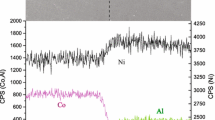
Abstract
A popular area of research in the field of high-temperature alloys concerns the search of substitutional elements for Re in order to manufacture single-crystal Ni-based superalloys with less or even no Re addition. To find the elements with similar or even lower diffusion coefficients than Re is an effective strategy. Based on 29 fcc diffusion couples in ternary Ni-Al-X (X = Re, Os, and Ir) systems, high-throughput measurement of composition- and temperature-dependent interdiffusivity matrices was performed using our recently developed numerical inverse method implemented in HitDIC software. The reliability of the determined interdiffusivities was validated by comprehensively comparing the model-predicted composition/interdiffusion flux profiles for each diffusion couple with the corresponding experimental data. Moreover, we also conducted a comparison with the interdiffusivities evaluated using the traditional Matano–Kirkaldy method as well as those from the literature and in boundary binary systems. After that, a comprehensive comparison of the interdiffusion coefficients in fcc Ni-2 wt pct Al-6 wt pct X (X = Ti, Co, Ni, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Ta, W, Re, Os, Ir, and Pt) alloys at 1423 K to 1573 K was conducted. Results indicate that the diffusion rate of Re is lower than that of Os at 1473 K and 1523 K; but higher at 1573 K, while the diffusion rate of Ir is always slightly higher than those of Os and Re at 1473 K to 1573 K. Further analysis of the magnitude of the interdiffusion coefficient correlates with the alloying concentration, activation energy, atomic number, and atomic radius of different diffusing transition metal species (i.e., Ti, Co, Ni, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Ta, W, Re, Os, Ir, and Pt) was conducted, which is expected to provide useful information regarding element choice in the development of new-generation Ni-based single-crystal superalloys.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Liu, M.R. Wen, Z. Li, W.Q. Liu, P. Yan, and C.Y. Wang: Mater. Des., 2017, vol. 130, pp. 157–165.
X. Xiong, P. Dai, D. Quan, Z. Wang, Q. Zhang, and Z. Yue: Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 86, pp. 482–486.
R.C. Reed: The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006.
W.R. Cannon, and O.D. Sherby: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1030–1032.
C.L. Zacherl: A computational investigation of the effect of alloying elements on the thermodynamic and diffusion properties of fcc nickel alloys, with application to the creep rate of dilute nickel-X alloys, Doctoral thesis, Pennsylvania State University, 2012.
W.Y. Gong, L.J. Zhang, D.Z. Yao, and C.G. Zhou: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 61, pp. 100–03.
M.J.H. Van Dal, M.C.L.P. Pleumeekers, A.A. Kodentsov, and F.J.J. Van Loo: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 385–396.
R.A. Hobbsa, M.S.A. Karunaratne, S. Tina, R.C. Reed, and C.M.F. Rae: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 460-461, pp. 587–594.
M.S.A. Karunaratne, and R.C. Reed: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 2905–2919.
M.S.A. Karunaratne, P. Carter, and R.C. Reed: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, vol. 281, pp. 229–233.
X.M. Zhang, H.Q. Deng, S.F. Xiao, Z. Zhang, J.F. Tang, L. Deng, and W.Y. Hu: J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 588, pp. 163–169.
A. Janotti, M. Krčmar, C.L. Fu, and R.C. Reed: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2004, vol. 92, art. no. 085901.
J. Chen, J.K. Xiao, L.J. Zhang, and Y. Du: J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 657, pp. 457– 463.
M. S. A. Karunaratne, P. Carter, and R. C. Reed: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 861-875.
Y. Wang, N.Q. Zhu, H. Wang, and X.G. Lu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 943–947.
T. Yamamoto, T. Takashima, and K. Nishida: Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1980, vol. 21, pp. 601–608.
G.C. Xu, Y.J. Liu, and Z.T. Kang: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 709, pp. 272–276.
S.Y. Wen, Y. Tang, J. Zhong, L.J. Zhang, Y. Du, and F. Zheng: J. Mater. Res., 2017, vol. 32, pp. 2188–2201.
M. Hattori, N. Goto, Y. Murata, T. Koyama, and M. Morinaga: Mater. Trans., 2006, vol. 47, pp. 331–334.
J. Chen, and L.J Zhang: CALPHAD, 2017, vol. 60, pp. 106–15.
J. Chen, L.J Zhang, J. Zhong, W.M. Chen, and Y. Du: J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 688, pp. 320–328.
S. Hayashi, D.J. Sordelet, L.R. Walker, and B. Gleeson: Mater. Trans., 2008, vol. 49, pp. 1550–1557.
Q. Zeng, S.W. Ma, Y.R. Zheng, S.Z. Liu, and T. Zhai: J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 480, pp. 987–990.
E. Mabruri, M. Hattori, K. Hasuike, T. Kunieda, Y. Murata, and M. Morinaga: Mater. Trans., 2006, vol. 47, pp. 1408–1411.
W.M. Chen, L.J. Zhang, Y. Du, C.Y. Tang, and B.Y. Huang: Scripta Mater., 2014, vol. 90-91, pp. 53–56 .
W.M. Chen, J. Zhong, and L.J. Zhang: MRS Commun., 2016, vol. 6, pp. 295– 300.
HitDIC software: https://hitdic.com/. Accessed 21 December 2017.
J. Zhong, W. Chen, and L. Zhang: CALPHAD, 2017, vol. 60, pp. 177– 190.
M.A. Dayananda: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1851-1858.
W. Huang, and Y.A. Chang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vol. 259, pp. 110–119.
L. Onsager: Ann. N. Y, Acad. Sci., 1945, vol. 46, pp. 241–65.
J. Léchelle, S. Noyau, L. Aufore, A. Arredondo, and E. Audubert: Diffus. Fundam. Org., 2012, vol. 17, pp. 1–39.
J.S. Kirkaldy, J.E. Lane, and G.R. Masson: Can. J. Phys., 1963, vol. 41, pp. 2174–2186.
J.S. Kirkaldy, and D.J. Young: Diffusion in the Condensed State, Institute of Metals, London, 1987.
R.A. Swalin, and A. Martin: J. Metals, 1956, vol. 8, pp. 567–572.
A. Volek, F. Pyczak, R.F. Singer, and H. Mughrabi: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 141–145.
C.C. Jia, K. Ishida, and T. Nishizawa: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 473–485.
T. Yokokawa, M. Osawa, K. Nishida, T. Kobayashi, Y. Koizumi, and H. Harada: Scripta Mater., 2003, vol. 49, pp. 1041–1046.
Acknowledgments
The financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51474239) and the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Program of China (Grant No. 2017RS3002)—Huxiang Youth Talent Plan is acknowledged. Lijun Zhang acknowledges that the project was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy Foundation, Central South University, Changsha, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 1, 2018.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11661_2018_4669_MOESM1_ESM.xls
Supplementary material 1 (XLS 898 kb) Supplemental material A1 Concentration profiles and interdiffusion coefficients evaluated by the numerical inverse method in fcc Ni–Al–X (X=Re, Os, and Ir) system.
11661_2018_4669_MOESM2_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 2 (XLSX 169 kb) Supplemental material A2 Evaluated mobility parameters adopted in the present numerical inverse method in fcc Ni–Al–X (X=Re, Os, and Ir) system.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Zhang, L. & Lu, XG. Screening of Possible Re-Substitutional Elements in Single-Crystal Ni-Based Superalloys: A Viewpoint From Interdiffusion Coefficients in Ni-Al-X Ternaries. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 2999–3010 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4669-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4669-1