vol.461, 94-98.
L. J. Swartzendruber, V. P. Itkin, C. B. Alcock, J. Phase Equilib., 1991, vol.12, 288-312.
Y. Baba, K. Sugioka, M. Kubo, T. Tsukada, K. Sugie, H. Kobatake, H. Fukuyama, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 2011, vol.44, 321-327.
T. Tsukada, K. Sugioka, T. Tsutsumino, H. Fukuyama, H. Kobatake, Int. J. Heat Mass Trans., 2009, vol. 52, 5152-5157.
K. Sugioka, T. Tsukada, H. Fukuyama, H. Kobatake, S. Awaji, Int. J. Heat Mass Trans., 2010, vol.53, 4228-4232.
H. Kobatake, H. Khosroabadi, H. Fukuyama: Proc. e-Therm., 2010, pp. 122–24.
T. Nishi, H. Shibata, H. Ohta, Y. Waseda, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol.34A, 2801-2807.
O. I. Ostrovski, V. A. Eremachenko, V. M. Popov, V. A. Grigoryan, L. E. Kogtan, Zhurnal Fizicheskoi Khimii, 1980, vol.54, 1291-1295.
V. Y. Zinovyev, V. F. Polev, S. G. Taluts, G. P. Zinovyeva, S. A. Ilinykh, Phys. Metal. Metallography, 1986, vol.61, 85-92.
Y. Kita, Z. Morita, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1984, vol.61-62, 1079-1084.
G. Pottlacher, J. Non-cryst. Solids, 1999, vol.250-252, 177-181.
M. J. Assael, A. Chatzimichailidis, K. D. Antoniadis, W. A. Wakeham, M. L. Huber, H. Fukuyama, High Temp. High Press., 2017, vol.46, 391-416.
Y. Ono, T. Yagi, Trans. ISIJ, 1972, vol. 12, 314-316.
Y.S. Touloukian, R.W. Powell, C.Y. Ho, P.G. Klemens: The TPRC Data Series 1 Thermal Conductivity Metallic Elements and Alloys, 1970, p. 169.
A. Seifter, G. Pottlacher, H. Jäger, G. Groboth, E. Kaschnitz, Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische chemie, 1998, vol. 102, 1266-1271.
A. M. Samarin, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1962, vol. 200, 95-101.
K. Mori, M. Kishimoto, T. Shimose, Y. Kawai, J. Inst. Met. Mater., 1975, vol. 39, 1301-1307.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Hiroyuki Shibata and Associate professor Sohei Sukenaga (Tohoku Univ.) for their helpful discussions and critical comments. This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Numbers 26249113 and 18J11474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted November 15, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, M., Adachi, M., Uchikoshi, M. et al. Thermal Conductivities of Fe-Ni Melts Measured by Non-contact Laser Modulation Calorimetry. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 3295–3300 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05250-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05250-9