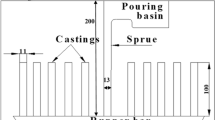
Abstract
As a standard test-bar permanent mold, the “Stahl” Mold has been widely used in foundries to assess the properties of cast alloys. However, inferior mechanical properties are often obtained with this mold due to shrinkage-induced microporosity in the gage section. In order to improve the mechanical properties, a design modification comprising a thin knife ingate between the feeder and test-bar cavity was evaluated in this work. The new design was studied by computer-aided simulation. Simulations predicted that the knife ingate improved the metal feeding capability and reduced the shrinkage microporosity at the gage section from 3 to 1 pct. Experimental verification work has been undertaken with aluminum alloy A356, and the results were analyzed by a statistics theory-based factorial analysis method. The new design resulted in main effects with ultimate tensile strength (UTS) improvement of 20 MPa (relative 12 pct) and elongation increment of 2 pct (relative 45 pct) for the as-cast test bars.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.F. Mondolfo: Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties, Butterworth and Co., London, 1976, pp. 3–11.
G.A. Edwards, K. Stiller, G.L. Dunlop, and M. Couper: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 3893–3904.
C.H. Cáceres, C.J. Davidson, J.R. Griffiths, and Q.G. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 2611–18.
R.I. Mackay and J.E. Gruzleski: Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 1998, vol. 10, p. 255.
Q.G. Wang and C.J. Davidson: J. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 36, pp. 739–50.
H. Xu, D.L. Xu, S. Zhang, and Q. Han: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54 (2), pp. 2191–96.
J.R. Davis: Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys, ASM International Handbook, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993, pp. 3–5 and p. 368.
G. Brodova, P.S. Popel, and G.I. Eskin: Liquid Metal Processing, Taylor and Francis, New York, NY, 2002, pp. 83–84.
H. Xu, X. Jian, T.T. Meek, and Q. Han: Mater. Lett., 2004, vol. 58, pp. 3669–73.
X. Jian, H. Xu, T.T. Meek, and Q. Han: Mater. Lett., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 190–93.
C. Allen and Q. Han: Int. J. Metalcasting, 2011, vol. 5, pp. 69–70.
H. Xu, Q. Han, and T.T. Meek: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 473, pp. 96–104.
G.K. Sigworth: AFS Trans., 1987, vol. 95, pp. 73–78.
A. Abdollahi and J.E. Gruzleski: Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 1998, vol. 11, pp. 145–55.
L. Bäckerud, J. Tamminen, and G. Chai: Solidification Characteristics of Aluminum Alloys, vol. 2, Foundry Alloys, Americans Foundrymen’s Society Inc., Schaumburg, IL, 1990, p. 266.
M. Djurdjevic, H. Jiang, and J. Sokolowski: Mater. Charact., 2001, vol. 46, pp. 31–38.
A. Knuutinen, K. Nogita, S.D. McDonald, and A.K. Dahle: J. Light Met., 2001, vol. 1, pp. 229–40.
D. Apelian, S. Shivkumar, and G. Sigworth: AFS Trans., 1989, vol. 97, p. 727.
S. Shivkumar, S. Ricci, C. Keller, and D. Apelian: J. Heat Treat., 1990, vol. 8, pp. 63–70.
S. Shivkumar, R. Ricci, Jr., B. Steenhof, D. Apelian, and G.K. Sigworth: AFS Trans., 1989, vol. 97, pp. 791–810.
D. Emadi, L.V. Whiting, M. Sahoo, P.D. Newcombe, T.M. Castles, P. Burke, and K.D. Callaghan: AFS Trans., 2001, 109: 487–98.
J. Campbell: Mod. Cast., 1997, vol. 87 (4), pp. 36–39.
F Chiesa, T. Boisvert, T. Houde, and D.e. Lavoie: AFS Trans., 2004, vol. 112, 04-077, pp. 1–10.
E.W. Miguelucci: AFS Trans., 1985, vol. 93, pp. 913–16.
L.J. Ebert, R.E. Spear, and G. Sacks: AFS Trans., 1948, vol. 56, pp. 315–33.
ISO 2378, International Organization for Standardization, Switzerland, 1972.
P. Grandier-Vazeille and S. Jacob: Fonderie, 1970, vol. 287, pp. 70–74.
K.R. Whaler: Stahl Specialty Company, Kingsville, MO, private communication, 2003.
G.K. Sigworth and T.A. Kuhn: AFS Trans., 2009, vol. 117, pp. 55–62.
D. Emadi, L.V. Whiting, M. Sahoo, and D. Larouche: AFS Trans., 2004, vol. 112, pp. 225–36.
MagmaSoft v4.4, Magma Foundry Technologies, Chicago, IL.
K.D. Carlson and C. Beckermann: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 163–75.
T.-G. Kim and Z.-H. Lee: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1997, vol. 40, pp. 3513–25.
H. Wen: Master Thesis, Case Western Reserve University, 2000, p. 50.
E. Niyama, T. Uchida, M. Morikawa, and S. Saito: Int. Cast Met. J., 1982, vol. 7 (3), pp. 52–63.
ASTM International E8M-09, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2009.
ASTM International B557M-10, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2010.
E.P. DeGarmo, J.T. Black, and R.A. Kosher: Material and Processing in Manufacturing, 9th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, 2003, p. 227.
Y. Murakami: Stress Intensity Factors Handbook, 3rd ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2001, Sect. 8.68, p. 658.
M. Tiryahioglu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct., 2008, vol. 497, pp. 512–14.
Q.G. Wang, D. Apelian, and D.A. Lados: J. Light Met., 2001, vol. 1, pp. 73–84.
A. Dean and D. Voss: Design and Analysis of Experiments, Springer, New York, NY, 1999, p. 145.
M. Drouzy, S. Jacob, and M. Richard: AFS Int. Cast Met. J., 1980, vol. 5, pp. 43–50.
Minitab v15, Minitab Inc., State College, PA.
G.K. Sigworth and C.H. Casares: AFS Trans., 2004, vol. 112, pp. 373–86.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the advice and consultation with Steve Sikorski, MagmaSoft, regarding the computer simulation studies; foundry casting and testing activity with Xuejun Zhu, Chai-Jung Chen, and Rich Miller, CWRU; assistance by Bob Pischel and Jason Place, FOSECO, on mold coating and Alspek measurements; General Aluminum for the donation of a standard test-bar mold; Dennis Daniels, Alumalloy, for the A356 alloy. Finally, the project team thanks the American Foundry Society for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 28, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Schwam, D., Neff, D.V. et al. Improvement in Mechanical Properties of A356 Tensile Test Bars Cast in a Permanent Mold by Application of a Knife Ingate. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 1048–1059 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0918-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0918-2