Abstract
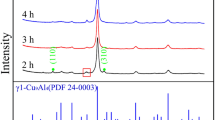
For many years, cerium-aluminum systems have been extensively studied because of their unusual magnetic behavior. As the atomic radii of cerium and aluminum differ greatly from each other, a solid solution is not obtained because of the Hume-Rothery rule. Therefore, intermetallic compounds are usually studied, and structural stability is crucial for further discussion of their physical properties. The present article reports on high-energy ball milling of the intermetallic compound Ce3Al at room temperature. It has been found that non-equilibrium supersaturated Ce solid solution was formed during the milling. The solubility of aluminum was estimated as 5 to 13 at. pct from the peak shifts of the X-ray diffraction pattern. The structural changes in the initial stages of the milling were also studied.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.-S. Zeng, Y. Ding, W. L. Mao, W. Luo, A. Blomqvist, R. Ahuja, W. Yang, J. Shu, S. V. Sinogeikin, Y. Meng, D. L. Brewe, J.-Z. Jiang, and H.-K. Mao, Proc. Nat. Aca. Sci., 2009, 106, 2515–18. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0813328106.
J. C. Slater, J. Chem. Phys., 1964, 41, 3199–203. DOI:10.1063/1.1725697.
W. Hume-Rothery, G.W. Mabbott, M. Channel-Evans, Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. (London), 1934, A233, 1–97.
W. B. Pearson, “Handbook of Lattice Spacings and Structures of Metals”, Pergamon Press, London, 1958.
M. Sera, T. Satoh and T. Kasuya, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1987, 63-64, 82–84.
J. Sakurai, Y. Murashita, Y. Aoki, T. Fujita, T. Takabatake and H. Fujii, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1989, 58, 4078–85.
W.-H. Li, J. C. Peng, Y.-C. Lin, C. Lee, J. W. Lynn and Y. Y. Chen, J. Appl. Phys., 1998, 83, 6426–28.
Y. Y. Chen, Y. D. Yao, C. R. Wang, W. H. Li, C. L. Chang, T. K. Lee, T. M. Hong, J. C. Ho, and S. F. Pan, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2000, 84, 4990–93. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4990
M. C. Gao, N. Unlu, G. J. Shiflet, M. Mihailkovic, and M. Widom, Metal. & Mater. Trans., 2005, 36A, 3269–79.
A. Ye. Yermakov, Ye. Ye. Ymrchikov, and V. A. Barinov, Phys. Met. Metall., 1981, 52, 50.
R. B. Schwarz and C. C. Koch, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1986, 49, 146–48. DOI:10.1063/1.97206.
R. B. Schwarz and W. L. Johnson, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1983, 51, 415–18. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.51.415
C. C. Koch, O. B. Cavin, C. G. McKamey, and J. O. Scarbrough, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1983, 43, 1017–19. DOI:10.1063/1.94213.
K. Sakurai, Y. Yamada, M. Ito, C. H. Lee, T. Fukunaga, and U. Mizutani, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1990, 57, 2660–62. DOI:10.1063/1.104190.
L.M. Di and H. Bakker, J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 1991, 3, 3427–32. DOI:10.1088/0953-8984/3/20/004.
L.M. Di and H. Bakker, J. Phys. Condens. Matter, 1991, 3, 9319–26.
M. Oehring and R. Bormann, J. Phys. Colloq., 1990, 51, C4-69 (Paris).
K. Togano, P. Badica, Y. Nakamori, S. Orimo, H. Takeya and K. Hirata, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2004, 93, 247004. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.247004.
H. Takeya, T. Hirano and K. Kadowaki, Physica C, 1996, 256, 220–26. DOI:10.1016/0921-4534(95)00651-6
H. Takeya, M. ElMassalami, S. Kasahara and K. Hirata, Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 76, 104506. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.76.104506.
K. Sakurai, M. Mori and U. Mizutani, Phys. Rev. B, 1992, 46, 5711–14. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.46.5711.
X. Guo, J. F. Qi, K. Sakurai, Scripta. Materialia. 2003, 48, 1185–88. DOI:10.1016/S1359-6462(02)00570-5.
F. R. Boer and D. G. Perrifor, “Cohesion in Metals”, Elsevier, Netherlands, 1988.
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue, Mater. Trans. JIM, 2000, 41, 1372–78.
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (YZ) wishes to thank the Nuclear Researcher Exchange Program of the Japanese government for financial support. The work was done during her leave from the Department of Nuclear Physics, China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 3, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yp., Takeya, H. & Sakurai, K. Phase Stability of Intermetallic Compound Ce3Al in Mechanical Milling. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 5635–5638 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4307-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4307-3