Abstract
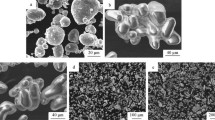
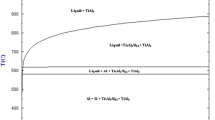
Al-Ti-C master alloys have a great potential as efficient grain refiners for aluminum and its alloys. In the present work, the Al-Ti-C master alloys are synthesized via a relatively novel technique through the reaction of a compacted mixture of K2TiF6 and graphite with molten aluminum. The obtained alloys are examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) methods. The results indicate that the produced Al-Ti-C master alloys contain TiC and TiAl3 particles within the aluminum matrix. Also, these alloys were evaluated using the KBI test mold. The results indicate that the produced Al-Ti-C master alloy is an efficient grain refiner for pure aluminum and its alloys compared with the Al-Ti-B one. The factors affecting the grain refinement of aluminum and its alloys are studied. The proper conditions for evaluating the efficiency of the produced Al-Ti-C master alloy to obtain a minimum grain size are as follows: temperature, 993 K (720 °C); holding time, 2 minutes; and (Ti/Al) weight ratio, 0.01 pct.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Backerud, H. Boettcher, J. Courtenary, and R. Vainikl: in Light Metals 2004, A.T. Tabereaux, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 833–35.
A.M. Omran, M.A. Shaheen, J.H. Aly, and A. Bastaweesy: in Light Metals 2004, A.T. Tabereaux, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004, pp. 817–20.
K.T. Kashyap and Chandrakar: Bull. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 24 (4), pp. 345–53.
D. Boot, P. Cooper, D.H. StJohn, and A.K. Dohle: in Light Metals 2002, W. Schneider, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2002, pp. 909–15.
G.K. Sigworth: U.S Patent No. 4812290, 1989.
I.H. Ali, M.A. Shaheen, and A.M. Omran: 2nd Minia Int. Conf. Advanced Trends in Engineering, Apr. 7–9, 2002, El Minia University, El Minia, Egypt, pp. 1403–10.
A.A. Abdel-Hamid and A.L.O. Zaid: Current Advances in Mechanical Design and Production, 7th Cairo University International MDP Conf., Cairo, Egypt, Feb. 2000, pp. 331–38.
J.A. Spittle and S. Sadli: Cast Met., 1995, vol. 7 (4), pp. 247–53.
Y. Lina and L. Xiangfa: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, vol. 82, pp. 519–24.
B.S. Murty, S.A. Kori, and M. Chakraborty: Int. Mater. Rev., 2002, vol. 47 (1), pp. 3–29.
A. Banerrji and W. Reif: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 2127–37.
A. Banerrji and W. Reif: Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 2065–68.
M.A. Hadia, A.A. Ghaneya, and A. Niazy: in Light Metals 1996, W. Hale, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 729–39.
A.J. Whitehead, S.A. Danilak, and D.A. Granger: in Light Metals 1997, R. Huglen, ed., Warrendale, PA, TMS, 1997, pp. 785–93.
M.A. Doheim, A.M. Omran, and A. Abdel-Gwad: J. Eng. Sci., 2008, vol. 36 (2), pp. 471–81.
P. Hoefs, W. Reif, A.H. Geen, P.C. Van Wiggen, W. Schneider, and D. Brandner: in Light Metals 1997, R. Huglen, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 777–84.
B.Q. Zang, L. Lu, M.O. Li, H.S. Fang, H.T. Ma, and J.G. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 1727–33.
Y. Birol: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 454, pp. 110–17.
A.M. Omran: Al-Azhar Univ. Eng. J., JAUES, 2008, vol. 3 (13), pp. 56–61.
A. Cibula: J. Inst. Met., 1951–52, vol. 80, pp. 1–16.
A.M. Kanury: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2349–56.
A.R. Kennedy: Proc. Int. Conf., HTC, Cracow, Poland, June–July 1997.
A.R. Kennedy, A.E. Karantzalis, and S.M. Wyatt: J. Mater. Sci., 1999, vol. 34 (5), pp. 933–40.
I.A. Mwamba: M.Sc. Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, 2006.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Eng. Sayed Abdel-Wahab, Chief of the Board of Directors, Aluminium Company of Egypt, for supporting this work. Thanks also to Eng. Shaher Abdulah, Director of the Laboratories Staff, and the RandD team for their help with the experimental part of this work. We extend our appreciation to the Derivados Del fluor, S.A. Espana Company, for supplying us with potassium fluotitanate.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 28, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doheim, M.A., Omran, A.M., Abdel-Gwad, A. et al. Evaluation of Al-Ti-C Master Alloys as Grain Refiner for Aluminum and Its Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 2862–2867 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0689-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0689-9