Abstract
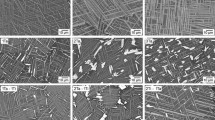
Nickel-base superalloys exhibit excellent high-temperature mechanical and physical properties and remain the first choice for structural components in advanced gas turbine engines for the aerospace propulsion and power generation applications. In response to the increasing demand for more efficient solutions and tighter requirements linked to gas turbine technologies, the properties of nickel-base superalloys can be improved by modification of their thermo-mechanical and/or compositional attributes. Recent investigations have revealed the potential use of ternary eutectic γ–γ′–δ Ni-base superalloys in advanced gas turbines due to high temperature mechanical properties that are comparable to state-of-the-art polycrystalline Ni-base superalloys. With properties largely dependent on microstructural strengthening mechanisms, both the composition and thermo-mechanical processing parameters of this novel class of alloys need to be optimized concurrently. The hot deformation characteristics of four γ–γ′–δ Ni-base superalloys with varying levels of Nb were evaluated at temperatures and strain rates between 1353 K and 1433 K (1080 °C and 1160 °C) and 0.01 to 0.001/s, respectively. Evidence of dislocation-based plasticity was observed following deformation at low temperatures and high strain rates, while high temperatures and low strain rates promoted superplasticity in these alloys. The extent of the microstructural changes and the magnitude of the cavitation damage which occurred during deformation was found to vary as a function of the alloy composition.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.M. Pollock and S. Tin: J. Propul. Power, 2006, vol. 22.2, pp. 361-74.
D. Furrer and H. Fecht: JOM, 1999, vol. 51.1, pp. 14-17.
C.T. Sims, N. S. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel: Superalloys II, Wiley, New York, NY, 1987.
R. F. Decker and C. T. Sims: The Metallurgy of Nickel-base Superalloys, Paul D. Merica Research Laboratory, New York, NY, 1972.
R.R. Unocic, G.B. Viswanathan, P.M. Sarosi, S.Karthikeyan, J.Li, and M.J. Mills: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 483-484, pp. 25-32.
R.R. Unocic, L. Kovarik, C. Shen, P.M. Sarosi, Y. Wang, J. Li, S. Ghosh, and M. J. Mills: Superalloys 2008, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2008.
D. Locq, P. Caron, S. Raujol, F. Pettinari-Sturmel, A. Coujou, and N. Clément: Superalloys 2008, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004.
R.M. Forbes Jones and L.A. Jackman: JOM, 1999, vol. 51, pp. 27-31.
A.D. Cetel, M. Gell, and J.W. Glatz: Conference on In Situ Composites III, Boston, MA, 1978, pp. 292–302.
R.W. Farley: The Superalloys, Wiley, New York, NY, 1972.
H.R. Gray: Material Show and Conference, NASA TM 73714, 1977.
R.L. Ashbrook: Meeting on Directionally Solidified In Situ Composites, NASA TM X-71514, 1974.
J. Stringer, D.M. Johnson, and D.P. Whittle: Oxid. Met., 1978, vol. 12.3, pp. 257-71.
D.M. Johnson, D.P. Whittle, and J. Stringer: Oxid. Met., 1978, vol. 12.3, pp. 273-91.
R.C. Reed: The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, 2006, pp. 372.
J. Tiley, G.B. Viswanathan, R. Srinivasan, R. Banerjee, D.M. Dimiduk, and H.L. Fraser: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57-8, pp. 2538-49.
Y. Gao, J.S. Stölken, M. Kumar, and R.O. Ritchie: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55-9, pp. 3155-67.
C. Stöcker, M. Zimmermann, H.-J. Christ, Z.-L. Zhan, C. Cornet, L.G. Zhao, M.C. Hardy, and J. Tong: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 518, pp. 27-34.
Y.F. Gu, C. Cui, D. Ping, H. Harada, T. Fukuda, and J. Fujioka: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 510-511, pp. 250-5.
C. Cui, Y. Gu, H. Harada, and A. Sato: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36, pp. 2921-27.
M. Xie, R.C. Helmink, and S. Tin: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 43, pp. 1259-67.
M. Xie, R.C. Helmink, and S. Tin: Superalloys 2012, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2012, pp. 633–42.
S. Tin, A. Rodriguez, A. DiScuillo-Jones, R.C. Helmink, and R. Hardy: Superalloys 2012, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2012, pp. 833–41.
X. Xie, G. Wang, J. Dong, C. Xu, W-D. Cao, and R. Kennedy: Superalloys 718, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005.
M. Detrois, R.C. Helmink, and S. Tin: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 586, pp. 236-44.
S. Azadian, L.-Y. Wei, and R. Warren: Mater. Charact., 2004, vol. 53, pp. 7-16.
H. M. Lalvani, M.A. Rist, and J.W. Brooks: Adv. Mater. Res., 2010, vol. 89-91, pp. 313-8.
Y. Wang, W.Z. Shao, L. Zhen, and B.Y. Zhang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 3218-27.
G.K. Bouse: Superalloys 1996, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996.
S.M. Seo, I.S. Kim, J.H. Lee, C.Y. Jo, H. Miyahara, and K. Ogi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 883-93.
X. Xie, C. Xu, G. Wang, J. Dong, W.-D. Cao, R. Kennedy: Superalloys 718, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by Rolls-Royce North American Technologies, Rolls-Royce Corporation, Rolls-Royce plc., and NSF-DMR-1006953.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 22, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Detrois, M., Helmink, R.C. & Tin, S. Microstructural Stability and Hot Deformation of γ–γ′–δ Ni-Base Superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 5332–5343 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2499-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2499-3