Abstract
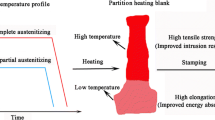
The hot stamping process has an extensive range of applications due to its advantages over the traditionally used stamping techniques developed in the past. To enhance the mechanical properties of the indirectly hot-stamped parts, the quenching and partitioning (Q&P) process has been recently applied on boron-alloyed steel. In the current research, it was observed that the tempering treatment on the directly hot-stamped boron steel resulted in better mechanical properties and higher formability index compared with the reported results using the Q&P process. The nano-carbide formation and the dislocation annihilation during the tempering treatment were suggested as the evident reasons for the occurrence of the mentioned robust properties. The ease of the practical implementation of the tempering route together with the markedly enhanced mechanical properties of the tempered parts make the suggested method privileged. Additionally, the variations in the yield strength before and after tempering were quantitatively evaluated.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Naderi, A. Saeed-Akbari, and W. Bleck: J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 487, pp. 445–55.
H. Karbasian and A.E. Tekkaya: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2010, vol. 210, pp. 2103–18.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Singapore, 1988.
M. Naderi, M. Ketabchi, M. Abbasi, and W. Bleck: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, vol. 211, pp. 1117–25.
M. Abbasi, M. Naderi, and A. Saeed-Akbari: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 45, pp. 1–5.
H. Liu, X. Jin, H. Dong, and J. Shi: Mater. Charact., 2011, vol. 49, pp. 223–27.
J. Min, J. Lin, J. Li, and W. Bao: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 49, pp. 326–32.
http://www.keytometals.com: Boron in steel.
M. Naderi, M. Ketabchi, M. Abbasi, and W. Bleck: Steel Res. Int., 2010, vol. 81, pp. 216–23.
K. Mori and D. Ito: CIRP Ann., 2009, vol. 58, pp. 267–70.
G. Schießl, T. Possehn, T. Heller, and S. Sikora: IDDRG International Deep Drawing Group 2004 Conference Sindelfingen, Germany, 2004, pp. 158–66.
M. Naderi, M. Ketabchi, M. Abbasi, and W. Bleck: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 369–76.
M. Naderi, M. Ketabchi, M. Abbasi, and W. Bleck: Procedia Eng., 2011, vol. 10, pp. 460–65.
H.L. Yi, S. Ghosh, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 4870–74.
H. Liu, X. Lu, X. Jin, H. Dong, and J. Shi: Scripta Mater., 2011, vol. 64, pp. 749–52.
M. Naderi: Doctoral Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Germany, 2007.
B. Schulz: Aust. Manuf. Technol., 2007, pp. 42–47.
DIN 50114, Zugversuch an dünnen Blechen.
DIN ISO 2768 Allgemeintoleranzen.
W. Bleck: Materials Science of Steel, Textbook for RWTH students, Verlag Mainz, Aachen, 2007.
A.C. Bannister and S.J. Trail: Structural Integrity Assessment Procedures for European Industry. British steel plc., 1996.
R.L. Brockenbrough & Associates, Inc, Effect of Yield-Tensile Ratio on Structural Behaviour-High Performance Steels for Bridge Construction, ONR-AISI Agreement No. N00014-94-2-0002, 1995.
I.V. Gorynin, V.V. Rybin, V.A. Malyshevskii, T.G. Semicheva, and L.G. Sherokhina: Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1999, vol. 41, pp. 377–83.
B. Hoffmann, O. Vöhringer, and E. Macherauch: J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, vol. 234–236, pp. 707–10.
L. Balogh, R.B. Figueiredo, T. Ungár, and T.G. Langdon: J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 528, pp. 533–38.
G. Krauss: Heat Treatment and Processing Principles, American Society for Metals, 1990.
D.A. Porter and K.E. Easterling: Phase Transformation in Metals and Alloys, 2nd Ed., Nelson Thornes Ltd., Cheltenham, 1992.
D. Holec and A. Dlouhy: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vol.482, pp. 159–62.
J. Pešička, R. Kužel, A. Dronhofer, and G. Eggerler: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 4847–62.
Y. Weng, H. Dong, and Y. Gan: Advanced Steels, Springer, 2011.
A.K. Sinha: Physical Metallurgy Handbook, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2003.
ImageJ 1.42q Software, National Institutes of Health, USA.
R.E. Reed-Hill and R. Abbaschian: Physical Metallurgy Principles, 3rd ed., PWS Publishing Company, Boston, 1991.
Heat Treater’s Guide: Practice and Procedures for Irons and Steels, ASM international, 1995.
E.V. Kozlov, N.A. Popova, S.I. Klimashin, V.E. Gromov, and N.A. Koneva: Russ. Phys. J., 2006, vol. 49, pp. 47–54.
J. Shi, X. Sun, M. Wang, W. Hui, H. Dong, and W. Cao: Scripta Mater., 2010, vol. 63, pp. 815–18.
G. Gottstein: Physical Foundations of Materials Science, Springer, Germany, 2004.
M. Säglitz, D.K. Matlock, and G. Krauss: International Conference on New Development in Advanced High-Strength Sheet Steels, Orlando, June 15–18, 2008, pp. 147–54.
S. Vandeputte, D. Vanderschhuern, S. Claessens, and L.T. Martinez: 9th International Conference on Steel Sheet Metal, Leuven, Belgium, 2001, pp. 405–14.
M. Abbasi, A. Saeed Akbari, and M. Naderi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 538, pp. 356–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 18, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naderi, M., Abbasi, M. & Saeed-Akbari, A. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of a Hot-Stamped Advanced High-Strength Steel via Tempering Treatment. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 1852–1861 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1546-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1546-1