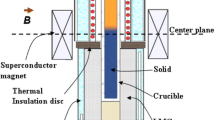
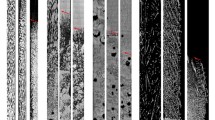
Abstract
This work investigated the thermoelectric magnetic convection (TEMC) during directional solidification under a transverse magnetic field numerically and experimentally. Numerical results show that the TEMC will form in liquid near the liquid/solid interface and in the dendritic network. The value of the TEMC mainly depends on the crucible diameter, the temperature gradient, and the magnetic field intensity. The value of the TEMC increases as the crucible diameter and the temperature gradient are increased. The value of the TEMC on the sample scale increases to a maximum when the magnetic field is of the order of 0.1 T, and then decreases as the magnetic field still increases. However, the value of the TEMC on the cell/dendrite scale continues to increase with the increase of the magnetic field intensity when the applied magnetic field is less then 1 T. Two alloys are solidified directionally in the vertical configuration under a transverse magnetic field, and results show that the application of a lower transverse magnetic field (B < 1 T) modified the liquid/solid interface shape and the cellular/dendritic array significantly. Indeed, it was observed that, along with the refinement of the cell/dendrite, the magnetic field caused the deformation of the liquid/solid interfaces and the extensive segregations (i.e., channel and freckle) in the mushy zone. Comparison of the numerical and experimental results shows that the modification amplitude of the liquid/solid interface and the cellular/dendritic morphology is in good agreement with the value of the TEMC at the liquid/solid interface and in the dendritic network. This implies that changes of the interface shape and the cellular/dendritic morphology should be attributed, respectively, to the TEMC on the sample and the cell/dendrite scales.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
FLUX-EXPERT is a trademark of SIMAP-EPM/G-INP/ CNRS, St Martin d’Heres Cedex, France.
References
M.D. Dupouy, B. Drevet, and D. Camel: J. Cryst. Growth, 1997, vol. 181, pp. 145–59.
M.D. Dupouy and D. Camel: J. Cryst. Growth, 1998, vol. 183, pp. 469–89.
J.R. Carruthers: in Preparation and Properties of Solid State Materials, W.R. Wilcox and R.A. Lefever, eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1997, vol. 3, pp. 1–6.
D.H. Matheson, M.S. Wargo, D. Motakef, J. Carlson, and A. Nakos: J. Cryst. Growth, 1987, vol. 85, pp. 557–68.
G.D. Robertson and D. O’Connor: J. Cryst. Growth, 1986, vol. 76, pp. 100–10.
S.N. Tewari, R. Shah, and H. Song: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 1535–44.
T. Alboussiere, R. Moreau, and D. Compte: Rendu de l’Acad. Sci., 1991, vol. 313, pp. 749–53.
O. Laskar: Ph.D Thesis, INPG, France, 1994.
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, and R. Bolcato: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4067–79.
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, Z.M. Ren, Y. Fautrelle, and R. Moreau: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 2180–97.
J.A. Shercliff: J. Fluid Mech., 1979, vol. 91, pp. 231–51.
Y.Y. Kline and J.S. Walker: J. Cryst. Growth, 1998, vol. 183, pp. 150–58.
A.K. Sample and A. Hellawell: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 2163–73.
S.D. Felicelli, J.C. Heinrich, and D.R. Poirier: Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22B, pp. 847–59.
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, and R. Bolcato: J. Cryst. Growth, 1998, vol. 183, pp. 690–704.
S. Steinbach and L. Ratke: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 1388–94.
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, and Z.M. Ren: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 1377–86.
K.A. Jackson, J.D. Hunt, D.R. Uhlmann, and T.P. Seward III: Trans. TMS-A1ME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 149–58.
P.A. Curreri, J.E. Lee, and D.M. Stefanescu: Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2671–76.
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 11–20.
G.S. Reddy and J.A. Sekhar: J. Mater. Sci., 1985, vol. 20, pp. 3535–40.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the project OPTIMAG (Bl-inter 09_473220) funded by the ANR in France, Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50801045 and 50911130365), the Shanghai “Phosphor” Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10QA1402500), and the Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at the Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning, Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai (Grant Nos. 09510700100, 08dj1400404, 2011CB610404 and 08DZ1130100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 10, 2011.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-1038-8
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LI, X., Ren, Z., Gagnoud, A. et al. Effects of Thermoelectric Magnetic Convection on the Solidification Structure During Directional Solidification under Lower Transverse Magnetic Field. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 3459–3471 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0741-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0741-9