Abstract
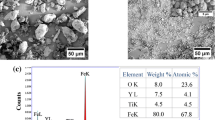
Y-O nanoparticles which are homogeneously distributed in the matrix can improve the thermal properties of steels. Several studies of mechanically alloyed steels showed that especially Y-Ti-O particles can cause a further improvement of the mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. It is also assumed that an addition of Zr instead of Ti may have a similar or even stronger effect. This study presents a new way of producing nanostructured ferritic alloys as Zr is incorporated by attrition of yttrium-stabilized zirconia balls during milling. Additionally, the effect of Zr incorporation is demonstrated as well as the particle size distribution of the Y-Zr-O nanoparticles analyzed by transmission electron microscopy. This is compared to a specimen milled with common steel balls. Atom probe tomography and transmission electron microscopy show that the incorporated zirconia lowers the minimum particle size and causes a finer particle distribution. This particle refinement causes a higher hardness after hipping.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. R. Odette, M. J. Alinger, and B. D. Wirth: Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2008, vol. 38, pp. 471-503.
M. K. Miller, D. T. Hoelzer, E. A. Kenik, and K. F. Russell: J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, vol. 329-333, pp. 338-341.
M. K. Miller, D. Hoelzer, E. Kenik, and K. Russell: Intermet., 2005, vol. 13, pp. 387-392.
C. A. Williams, E. A. Marquis, A. Cerezo, and G. D. W. Smith: J. Nucl. Mater., 2010, vol. 400, pp. 37-45.
C. A. Williams, P. Unifantowicz, N. Baluc, G. D. W. Smith, and E. A. Marquis: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 2219-2235.
G. Ressel, S. Primig, and H. Leitner: Int. J. Mater. Res. DOI:10.3139/146.110964.
S. Ukai, T. Nishida, T. Okuda, and T. Yoshitake: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 1998, vol. 35, pp. 294-300.
S. Ukai, T. Nishida, H. Okada, T. Okuda, M. Fujiwara, and K. Asabe: J. Nucl. Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 34, pp. 256-263.
M. Klimiankou: J. Nucl. Mater., 2004, vol. 329-333, pp. 347-351.
A. Hirata, T. Fujita, Y. R. Wen, J. H. Schneibel, C. T. Liu, and M. W. Chen: Nat. Mater., 2011, vol. 10, no.12, pp. 922-926.
S. Nomura, T. Okuda, S. Shikakura, M. Fujiwara, and K. Asabe: Solid State Powder Processing, Metals & Materials Society, Indianapolis, 1989, pp. 203–211.
Y. Uchida, N. Ohnuki, N. Hashimoto, T. Suda, T. Nagai, T. Shibayama, K. Hamada, S. Akasaka, S. Yamashita, S. Ohstuka, and T. Yoshitake: Mater.Res.Soc.Symp.Proc., 2007, vol. 981, pp. 107-112.
P. Unifantowicz, R. Schäublin, C. Hebert, T. Plocinski, G. Lucas, and N. Baluc: J. Nucl. Mater., 2012, vol. 422, pp. 131-136.
D. Larson: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 359-364.
M. K. Miller, E. Kenik, K. Russell, L. Heatherly, D. Hoelzer, and P. Maziasz: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 353, pp. 140-145.
M.K. Miller, A. Cerezo, M.G. Hetherington, and G.D. W. Smith: Atom Probe Field Ion Microscopy, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1996, pp. 476–438.
H.J. Penkalla: Proc. 1st Summer Sch. Adv. Electron Microsc., A. Czyrska-Filemonowicz and B. Dubiel, eds., 2003, pp. 4–23.
L. T. Stephenson, M. P. Moody, P. V. Liddicoat, and S. P. Ringer: Microsc. Microanal., 2007, vol. 13, pp. 448-463.
D. Vaumousse, A. Cerezo, and P. J. Warren: Ultramicroscopy, 2003, vol. 95, pp. 215-221.
E. A. Marquis: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, vol. 93, no. 18, pp. 181904.
F. Vurpillot: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2000, vol. 76, pp. 3127.
M.K. Miller, A. Cerezo, M.G. Hetherington, and G.D.W. Smith: Atom Probe Field Ion Microscopy, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1996, pp. 196–199.
D. Murali, B. K. Panigrahi, M. C. Valsakumar, S. Chandra, C. S. Sundar, and B. Raj: J. Nucl. Mater., 2010, vol. 403, no. 1-3, pp. 113-116.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the Institute of Chemical Technologies and Analytics at the University of Technology in Vienna for the use of its facilities. The authors especially thank Dr. Johannes Zbiral helping at the mechanical alloying process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 12, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ressel, G., Primig, S. & Leitner, H. The Effect of Zr Incorporation Caused by Ball Abrasion in a Milled Fe-Y2O3 Model Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 1552–1558 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2052-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2052-9