Abstract
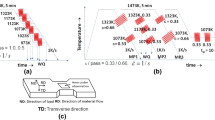
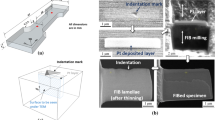
Plane-strain compression testing was carried out on a Nb-Ti-V microalloyed steel, in a GLEEBLE3500 simulator using a different amount of roughing, intermediate, and finishing deformation over the temperature range of 1373 K to 1073 K (1100 °C to 800 °C). A decrease in soaking temperature from 1473 K to 1273 K (1200 °C to 1000 °C) offered marginal refinement in the ferrite (α) grain size from 7.8 to 6.6 μm. Heavy deformation using multiple passes between A e3 and A r3 with true strain of 0.8 to 1.2 effectively refined the α grain size (4.1 to 3.2 μm) close to the ultrafine size by dynamic-strain-induced austenite (γ) → ferrite (α) transformation (DSIT). The intensities of microstructural banding, pearlite fraction in the microstructure (13 pct), and fraction of the harmful “cube” texture component (5 pct) were reduced with the increase in finishing deformation. Simultaneously, the fractions of high-angle (>15 deg misorientation) boundaries (75 to 80 pct), beneficial gamma-fiber (ND//〈111〉) texture components, along with {332}〈133〉 and {554}〈225〉 components were increased. Grain refinement and the formation of small Fe3C particles (50- to 600-nm size) increased the hardness of the deformed samples (184 to 192 HV). For the same deformation temperature [1103 K (830 °C)], the difference in α-grain sizes obtained after single-pass (2.7 μm) and multipass compression (3.2 μm) can be explained in view of the static- and dynamic-strain-induced γ → α transformation, strain partitioning between γ and α, dynamic recovery and dynamic recrystallization of the deformed α, and α-grain growth during interpass intervals.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
GLEEBLE is a trademark of Dynamic Systems Inc., Poestenkill, NY.
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
LECO is a trademark of LECO Corporation, St. Joseph, MI.
References
T. Gladman: The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, The Institute of Materials, London, 1997, Book 615, pp. 80–15.
F. Siciliano and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 511–30.
H. Beladi, G.L. Kelly, and P.D. Hodgson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 450–63.
R. Song, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 441, pp. 1–17.
R. Priestner and A.K. Ibraheem: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 1267–72.
P.D. Hodgson, M.R. Hickson, and R.K. Gibbs: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 40, pp. 1179–84.
T. Morimoto, I. Chikushi, R. Kurahashi, and J. Yanagimoto: Proc. Int. Conf. on Thermomechanical Processing of Steels, Stahleisen Verlag GmbH, Dusseldorf, Germany, 2004, pp. 415–22.
M. Miyata, W. Wakita, F. Fukushima, M. Eto, T. Sasaki, and T. Tomida: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 539–543, pp. 4698–03.
R. Barbosa, D.B. Santos, and R.E. Lino: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 558–559, pp. 471–75.
H. Dong and X. Sun: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2005, vol. 9, pp. 269–76.
B. Dutta and C.M. Sellars: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1987, vol. 3, p. 197–206.
D. Chakrabarti, M. Strangwood, and C.L. Davis: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 780–95.
S.J. Wu and C.L. Davis: J. Microsc., 2004, vol. 213, pp. 262–72.
S. Patra, S. Roy, Vinod Kumar, A. Haldar, and D. Chakrabarti: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 2575–90.
R.K. Ray, J.J. Jonas, M.P. Butron-Guillen, and J. Savoie: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 927–42.
R.K. Ray, M.P. Butron-Guillen, J.J. Jonas, and G.E. Ruddle: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 203–12.
V. Randle: Text. Microstr., 1993, vol. 20, pp. 231–42.
S.C. Hong and K.S. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, vol. A323, pp. 148–59.
D.Q. Bai, S. Yue, W.P. Sun, and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 2151–59.
S. Lee, D. Kwon, Y.K. Lee, and O. Kwon: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 1093–1100.
B. Eghbali: Mater. Charact., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 473–78.
Z.Q. Sun, W.Y. Yang, J.J. Qi, and A.M. Hu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 334, pp. 201–06.
B. Eghbali and M. Shaban: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2011, vol. 18, pp. 41–46.
J.L. Ferrieira, T.M.F. de Melo, I. de S. Bott, D.B. Santos, and P.R. Rios: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 1638–46.
G.L. Kelly, H. Beladi, and P.D. Hodgson: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 12, pp. 1585–90.
A. Shokouhi and P.D. Hodgson: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 23, pp. 1233–42.
T. Tomida, N. Imai, K. Miyata, S. Fukushima, M. Yoshida, M. Wakita, M. Etou, T. Sasaki, Y. Haraguchi, and Y. Okada: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1148–57.
W.R. Calado and R.A.N.M. Barbosa: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 1471–75.
S.V.S. Narayana Murty, S. Torizuka, K. Nagai, T. Kitai, and Y. Kogo: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 763–68.
D. Chakrabarti, C.L. Davis, and M. Strangwood: Mater. Charact., 2007, vol. 58, pp. 423–38.
D. Chakrabarti, C.L. Davis, and M. Strangwood: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 1963–77.
E.J. Palmiere, C.I. Garcia, and A.J. DeArdo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 277–86.
L.J. Cuddy and J.C. Raley: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1989–95.
F. Boratto, R. Barbosa, S. Yue, and J.J. Jonas: Proc. Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, Tokyo, Thermec 88, 1988, pp. 383–90.
T. Sakai and J.J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 189–209.
T. Sakai, M. Ohashi, K. Chiba, and J.J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 1781–90.
A.I. Fernandez, P. Uranga, B. Lopez, and J.M. Rodriguez Ibabe: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 361A, pp. 367–76.
H. Beladi, G.L. Kelly, A. Shokouhi, and P.D. Hodgson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 367, pp. 152–61.
J.K. Choi, D.H. Seo, J.S. Lee, K.K. Um, and W.Y. Choo: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 746–54.
E.I. Poliak and J.J. Jonas: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 127–36.
S.C. Hong, S.H. Lim, H.S. Hong, K.J. Lee, D.H. Shin, and K.S. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 355, pp. 241–48.
J.D. Verhoeven: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2000, vol. 9, pp. 286–96.
G. Krauss: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 34B, pp. 781–92.
Eric A. Jägle: Master’s Thesis, The University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2007, pp. 13–23.
M. Militzer and Y. Brechet: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 2273–82.
C.M. Sellars and J.H. Beynon: Proc. Conf. on HSLA Steels, D.P. Dunne and T. Chandra, eds., South Coast Printers, Port Kembla, Australia, 1985, pp. 142–50.
T. Furuhara, K. Kikumoto, H. Saito, T. Sekina, T. Ogawa, S. Morito, and T. Maki: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1038–45.
J. Majta, A.K. Zurek, M. Cola, P. Hochanadel, and M. Pietrzyk: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 1509–20.
P.D. Hodgson, A. Shokouhi, and H. Beladi: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1046–49.
A. Najafi-Zadeh, J.J. Jonas, and S. Yue: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2607–18.
M.R. Barnett, G.L. Kelly, and P.D. Hodgson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 1893–1900.
H. Mabuchi, T. Hasagawa, and T. Ishikawa: ISIJ Int., 1999, vol. 39, pp. 477–85.
G. Glover and C.M. Sellars: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 765–75.
B. Mintz, J. Lewis, and J.J. Jonas: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 13, pp. 379–88.
K. Mukherjee, S.S. Hazra, and M. Militzer: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 2145–59.
R. Song, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, and R. Kaspar: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 845–58.
Acknowledgments
Sincere thanks to the Department of Science and Technology (DST, New Delhi), the Research and Development Division (R&D) of Tata Steel for the provision of research funding, and RDCIS, SAIL (Ranchi) for providing the research material and offering the GLEEBLE testing facility. The authors acknowledge the help of the faculty and staff members from the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Steel Technology Centre (STC), and the Central Research Facility (CRF), I.I.T. Kharagpur. Drs. G.K. Dey and D. Srivastiava, Materials Science Division of BARC (Mumbai, India), deserve special mention for their support behind the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 13, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patra, S., Neogy, S., Kumar, V. et al. Refinement of Ferrite Grain Size near the Ultrafine Range by Multipass, Thermomechanical Compression. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 4296–4310 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1213-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1213-6