Abstract
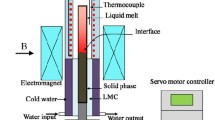
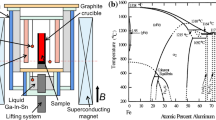
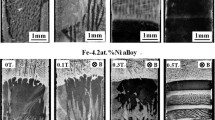
The influence of a transverse magnetic field (B < 1 T) on the solidification structure in directionally solidified Al-Si alloys was investigated. Experimental results indicate that the magnetic field caused macrosegregation, dendrite refinement, and a decrease in the length of the mushy zone in both Al-7 wt pct Si alloy and Al-7 wt pct Si-1 wt pct Fe alloys. Moreover, the application of the magnetic field is capable of separating the Fe-rich intermetallic phases from Al-7 wt pct Si-1 wt pct Fe alloy. Thermoelectric magnetic convection (TEMC) was numerically simulated during the directional solidification of Al-Si alloys. The results reveal that the TEMC increases to a maximum (\( u_{\rm{max} } \)) when the magnetic field reaches a critical magnetic field strength (\( B_{\rm{max} } \)), and then decreases as the magnetic field strength increases further. The TEMC exhibits the multi-scales effects: the \( u_{\rm{max} } \) and \( B_{\rm{max} } \) values are different at various scales, with \( u_{\rm{max} } \) decreasing and \( B_{\rm{max} } \) increasing as the scale decreases. The modification of the solidification structure under the magnetic field should be attributed to the TEMC on the sample and dendrite scales.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.L. Rooy: Metals Handbook, vol. 15, ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 1988, pp. 743–70.
Timpel M, Wanderka N, Murty BS, Banhart J. Acta Materialia 2010; 58: 6600–08.
Turchin AN, Zuijderwijk M, Pool J, Eskin DG, Katgerman L. Acta Materialia 2007: 55: 3795–3801.
Osawa Y, Takamori S, Kimura T, Minagawa K, Kakisawa H. Materials Transactions 2007; 48: 2467–75.
Steinbach S, Ratke L. Materials Science and Engineering A 2005; 413: 200–04.
Yasuda H, Ohnaka I, Fujimoto S, Takezawa N, Tsuchiyama A, Nakano T, Uesugi K. Scripta Materialia 2006; 54: 527–32.
Li L, Zhang YD, Esling C, Jiang HX, Zhao ZH, Zuo YB, Cui JZ. Journal of Crystal Growth 2012; 339: 61–69.
Li X, Fautrelle Y, Ren ZM. Acta Materialia 2007; 55: 3803–13.
Beckermann C. Int Mat Rev 2002; 47: 243–61.
Kurz W, Fisher DJ. Fundamentals of Solidification, Trans Tech Publ., Ackermannsdorf, (1989).
Flemings MC, Nereop G E. Trans AIME 1967; 239: 1449–61.
Davidson PA, Boysan F. Appl Sci Res 1987; 44: 241–59.
Hainke M, Friedrich J, Müller G. J Mater Sci 2004; 39: 2011–2475.
Heinrich J C, Poirier D R. Comptes Rendus Mecanique 2004; 332: 429–45.
Poirier D R. Metall Trans B 1987; 18B: 245–49.
Churchill S W. Viscous Flow, Butterworths, Boston (1988).
Dantzig J, Rappaz M. Solidification, EPFL Press, Lausanne, Switzerland (2009).
Li X, Gagnoud A, Ren ZM, Fautrelle Y, Moreau R. Acta Materialia 2009; 57: 2180–97.
Shercliff JA. J. Fluid Mech. 1979; 91: 235–51.
Li X, Fautrelle Y, Ren ZM. Acta Materialia 2007; 55: 1377–86.
K.A. Jackson, J.D. Hunt, D.R. Uhlmann, and T.P. Seward III: Trans TMS-A1ME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 149−58.
Curreri PA, Lee JE, Stefanescu DM. Metall Trans A 1988; 19A: 2671–76.
Shankar S, Riddle YW, Makhlouf M M. Acta Materialia 2004; 52: 4447–60.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported partly by the European Space Agency through the Bl-inter 09_473220, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51271109 and 51171106), and the Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning. The authors are indebted to Prof. Thierry Duffar in EPM/CNRS, Grenoble, for helpful and fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 30, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Du, D., Gagnoud, A. et al. Effect of Multi-Scale Thermoelectric Magnetic Convection on Solidification Microstructure in Directionally Solidified Al-Si Alloys Under a Transverse Magnetic Field. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 5584–5600 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2496-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2496-6