Abstract
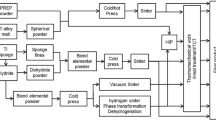
Ti-6Al-4V alloy powders produced using a hydrogenation–dehydrogenation process and a gas atomization process, respectively, were rapidly consolidated into near-net-shaped parts by powder compact forging. The porosity, microstructure, and tensile mechanical properties of specimens cut from regions at different distances from the side surfaces of the forged parts were examined. The regions near the side surfaces contained a fraction of pores due to the circumferential tensile strain arising during the powder compact forging process, and the porosity level decreased rapidly to zero with increasing the distance from the side surface. The forged parts had a fully lamellar structure with the α + β colony sizes and α lamella thickness changing little with the distance from the side surface. The specimens cut from the regions near the side surfaces had a lower yield strength and tensile strength. The correlation of porosity with the yield strength of the specimens suggested that the reduction of load bearing areas due to the porosity and unbonded or weakly bonded interparticle boundaries was not the only reason for the lower strength, and the stress concentration at the pores and associated with their geometry also played an important role in this. It is likely that the effect of stress concentration on yield strength reduction of the forged part increases with oxygen content. The Hall–Petch relationship of the yield strength and the average α lamella thickness suggested that the strength of the fully dense and fully consolidated forged parts was increased by oxygen solution strengthening.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Froes: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1994, vol. 184, pp. 119-133.
R. Boyer: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1996, vol. 213, pp. 103-114.
M. Niinomi: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol. 243, pp. 231-236.
M. Niinomi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33, pp. 477-486.
T. Saito: JOM, 2004, vol. 56, pp. 33-36.
C. Elias, J. Lima, R. Valiev and M. Meyers: JOM, 2008, vol. 60, pp. 46-49.
A.A. Kalam and Y.S. Rajan: India 2020: A vision for the new millennium. Westminster: Penguin UK, 2014.
M. Qian: Int. J. Powder Metall., 2010, vol. 46.
W. Chen, Y. Yamamoto, W.H. Peter, M.B. Clark, S.D. Nunn, J. Kiggans, T.R. Muth, C.A. Blue, J.C. Williams and K. Akhtar: J. Alloys Compd., 2012, vol. 541, pp. 440-447.
F.S. Froes: Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 2007, vol. 46, pp. 303-310.
M. Köhl, T. Habijan, M. Bram, H.P. Buchkremer, D. Stöver and M. Köller: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2009, vol. 11, pp. 959-968.
W. Yuan, J. Mei, V. Samarov, D. Seliverstov and X. Wu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, vol. 182, pp. 39-49.
K. Zhang, J. Mei, N. Wain and X. Wu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 1033-1045.
H. Guo, Z. Zhao, C. Duan and Z. Yao: JOM, 2008, vol. 60, pp. 47-49.
M.T. Jia, D.L. Zhang and B. Gabbitas: Key Eng. Mater., 2012, vol. 520, pp. 82-88.
J. Qiu, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, B. Liu, B. Wang, E. Ryba and H. Tang: Mater. Des., 2012, vol. 33, pp. 213-219.
J. Qiu, Y. Liu, B. Liu, Y. Liu, B. Wang, E. Ryba and H. Tang: Journal of Materials Science, 2012, vol. 47, pp. 3837-3848.
M. Jia, J. Liang, D. Zhang, C. Kong and B. Gabbitas: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, vol. 655, pp. 113-121.
G. Lütjering and J.C. Williams: Titanium. New York: Springer, 2003.
M. Benedetti and V. Fontanari: Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2004, vol. 27, pp. 1073-1089.
Z. Esen and Ş. Bor: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 3200-3209.
J.-H. Lee, Y.-H. Kim and W.-B. Bae: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1997, vol. 72, pp. 371-379.
R. Narayanasamy and K. Pandey: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, vol. 100, pp. 87-94.
J.-O. Park, K.-J. Kim, D.-Y. Kang, Y.-s. Lee and Y.-H. Kim: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, vol. 113, pp. 486-492.
R. Dashwood and G. Schaffer: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2002, vol. 323, pp. 206-212.
A. Ragab: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2002, vol. 334, pp. 114-119.
M. Leonowicz, D. Derewnicka, M. Wozniak and H. Davies: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, vol. 153, pp. 860-867.
S. Singh, A. Jha and S. Kumar: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, vol. 194, pp. 134-144.
J. Das, K. Chandra, P. Misra and B. Sarma: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 479, pp. 164-170.
G.R. Shaik and W. Milligan: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28, pp. 895-904.
C. Liang, M. Ma, M. Jia, S. Raynova, J. Yan and D. Zhang: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, vol. 619, pp. 290-299.
C. Liang, M. Ma, M. Jia, S. Raynova, J. Yan and D. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 5095-5102.
H.A. Kuhn and B.L. Ferguson: Powder forging. Metal Powder Industries Federation: Princeton, NJ, 1990.
H. Dong and X. Li: Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2000, vol. 280, pp. 303-310.
T. Griffiths, R. Davies and M. Bassett: Powder Metallurgy, 1979, pp. 119–23.
R. Rice: Journal of Materials Science, 1993, vol. 28, pp. 2187-2190.
H. Kuhn: Powder metallurgy processing: the techniques and analyses. New York: Elsevier, 2012.
M. Yan, W. Xu, M. Dargusch, H. Tang, M. Brandt and M. Qian: Powder Metallurgy, 2014, vol. 57, pp. 251-257.
R. Haynes: Powder Metall., 1977, vol. 20, pp. 17-20.
Q. Xu, B. Gabbitas and S. Matthews: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 587, pp. 123-131.
S. Semiatin and T. Bieler: Acta materialia, 2001, vol. 49, pp. 3565-3573.
D. Kohn and P. Ducheyne: Journal of Materials Science, 1991, vol. 26, pp. 328-334.
D.-G. Lee, S. Lee, C.S. Lee and S. Hur: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34, pp. 2541-2548.
I. Sen: J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2010, vol. 240, pp. 1-4.
J. Sieniawski, W. Ziaja, K. Kubiak and M. Motyka, In Titanium Alloys-Advances in Properties Control. Rijeka: InTech, 2013, pp 69–80.
C. Leyens and M. Peters: Titanium and titanium alloys. New York: Wiley, 2003.
J.-M. Oh, B.-G. Lee, S.-W. Cho, S.-W. Lee, G.-S. Choi and J.-W. Lim: Met. Mater. Int., 2011, vol. 17, pp. 733-736.
Acknowledgments
The work presented in this paper was financially supported by the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment, New Zealand (Contract No. UOWX0802) and the National Natural Science Foundation, China (Project Approval No.: 51271115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 15, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, M., Zhang, D., Liang, J. et al. Porosity, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Parts Fabricated by Powder Compact Forging. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 2015–2029 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-3965-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-3965-5