Abstract
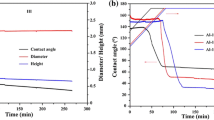
The wetting behavior and the interfacial reactions between TiC x substrate and molten Ti-Al alloys with different Al contents were studied using the Sessile Drop method at 1758 K (1485 °C) in argon atmosphere. It is found that the wettability and interface reaction products depend on Al content in the molten alloy. The initial contact angles between the molten Ti-Al alloy and TiC0.78 surface reduces from 110 to 80 deg when Al content in the alloy changes from 40 to 80 wt pct. The reduction in the initial contact angle is due to the decrease of surface tension of the molten Ti-Al alloys with increasing Al contents. The segregation of Al atoms to the surface occurred at all bulk concentrations of Ti-Al alloys. Al with lower surface tension tends to segregate on the surface of liquid Ti-Al alloy. In the spreading stage, the interfacial reaction led to the decrease in the contact angle. The adhesion in Ti-Al/TiC x system can be interpreted in terms of strong chemical interactions, which is greatly affected by the diffusion of C. The equilibrium contact angle was measured less than 10 deg. Finally, the reaction sequence at the Ti-Al melt and TiC x substrate interface is proposed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Contreras, V. Lopez, and E. Bedolla: Scr. Mater., 2004, vol.51, pp.249-253.
K. Das, T. Bandyopadhyay and S. Das: J. Mater. Sci., 2002, vol.37, pp. 3881-3892.
G. Wen, S. Li, B. Zhang, and Z. Guo: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp.1463-1470.
Y. Qin, W. Lu, D. Zhang, J. Qin, and B. Ji: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, vol. 404, pp. 42-48.
S. Zhu, D. Mukherji, W. Chen, Y. Lu, Z. Wang, and R. Wahi: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol.256, pp. 301-307.
D. Zhang, P. Shen, L. Shi, and Q. Jiang: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, vol.130, pp. 665-671.
Q. Lin, P. Shen, L. Yang, S. Jin, and Q. Jiang: Acta Mater., 2011, vol.59, pp.1898-1911.
C. Leon, V. Lopez, E. Bedolla, and R. Drew: J. Mater. Sci., 2002, vol.37, pp.3509-3514.
N. Frage, N. Froumin, and M. Dariel: Acta Mater., 2002, vol.50, pp. 237-245.
A. Contreras, E. Bedolla, and R. Perez: Acta Mater., 2004, vol.52, pp. 985-994.
N. Froumin, N. Frage, M. Polak, and M. Dariel: Scr. Mater., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 1263-1266.
P. Xiao, and B. Derby: Acta Mater., 1996, vol.44, pp. 307-314.
K. Landry, S. Kalogeropoulou, and N. Eustathopoulos: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol.254, pp. 99-111.
Y. Li, and T. Zhou: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol.44, pp.3337-3343.
M. Renkel and W. Smarsly: Google Patents, 2008.
W.A. Zisman: Adv. Chem. Ser., 1964, vol. 43, pp.1-51.
H. Fox, and W. Zisman: J. Colloid Sci., 1950, vol.5, pp.514-531.
L.A. Oden and R. McCune: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 2005–14.
M. Pietzka, and J. Schuster: J. Phase Equilib., 1994, vol.15, pp.392-400.
P.R. Sharps, A.P. Tomsia, and J.A. Pask: Acta Mater., 1981, vol.29, pp. 855-865.
E. Saiz, R. Cannon, and A. Tomsia: Acta Mater., 2000, vol.48, pp.4449-4462.
N. Eustathopoulos: Acta Mater., 1998, vol.46, pp.2319-2327.
N. Frage, L. Levin, E. Manor, R. Shneck, and J. Zabicky: Scr. Mater., 1996, vol.35, pp.791-797.
D.R. Stull and H. Prophet: J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1998, vol. 9, pp. 1–1951.
A. Subvolume: Thermodyn. Prop. Inorg. Mater., 1965, vol. 19(A2), pp. 1–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors are especially grateful to the National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program) (Project No. 2013CB632603) and Chongqing University Postgraduates’ Innovation Fund (Project No. CDJXS12131105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 17, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Lv, X., Dong, H. et al. Effect of Al on the Wetting Behavior Between TiC x and Molten Ti-Al Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 4783–4792 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3058-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3058-2