Abstract
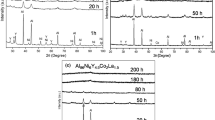
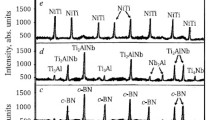
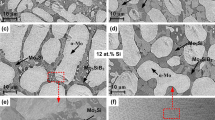
The effect of 2 at. pct Zr addition at the expense of Mo on microstructural evolution, hardness as well as non-isothermal and isothermal oxidation behavior of arc-melted or spark-plasma sintered (SPS) 76Mo14Si10B and 79.5Mo12Si8.5B alloys, has been examined. The microstructures of both arc-melted and SPS alloys have exhibited α-Mo, Mo3Si and Mo5SiB2.These alloys, particularly those processed by SPS have also shown dispersion of SiO2 particles, and these are largely replaced by ZrO2 at interphase boundaries in the Zr-containing alloys. Alloying with Zr or processing by SPS has led to refinement of microstructure, which in turn has caused significant hardness enhancement. During heating from ambient temperature to 1250 °C in air inside a thermogravimetric analyzer, initial mass gain at ≈ 800 °C is found to be followed by rapid mass loss. Isothermal oxidation studies in the temperature range of 800 °C–1300 °C have shown initial mass loss caused by vaporization of MoO3 being followed by a regime of no change in mass. Besides B2O3-SiO2, MoO2 and Mo have been found in the oxide scales of all alloys, whereas ZrO2 and ZrSiO4 have been found along with Zr(MoO4)2 in case of Zr-containing alloys. Reduced mass loss is observed in Zr-containing alloys with the maximum improvement being observed for exposure at 800 °C, not only due to higher volume fractions of Mo3Si and Mo5SiB2 contributing to formation of B2O3-SiO2, but also because MoO3 is partly consumed to form non-volatile Zr(MoO4)2. Furthermore, refinement of microstructures obtained by Zr addition or processing by SPS increases the net area covered by interphase interfaces, which provides short circuit paths for diffusion and enhances the kinetics of formation of protective B2O3-SiO2 scale.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] M.K. Meyer, M.J. Kramer, and M. Akinc: Intermetallics, 1996, vol. 4, pp. 273–281.
[2] J.H. Schneibel, M.J. Kramer, Ö. Ünal, and R.N. Wright: Intermetallics, 2001, vol. 9, pp. 25–31.
[3] M.G. Mendiratta, T.A. Parthasarathy, and D.M. Dimiduk: Intermetallics, 2002, vol. 10, pp. 225–232.
[4] V. Supatarawanich, D.R. Johnson, and C.T. Liu: Intermetallics, 2004, vol. 12, pp. 721–725.
[5] N. Sekido, R. Sakidja, and J.H. Perepezko: Intermetallics, 2007, vol. 15, pp. 1268–1276.
[6] T. Karahana, G. Ouyang, P.K. Ray, M.J. Kramer, and M. Akinc: Intermetallics, 2017, vol. 87, pp. 38–44.
[7] N.K. Kumar, B. Roy, R. Mitra, and J. Das: Intermetallics, 2017, vol. 88, pp. 28–30.
[8] J. Das, B. Roy, N.K. Kumar, and R. Mitra: Intermetallics, 2017, vol. 83, pp. 101–109.
[9] H. Long, S. Mao, Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, and X. Han: J. Alloys Compd., 2018, vol. 743, pp. 203–220.
[10] A. Suzuki, H. Inui, and T.M. Pollock: Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2015, vol. 45, pp. 345–368
[11] M. Krüger, P. Jain, K.S. Kumar, and M. Heilmaier: Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 48 pp. 10–18.
[12] B. Li, G.-j. Zhang, F. Jiang, S. Ren, G. Liu, and J. Sun: J. of Alloys and Comp., 2014, vol. 609, pp. 80–85.
[13] C. Hochmuth, D. Schliephake, R. Völkl, M. Heilmaier, and U. Glatzel: Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 48, pp. 3–9.
[14] P. Jain, and K.S. Kumar: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 2124–2142;
[15] P. Jain, and K.S. Kumar: Scr. Mater., 2010, vol. 62, pp. 1–4.
[16] G. Zhang, W. He, B. Li, Y. Zha, and J. Sun: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 577, pp. 217–221.
[17] J.H. Schneibel, M.J. Kramer, and D.S. Easton: Scr. Mater., 2002, vol. 46, pp. 217–221.
[18] R. Mitra, A.K. Srivastava, N.E. Prasad, and S. Kumari: Intermetallics, 2006, vol. 14, pp. 1461–1471.
[19] G. Hasemann, D. Kaplunenko, I. Bogomol, and M. Krüger: JOM, 2016, vol. 68 (11), pp. 2847–2853.
[20] S. Paswan, R. Mitra, and S.K. Roy: Intermetallics, 2007, vol. 15, pp. 1217–1227.
[21] S. Burk, B. Gorr, V.B. Trindade, and H.-J. Christ: Oxid. Met., 2010, vol. 73, pp. 163–181.
[22] B. Gorr, L. Wang, S. Burk, M. Azim, S. Majumdar, H.-J. Christ, D. Mukherji, J. Rösler, D. Schliephake, and M. Heilmaier: Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 48, pp. 34–43.
[23] T. Sossaman, R. Sakidja, and J.H. Perepezko: Scr. Mater., 2012, vol. 67, pp. 891–894.
[24] T. Sossaman, and J.H. Perepezko: Corr. Sci., 2015, vol. 98, pp. 406–416.
[25] M. Mousa, N. Wanderka, M. Timpel, S. Singh, M. Krüger, M. Heilmaier, and J. Banhart: Ultramicroscopy, 2011, vol. 111, pp. 706–710.
[26] H. Saage, M. Krüger, D. Sturm, M. Heilmaier, J.H. Schneibel, E. George, L. Heatherly, Ch. Somsen, G. Eggeler, and Y. Yang: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 3895–3901.
[27] M. Krüger, D. Schliephake, P. Jain, K. S. Kumar, G. Schumacher, and M. Heilmaier: JOM, 2013, vol. 65 (2), pp. 301–306
[28] J.H. Schneibel, R.O. Ritchie, J.J. Kruzic, and P.F. Tortorelli: Metal. Mater. Trans. A., 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 525–531.
[29] J. Wang, B. Li, R. Li, T. Wang, X. Chen, and G. Zhang: Ceram. Inter., 2019, vol. 45, pp. 1182-1188.
[30] R. Mitra: Int. Mater. Rev., 2006, vol. 51, pp. 13–64.
[31] V. Supatarawanich, D.R. Johnson, and C.T. Liu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2003, vol. 344, pp. 328–339.
[32] F. Wang, A. Shan, X. Dong, and J. Wu: Scr. Mater., 2007, vol. 56, pp. 737–740.
[33] A.G. Evans, and E.A. Charles: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1976, vol. 59, pp. 371–372.
[34] G.R.Anstis, P. Chantikul, B.R. Lawn, and D.B. Marshall, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1981, vol. 64(9), pp. 533–538.
K. Niihara, R. Morena, and D.P.H. Hasselman: J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1982, vol. 1, pp. 13–16.
C.A. Nunes, R. Sakidja, Z. Dong, and J.H. Perepezko: Intermetallics, 2000, vol. 8, pp. 327–337.
[37] S.-H. Ha, K. Yoshimi, K. Maruyama, R. Tu, and T. Goto: Mater. Trans., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 1699–1704.
[38] A. Misra, J. J. Petrovic and T. E. Mitchell: Scr. Mater., 1999, vol. 40, pp. 191–196.
S. Paswan, R. Mitra, and S.K Roy: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2009, vol. 44, pp. 2644–58.
N. Okamoto: J. Phase Equil. Diffus., 2011, vol. 32 (2), p. 176.
P. Franke and D. Neuschütz: Scientific Group Thermodata Europe (SGTE): Mo-Zr (Molybdenum – Zirconium), Binary Systems. Part 5: Binary Systems Supplement 1. Landolt-Börnstein - Group IV Physical Chemistry (Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology), vol 19B5. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
[42] R.J. Pérez, and B. Sundman: Calphad, 2003, vol 27, pp. 253–262.
A. Zavaliangos, J. Zhang, M. Krammer, and J.R Groza: Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2004, vol. 379, pp. 218–28.
[44] H. Tomino, H. Watanabe, and Y. Kondo: J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall., 1997, vol. 44 pp. 974–979.
[45] I. Tomaszkiewicz, G. A. Hope, C. M. Beck, and P.A.G. O’Hare: J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1996, vol. 28, pp. 29–42.
[46] P.A.G. O’Hare: Pure Appl. Chem., 1999, Vol. 71, pp. 1243–1248.
[47] Y.S. Pogozhev, A.Y. Potanin, E.A. Levashov, A.V. Novikov, T.A. Sviridova, and N. A. Kochetov: Russ. J. Non Ferrous Met., 2014, Vol. 55, pp. 632–638.
[48] I. Barin: Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, 3rd ed, VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 1989.
[49] B. Roy, J. Das, and R. Mitra: Corr. Sci., 2013, vol. 68, pp. 231–237.
[50] F.A. Rioult, S.D. Imhoff, R. Sakidja, and J.H. Perepezko: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 4600–4613.
[51] Y. Kawamoto, K. Clemens, and M. Tomozawa: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1981, vol. 64 pp. 292–296.
[52] M. Suzuki, S. Sodeoka, and T. Inoue: Mater. Trans. JIM, 2005, vol. 46, pp. 669–674.
[53] Q. Zhang, H. Yang, F. Zeng, S. Wang, D.Tang, and T. Zhang: RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, pp. 41772–41779.
[54] A. Quintas, D. Caurant, O. Majérus, P. Loiseau, T. Charpentier, and J.L. Dussossoy: J. Composite. Compd., 2017, vol. 714, pp. 47–62.
[55] K.H. Sun: J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 1947, vol. 30, pp. 277–281.
[56] D.A. McKeown, I.S. Muller, A.C. Buechele, I.L. Pegg, and C.A. Kendziora, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2000, vol. 262, pp. 126–134.
[57] A.M. Huntz: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1987, vol. 87, pp. 251–260.
[58] K. Yoshimi, S. Nakatani, S. Hanada, S.-H. Ko and Y.-H. Park: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2002, vol. 3(2), pp. 181-192.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Mithun Das, Mr. Nirmal Das, and Mr. Srikrishna Maity of the Central Research Facility, IIT Kharagpur for technical assistance. The financial support provided by DRDO (ERIP/ER/1200425/M/01/1482), New Delhi, Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted 26 August, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N.K., Das, J. & Mitra, R. Effect of Zr Addition on Microstructure, Hardness and Oxidation Behavior of Arc-Melted and Spark Plasma Sintered Multiphase Mo-Si-B Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 2041–2060 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05111-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05111-5