Abstract
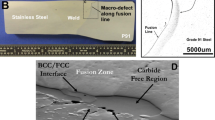
The microstructure and fracture morphology of AISI 8630-IN625 and ASTM A182-F22-IN625 dissimilar metal weld interfaces were compared and contrasted as a function of postweld heat treatment (PWHT) duration. For both systems, the microstructure along the weld interface consisted of a coarse grain heat-affected zone in the Fe-base metal followed by discontinuous martensitic partially mixed zones and a continuous partially mixed zone on the Ni side of the fusion line. Within the partially mixed zone on the Ni side, there exists a 200-nm-wide transition zone within a 20-μm-wide planar solidification region followed by a cellular dendritic region with Nb-Mo–rich carbides decorating the dendrite boundaries. Although there were differences in the volume of the partially mixed zones, the major difference in the metal weld interfaces was the presence of M7C3 precipitates in the planar solidification region, which had formed in AISI 8630-IN625 but not in ASTM A182-F22-IN625. These precipitates make the weldment more susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement and provide a low energy fracture path between the discontinuous partially mixed zones.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo, Japan.
PHILIPS is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
References
I.M. Robertson, D. Lillig, and P.J. Ferreira: in Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf.—Effects of Hydrogen on Materials, W.Y. Jackson Hole, B. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R. Jones, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 2009, pp. 22–37.
I.M. Robertson, H.K. Birnbaum, and P. Sofronis: in Dislocations in Solids, J.P. Hirth and L. Kubin, eds., Elsevier, New York, NY, 2009, vol. 19, pp. 249–93.
R.P. Gangloff: in Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf. —Effects of Hydrogen on Materials, W.Y. Jackson Hole, B. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R. Jones, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 2009, pp. 1–21.
R.P. Gangloff: Critical Issues in Hydrogen Assisted Cracking of Structural Alloys, Elsevier, New York, NY, 2008, pp. 141–65.
H.K. Birnbaum: J. Less-Common Met., 1984, vol. 104, pp. 31–41.
B.G. Pound: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 5733–43.
G.M. Pressouyre: Acta Metall., 1980, vol. 28, pp. 895–911.
G.M. Pressouyre and I.M. Bernstein: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 1571–80.
G.M. Pressouyre and I.M. Bernstein: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 835–44.
F. Wei and K. Tsuzaki: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 331–53.
J. Takahashi, K. Kawakami, Y. Kobayashi, and T. Tarui: Scripta Mater., 2010, vol. 63, pp. 261–64.
D.F. Johnson and E.A. Carter: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 58, pp. 638–48.
A. Van der Ven and G. Ceder: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 1223–35.
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy, 2nd ed., Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken, NJ, 2003.
H.I. Lange, S. Aldstedt, and E. Ostby: Investigation of Fractured Weld Connection on Hub No. AB-103 Asgard B, SINTEF, Trondheim, Norway, 2001.
V.C.M. Beaugrand, L.S. Smith, and M.F. Gittos: Corrosion 2009, Atlanta, GA, NACE International, Houston, TX, 2009, 12 p.
V. Olden, P.E. Kvaale, P.A. Simensen, S. Aaldstedt, and J.K. Solberg: ASME 2003 22nd Int. Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering (OMAE2003), Cancun, Mexico, ASME, New York, NY, 2003, pp. 109–15.
V.C.M. Beaugrand, L.S. Smith, and M.F. Gittos: 28th Int. Conf. on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, OMAE2009, Honolulu, HI, 2009, vol. 6, pp. 227–36.
M.F. Gittos and H.G. Pisarski: “Materials Selection for Dissimilar Joints in Subsea Hubs,” Final Report, The Welding Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2006.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy Third Edition, McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York, NY, 1986.
J.A. Fenske: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign, 2010.
S. Kou and Y.K. Yang: Weld. J., 2007, vol. 86, pp. 303–12.
M.L. Santella: J. Press. Vess. Technol., 2012, vol. 134, pp. 021404–5.
J.P. Hirth: Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 861–90.
E. Bain and H.W. Paxton: Alloying Elements in Steel, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1961.
R.A. Oriani and P.H. Josephic: Scripta Metall., 1979, vol. 13, pp. 469–71.
P. Novak, R. Yuan, B.P. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R.O. Ritchie: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2010, vol. 58, pp. 206–26.
G.M. Pressouyre and I.M. Bernstein: Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 89–100.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge ExxonMobil for providing funding and materials, The Welding Institute for providing fracture specimens and Acute Technological Services for fabrication of test weld samples. One of the authors (JAF) acknowledges several members of the University of Illinois Materials Research Lab staff for their assistance in training on a variety of equipment, especially Mike Marshall, Jim Mabon, and Changhui Lei as well as Bill Lamberti and Bill Horn from ExxonMobil for the nanoSIMS results. The research for this publication was carried out, in part, in the Center for Microanalysis of Materials in the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory at the University of Illinois. IMR acknowledges support from the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 15, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fenske, J.A., Robertson, I.M., Ayer, R. et al. Microstructure and Hydrogen-Induced Failure Mechanisms in Fe and Ni Alloy Weldments. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 3011–3022 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1129-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1129-1