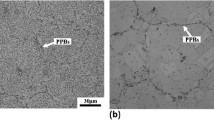
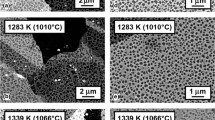
Abstract
The effect of subsolvus forging temperature and strain rate on the grain size developed during final supersolvus heat treatment (SSHT) of two powder-metallurgy, gamma–gamma prime superalloys, IN-100 and LSHR, was established. For this purpose, isothermal, hot compression tests were performed at temperatures ranging from 1144 K (871 °C) and 22 K (22 °C) below the respective gamma-prime solvus temperatures (T γ′) and strain rates between 0.0003 and 10 s−1. Deformed samples were then heat treated 20 K (20 °C) above the solvus for 1 h with selected additional samples exposed for shorter and longer times. For both alloys, the grain size developed during SSHT was in the range of 15 to 30 μm, except for those processing conditions consisting of pre-deformation at the highest temperature, i.e., T γ′—22 K (T γ′—22 °C), and strain rates in the range of ~0.001 to 0.1 s−1. In these latter instances, the heat-treated grain size was approx. four times as large. The observations were interpreted in terms of the mechanisms of deformation during hot working and their effect on the driving forces for grain-boundary migration which controls the evolution of the gamma-grain size.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Compressive strains, strain rates, and stresses are reported as positive quantities here and throughout the balance of this work.
References
M.J. Donachie Jr., ed.: Superalloys Source Book, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1984.
J.-P.A. Immarigeon and P.H. Floyd: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1177–1186.
A.K. Koul and J.-P.A. Immarigeon: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 1791–05.
Y. Combres and C. Levaillant: Inter. J. Plasticity, 1990, vol. 6, pp. 505-519.
M.O. Alniak and F. Bedir: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. A429, pp. 295-303.
M.O. Alniak and F. Bedir: Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2006, vol. B130, pp. 254-263.
W. Tu and T.M. Pollock: in Superalloys, R.C. Reed, K.A. Green, P. Caron, T.P. Gabb, M.G. Fahrmann, E.S. Huron, and S.A. Woodard, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2008, pp. 395–403.
W.J. Tu: PhD Dissertation, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, 2010.
W.J. Tu and T.M. Pollock: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 2002-2009.
M. Soucail, M. Marty, and H. Ocor: in Superalloys 1996, R.D. Kissinger, D.J. Deye, D.L. Anton, A.D. Cetel, M.V. Nathal, T.M. Pollock, and D.A. Woodford, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 663–66.
E. Huron, S. Shrivatsa, and E. Raymond: in Superalloys 2000, T.M. Pollock, R.D. Kissinger, R.R. Bowman, K.A. Green, M. McLean, S. Olson, and J.J. Schirra, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 49–58.
E.J. Payton: PhD Dissertation, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 2009.
P.R. Rios: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 1785-1789.
K. Song and M. Aindow: Proc. Mater. Sci. Technol. (MS&T) 2006: Fundamentals and Characterization, vol. 2, Z-K. Lu, C.E. Campbell, L.Q. Chen, E. B. Damm, J.E. Morral, and J.L. Murray, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2006, pp. 211–20.
G. Wang, D.S. Xu, E.J. Payton, N. Ma, R. Yang, M.J. Mills, and Y. Wang: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, pp. 4587-4594.
T.P. Gabb, J. Gayda, and J. Falsey: Report NASA/TM-2005-213649, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH, June 2005. http://gltrs.grc.nasa.gov.
D.D. Krueger, R.D. Kissinger, R.G. Menzies, and C.S. Wukusick: US Patent 4,957,567, September 1990.
E.L. Raymond, R.D. Kissinger, A.J. Paxson, and E.S. Huron: US Patent 5,584,947, December 1996.
E.S. Huron, J.A. Heaney, D.P. Mourer, J.R. Groh, E.L. Raymond, D.A. Utah, M.J. Weimer, and K.R. Bain: US Patent Application 11/770,257, January 2009.
D.P. Mourer and K.R. Bain: US Patent Application 12/494,896, December 2010.
S.L. Semiatin, K. E. McClary, A.D. Rollett, C.G. Roberts, E.J. Payton, F. Zhang, and T.P. Gabb: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 2778-2798.
J. Gayda, T.P. Gabb, and P.T. Kantzos: in Superalloys 2004, K.A. Green, T.M. Pollock, H. Harada, T.E. Howson, R.C. Reed, J.J. Schirra, and S. Walston, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 323–30.
J. Lemsky: Report NASA/CR-2005-213574, Ladish Company, Inc., Cudahy, WI, February 2005. http://gltrs.grc.nasa.gov.
S.L. Semiatin, K.E. McClary, A.D. Rollett, C.G. Roberts, E.J. Payton, F. Zhang, and T.P. Gabb: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43A, pp. 1649-1661.
S.I. Wright: Prakt. Metallogr., 2010, vol. 47, pp. 16-33.
A.A. Salem, M.G. Glavicic, and S.L. Semiatin: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. A494, pp. 350-359.
C. Zener: Private Communication to C.S. Smith in Trans. AIME, 1948, vol. 175, pp. 15–51.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Phenomena, Elsevier Science Ltd., Oxford, UK, 1996, chapters 3 and 9.
Aerospace Structural Metals Handbook, CINDAS LLC, West Lafayette, IN, 2000, vol. 5, code 4212.
E.J. Payton, T.A. Wynn, and M.J. Mills: J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, pp. 7305-7311.
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted as part of the in-house research of the Metals Branch of the Air Force Research Laboratory’s Materials and Manufacturing Directorate. The support and encouragement of the Laboratory management are gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank P.N. Fagin and T.M. Brown for their yeoman service in conducting the experiments. Technical discussions with T.P. Gabb, A.D. Rollett, and E.J. Payton are also much appreciated. Three of the authors were supported under the auspices of contracts FA8650-08-D-5200 (JMS, ARS) and FA8650-09-2-5800 (WMS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 7, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semiatin, S.L., Shank, J.M., Shiveley, A.R. et al. The Effect of Forging Variables on the Supersolvus Heat-Treatment Response of Powder-Metallurgy Nickel-Base Superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 6231–6251 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2572-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2572-y