Abstract
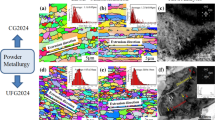
Uniaxial compression test at different temperatures [573 K to 723 K (300 °C to 450 °C)] and strain rates (0.01 to 1 s−1) was employed to study the hot deformation behavior of an ultrafine-grained (UFG) Al6063 alloy prepared by the powder metallurgy route. The UFG alloy with an average grain size of ~0.3 µm was prepared by mechanical milling of a gas-atomized aluminum alloy powder for 20 hours followed by hot powder extrusion at 723 K (450 °C). To elaborate the effect of grain size, the aluminum alloy powder was extruded without mechanical milling to attain a coarse-grained (CG) structure with an average grain size of about 2.2 µm. By employing the dynamic materials model, processing maps for the hot deformation of the UFG and CG Al alloy were constructed. For investigation of microstructural evolutions and deformation instability occurring upon hot working, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy coupled with electron backscattered diffraction and transmission electron microscopy were utilized. It is shown that the grain refinement increases the deformation flow stress while reducing the strain hardening and power dissipation efficiency during the deformation process at the elevated temperatures. Restoration mechanisms, including dynamic recovery and recrystallization are demonstrated to control microstructural evolutions and thus the deformation behavior. Coarsening of the grain structure in the UFG alloy is illustrated, particularly when the deformation is performed at high temperatures and low strain rates. The manifestations of instability are observed in the form of cracking and void formation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] S.B. Bhimavarapu, A.K. Maheshwari, D. Bhargava and S.P. Narayan: J. Mater. Sci., 2011, vol. 46, pp. 3191-9.
[2] J. Zhang, H. Di, H. Wang, K. Mao, T. Ma and Y. Cao: J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, pp. 4000-11.
[3] J.K. Chakravartty, G.K. Dey, S. Banerjee and Y.V.R.K. Prasad: J. Nucl. Mater., 1995, vol. 218, pp. 247-55.
[4] A. Momeni and K. Dehghani: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 5467-73.
[5] S. Anbuselvan and S. Ramanathan: Mater. Des., 2010, vol. 31, pp. 2319-23.
[6] Y. Ning, Z. Yao, H. Guo, M.W. Fu and X. Xie: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 6794-9
[7] Y.V.R.K. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lark and D.R. Barker: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15, pp. 1883-92.
[8] E. Cerri, S. Spigarelli, E. Evangelista, and P. Cavaliere: Mater. Sci. Eng A, 2002, vol. 324, pp. 157-61.
Y.V.R.K Prasad: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2003, vol. 12, pp. 638-45
[10] N. Srinivasa and Y.V.R.K. Prasad: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1995, vol. 51, pp. 171-92.
[11] J. Sarkar, Y.V.R.K. Prasad and M.K. Surappa: J. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 2843-8.
[12] H.R. Ezatpour, M. Haddad Sabzevar, S.A. Sajjadi and Y. Huang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 606, pp. 240-7.
[13] Richard W. Hertzberg: Deformation and fracture mechanics of engineering materials, 4 th ed., John Wiley and Sons, Inc., USA, 1996, pp. 129-30.
[14] A. Azushima, R. Kopp, A. Korhonen, D.Y. Yang, F. Micari, G.D. Lahoti, P. Grocheg, J. Yanagimotoh, N. Tsujii, A. Rosochowskij and A. Yanagidaa: CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol., 2008, vol. 57, pp. 716-35.
[15] V.V. Stolyarov, Y.T. Zhu, T.C. Lowe, R.K. Islamgaliev and R.Z. Valiev: Nanostruct. Mater, 1999, vol. 11, pp. 947-54.
[16] C. Suryanarayana and G.E. Korth: Met. Mater. Int., 1999, vol. 5, pp. 121-8.
F. Thümmler and R. Oberacker: Introduction to Powder Metallurgy, The Institute of Materials, Maney Publishing, U.K., 1994, p. 252.
[18] B.Q. Han, E.J. Lavernia and A. Mohamed. Farghalli: Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 2005, vol. 9, pp. 1-16.
[19] J.K. Kim, H.K. Kim, J.W. Park and W.J. Kim: Scripta Mater. 2005, vol. 53, pp. 1207-11.
[20] C. Xu and T.G. Langdon: J. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 42, pp. 1542-50.
[21] B. Cherukuri, S. Nedkova Teodora and R. Srinivasan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 410, pp. 394-7.
[22] H. Asgharzadeh, A. Simchi and H.S. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 3981-9.
H. Asgharzadeh, S.H. Joo and H.S. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45, vol. 4129-37
[24] M. S. Mohebbi, A.Akbarzadeh, Y.O. Yoon and S.K. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 593, pp. 136-44.
[25] C. Xu, Z. Horita and T.G. Langdon: Mater. Trans., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 2-7.
[26] B.O. Han, F.A. Mohamed, Z. Lee, S.R. Nutt and E.J. Lavernia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34, pp. 603-13.
[27] X. Sauvage, A. Ganeev, Y. Ivanisenko, N. Enikeev, M. Murashkin and R. Valiev: Adv. Eng. Mater, 2012, vol. 14, pp. 968-74.
[28] X. Sauvage, G. Wilde, S. V. Divinski, Z. Horita and R. Z. Valiev: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 540, pp. 1-12.
[29] D. Chicot, M. Voda, X. Decoopman, V.A. Serban, E.S. Puchi-Cabrera, M.H. Staia and C. Codrean: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 7041-51.
[30] B.Q. Han, E.J. Lavernia, F.A. Mohamed: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36, pp. 345-55.
[31] H. Asgharzadeh, A. Simchi and H. S. Kim. Scripta Mater., 2012, vol. 66, pp. 911-4.
[32] H. Asgharzadeh, A. Simchi and H.S. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 4897-905.
[33] H. Asgharzadeh, A. Simchi and H.S. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 16-824.
[34] D.P. Field, L.T. Bradford, M.M. Nowell and T.M. Lillo: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, 4233-41.
[35] A.A. Saleh, A.A. Gazder and E. V. Pereloma: T. Indian. I. Metals, 2013, vol. 66, pp. 621-9.
[36] S.W. Cheong and H. Weiland: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vol. 558, pp. 153-8.
[37] Y.V.R.K. Prasad and T. Seshacharyulu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 243, pp. 82-8.
[38] E. Ma: Scripta. Mater, 2003, vol. 49, pp. 663-8.
[39] Y. Yang, Z. Zhang, X. Li, Q. Wang and Y. Zhang: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 51, pp. 592-7.
[40] W. Liu, H. Zhao, D. Li, Z. Zhang, G. Huang and Q. Liu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 596, pp. 176-82.
[41] H. Ahamed and V. Senthilkumar: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 539, pp. 349-59.
[42] H. Asgharzadeh, A. Simchi and H. S. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 542, pp. 56-63.
[43] H.J. McQueen, S. Spigarelli, M E. Kassner and E. Evangelista: Hot deformation and processing of aluminum alloys, CRC Press, FL, 2011, p. 128.
[44] D.L. Zhang: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 49, pp. 537-60.
[45] C. Suryanarayana: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 46, pp. 1-184.
[46] B.C. Ko and Y.C. Yoo: J. Mater. Sci., 2000, vol. 35, pp. 4073-7.
[47] F.J. Humphreys, P.B. Prangnell, R. Priestner: Curr. Opin. Solid St. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 5, pp. 15-21.
[48] J. May, H.W. Hoppel and M. Goken: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 189-94.
[49] H. Asgharzadeh and H.J. McQueen: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, 31, pp. 1016-1034.
[50] G.S. Rohrer: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 457-94.
[51] H. Agarwal, A.M. Gokhale, S. Graham and M. F. Horstemeyer: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 341, pp. 35-42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 1, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asgharzadeh, H., Rahbar Niazi, M. & Simchi, A. A Processing Map for Hot Deformation of an Ultrafine-Grained Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloy Prepared by Mechanical Milling and Hot Extrusion. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 5900–5908 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3162-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3162-3