Abstract
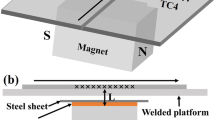
For decades, post-welding magnetic treatment has been used to reduce residual stress of welds by improving the crystal structure of solid-state welds. In this paper, we propose a new magnetic treatment method, which can reduce the time-dependent thermal stress field in situ and reduce the final residual stress of welds by simply exerting an assisted weak magnetic field perpendicular to the welding direction and workpiece during laser welding. A new finite-element model is developed to understand the thermal–mechanical physical process of the magnetic-assisted laser welding. For the widely used 304 austenite stainless steel, we theoretically observed that this method can reduce around 10 pct of the time-dependent thermal stress field, and finally reduce approximately 20 MPa of residual stress near the heat-affected zone with a 415-mT magnetic field for typical welding process parameters. A new mechanism based on magneto-fluid dynamics is proposed to explain the theoretical predications by combining high-speed imaging experiments of the transient laser welding process. The developed method is very simple but surprisingly effective, which opens new avenues for thermal stress reduction in laser welding of metals, particularly heat-sensitive metallic materials.











Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
J.F. Lancaster: Phys. Technol., 1984, vol. 15, pp. 73–79.
L. Lindgren, and L. Karlsson: Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 1998, vol. 25, pp. 635–55.
S.A. Tsirkas, P. Papanikos, T. Kermanicis: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, vol. 134, pp. 59–69.
T.L. Teng, P.H. Chang, and W.C. Tseng: Comput. Struct., 2003, vol. 81, pp. 273–86.
X. Cheng, J.W. Fisher, H.J. Prask, T. Gnaupel-Herold, B.T. Yen, and S. Roy: Int. J. Fatigue, 2003, vol. 25, pp. 1259–69.
J. Lin, S. Huang, Z.P. Cai, H.Y. Zhao, and A.L. Lu: Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2006, pp. 208–13.
A.L. Lu, F. Tang, X.J. Luo, J.F. Mei, and H.Z. Fang: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1998, vol. 74, pp. 259–62.
J. Lin, H.Y. Zhao, Z.P. Cai, and A.L. Lu: J. Mater. Eng., 2005.
Z.P. Cai, J. Lin, H.Y. Zhao, and A.L. Lu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 398, pp. 344–48.
M. Kern, P. Berger, and H. Hugel: Weld. J., 2000, pp. 72–78.
M. Bachmann, V. Avilov, A. Gumenyuk, and M. Rethmeier: Phys. Proc., 2014, vol. 56, pp. 515–24.
V. Avilov, A. Gumenyuk, M. Lammers, and M. Rethmeier: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2012, vol. 17, pp. 128–33.
G. Ambrosy, P. Berger, H. Hugel, and D. Lindenau: Proc. of SPIE.
M. Bachmann, V. Avilov, A. Gumenyuk, and M. Rethmier: Int. J. Thermal. Sci., 2016, vol. 101, pp. 24–34.
M. Bachmann, V. Avilov, A. Gumenyuk, and M. Rethmeier: Int. J. Heat. Mass. Trans., 2013, vol. 60, pp. 309–21.
H.C. Tse, H.C. Man, and T.M. Yue: Opt. Laser Technol., 1999, vol. 31, pp. 363–68.
Y. Peng, W.Z. Chen, C. Wang, G. Bao, and Z.L. Tian: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2001, vol. 34, pp. 3145–49.
J. Kim and Y. Peng: KSME Int. J., 2000, vol. 14, pp. 177–87.
C. Tix and G. Simon: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 1993, vol. 26.
Z. Sun, A.S. Salminen and T.J.I. Moisio: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1993, vol. 12, pp. 1131–33.
A. Schneider, V. Avilov, A. Gunmenyuk, and M. Rethmeier: Phys. Procedia, 2013, vol. 41.
G. Ambrosy, V. Avilov, P. Berger, and H. Hugel: Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng., 2007.
A. Falvo, F. M. Furgiule, C. Maletta: J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 412, pp. 235–400.
T. A. Mai, A. C. Spowage: J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 374, pp. 224–33.
S. A. Tsirkas, P. Papanikos, T.H. Kermanidis: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, vol. 134, pp. 59–69.
D.A. Deng: Mater. Des., 2009, vol. 30, pp. 359–66.
R.W. Lewis, P. Nithiarasu, and K.N. Seetharamu: Fundamentals of the Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow, 1st ed., Wiley, Chichester, 2004.
Y. Ueda and Y. Yamakawa: Trans. Jpn. Weld. Soc. 1971.
S. Wu, H.Y. Zhao, Y. Wang, and X.H. Zhang: Trans. China Weld. Inst., 2004, vol. 25, pp. 91–94.
A. Matsunawa, N. Seto, J. Kim, M. Mizutani, S. Ktayama: J. Laser Appl., 2000, vol. 3888, pp. 247–54.
Y. Kawahito, M. Mizutani, and S. Katayama: Sic. Technol. Weld. Join, 2009, vol. 14, pp. 288–94.
S. Pang, L. Chen, J. Zhou, Y. Yin, and Tao Chen: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 44.
S. Pang, X. Chen, J. Zhou, X. Shao, and C. Wang: Opt. Laser. Eng., 2015, vol. 74, pp. 47–58.
R. Rai, J.W. Elmer, T.A. Palmer, and T. DebRoy: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2007, vol. 40.
X. He, P.W. Furschbah, and T. DebRoy: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2003, vol. 36, pp. 1388.
S. Pang, W. Chen, and W. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 2808–18.
M. Sathiyamoorthy, and A. Chamkha: Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2010, vol. 49, pp. 1856–65.
R. Rai, S.M. Kelly, R.P. Martukanitz, and T. Debroy: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39, pp. 98–112.
X.Z. Jin, L.J. Li, and Y. Zhang: Int. J. Heat. Mass. Trans., 2003, vol. 46, pp. 15–22.
Q. Tang, S. Pang, B. Chen, H. Suo, and J. Zhou: Int. J. Heat. Mass. Trans., 2014, vol. 78, pp. 203–15.
V.G. Navas, J. Leunda, J. Lambarri, and C. Sanz: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 3140–56.
S. Pang, W. Chen, J. Zhou, and D. Liao: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 217, pp. 131–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 08, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, L., Pang, S., Shao, X. et al. In situ Weak Magnetic-Assisted Thermal Stress Field Reduction Effect in Laser Welding. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 198–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4408-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4408-z