Abstract
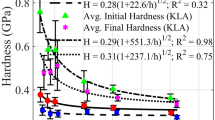
The characteristic length scale of deformation in copper specimens subjected to severe plastic deformation (SPD) through surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) was studied with indentation experiments. Annealed copper disks were shot peened with 6-mm diameter tungsten carbide spheres with an average velocity of 2.3 m/s for 15 minutes in a vibrating chamber. The SMAT-treated specimens were cross-sectioned, and the exposed face was studied under nanoindentation in order to determine the effect of dislocation density on surface hardness and indentation size effect (ISE). Since the specimen preparation of the exposed face involved mechanical polishing, which in turn introduced additional SPD on the indenting face, the effect of mechanical polishing on hardness measurement was investigated first. To this end, the mechanically polished specimens were subjected to various durations of electrochemical polishing. Hardness measurements on these specimens showed that the effect of mechanical polishing was substantial for both microindentation and nanoindentation, the impact being significantly larger for nanoindentation. Consequently, the measured depth of influence of the SMAT process, determined on specimens subjected to longer durations of electrochemical polishing, shows larger values compared to those previously reported in the literature. The ISE shows a bilinear relationship between the square of hardness and the reciprocal of indentation depth. The slope of this behavior, corresponding to smaller indentation loads, which is a measure of the ISE associated with a strain gradient, shows a power-law relationship with an increase in the distance away from the SMAT surface, instead of the constant value expected with the Nix–Gao type model.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Dub, Y. Lim, M. Chaudhri, J. Appl. Phys. 107 (2010) 043510-15.
W. D. Nix, H. Gao, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46 (1998) 411 –25.
Q. Ma, D. R. Clarke, J. Mater. Res. 10 (1995) 853 –63.
K. McElhaney, J. Vlasssak, W. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 13 (1998) 1300–6.
Y. Y. Lim, M. M. Chaudhri, Philos. Mag. A 79 (1999) 2979–3000.
K. Durst, B. Backes, M. Gken, Scr. Mater. 52 (2005) 1093 –7.
G. Feng, W. D. Nix, Scr. Mater. 51 (2004) 599 – 603.
J. Swadener, E. George, G. Pharr, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50 (2002) 681 –94.
M. Rester, C. Motz, and R. Pippan, J. Mater. Res. 24(3) (2009) 647–51.
M. Rester, C. Motz, R. Pippan, Scr. Mater. 59 (2008) 742 –5.
M. Rester, C. Motz, R. Pippan, Acta Mater. 55 (2007) 6427 –35.
A. Elmustafa, D. Stone, Acta Mater. 50 (2002) 3641 –50.
B. Yang, H. Vehoff, Acta Mater. 55 (2007) 849 –56.
G. M. Pharr, E. G. Herbert, Y. Gao, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 40 (2010) 271–92.
Y. Liu, A. Ngan, Scr. Mater. 44 (2001) 237 –41.
H. Fecht and Y. Ivanisenko: in Nanostructured Materials, 2nd ed., C.C. Koch, ed., William Andrew Publishing, Norwich, NY, 2007, pp. 119–72.
J. Jiang, J. Ren, A. Shan, J. Liu, H. Song, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 520 (2009) 80 –9.
J. Lu and K. Lu: in Comprehensive Structural Integrity, I. Milne, R.O. Ritchie, and B. Karihaloo, eds., Pergamon, Oxford, 2003, pp. 495–528.
K. Lu, J. Lu, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 375 (2004) 38 – 45.
B. Arifvianto, M. Suyitno, M. Mahardika, P. Dewo, P. Iswanto, and U. Salim: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, vol. 125, pp. 418–26.
U. Erb, K.T. Aust, and G. Palumbo: in Nanostructured Materials: Processing, Properties and Applications, chap. 6, C.C. Koch, ed., William Andrew Publishing, Norwich, NY, 2007, pp. 119–72.
L. Huang, J. Lu, M. Troyon, Surf. Coat. Technol. 201 (2006) 208 –13.
J. Chen, L. Lu, K. Lu, Scripta Materialia 54 (2006) 1913 –8.
Y. Zhang, Z. Han, K. Wang, K. Lu, Wear 260 (2006) 942 –8.
A. M. Gatey, S. S. Hosmani, R. Singh, S. Suwas, Advanced Materials Research 794 (2013) 238–47.
J. Tian, J. Villegas, W. Yuan, D. Fielden, L. Shaw, P. Liaw, D. Klarstrom, Materials Science and Engineering A 468-470 (2007) 164 –70.
H. Gao, Y. Huang, W. Nix, J. Hutchinson, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 47 (1999) 1239 –63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 4, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gale, J.D., Achuthan, A. & Morrison, D.J. Indentation Size Effect (ISE) in Copper Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD). Metall Mater Trans A 45, 2487–2497 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2201-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2201-9