Abstract
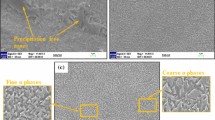
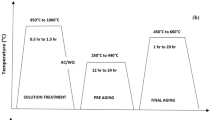
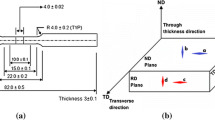
Aging of highly β-stabilized titanium alloys commonly leads to the formation of precipitate-free zones being susceptible to fatigue crack initiation. Duplex aging improves the fatigue properties of metastable β titanium alloys by enhancing a homogeneous α phase formation. In this study a duplex-aging cycle was designed for Ti 38-644 (β-C). Depending on the prior processing history heat treatment parameters were adapted on the basis of microstructure studies, hardness measurements and comparative tensile tests. The fatigue limit and fatigue crack growth threshold were determined for duplex-aged β-C. The results indicate that duplex aging promotes a homogeneously precipitated α phase providing excellent values of the fatigue limit. Surface-related fatigue crack initiation was observed. Comparing the fracture surfaces of direct- and duplex-aged β-C a transition of the tensile fracture mode from intergranular to predominantly transgranular was observed accompanied by a gain in ductility at comparable yield strengths. This was assumed to be the reason for the slightly improved fatigue crack growth behavior of duplex-aged as compared to direct-aged β-C. Along the entire heat treatment cycle the microstructure response was evaluated with regard to the particular effects on the fatigue properties. The results indicate clearly that key to success is a completely recrystallized β microstructure and the reasonably controlled aging response.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Schmidt and H.-J. Christ: Int. J. Mater. Res., 2008, vol. 99, pp. 1098–1106.
J.G. Ferrero, J.R. Wood, and P.A. Russo: in Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1990’s, D. Eylon, R.R. Boyer, and D.A. Koss, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 211–26.
H.-E. Krugmann and J.K. Gregory: in Microstructure/Property Relationships in Titanium Aluminides and Alloys, Y.-W. Kim and R.R. Boyer, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1991, pp. 549–61.
L. Wagner and J.K. Gregory: Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1990’s, D. Eylon, R.R. Boyer, and D.A. Koss, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 199–209.
G. Lütjering and J.C. Williams: Titanium, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, 2003, pp. 247–81.
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings: Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1994, pp. 797–827.
P. Schmidt, G.M. Lohse, and H.-J. Christ: in Ti-2007 Science and Technology, M. Niinomi, S. Akiyama, M. Hagiwara, M. Ikeda, and K. Maruyama, eds., The Japan Institute of Metals (JIM), Sendai, 2007, pp. 769–72.
P. Schmidt and H.-J. Christ: Effects of Hydrogen on Materials, B. Somerday, P. Sofronis, and R. Jones, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 2009, pp. 227–34.
E. Deubelbeiss: Materialprüfung, 1974, vol. 16, pp. 240–44.
A. Saxena, S.J. Hudak, J.K. Donald, and D.W. Schmidt: J. Test. Evol., 1978, vol. 6, pp. 167–74.
H.J. Rack and T.J. Headley: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 909–20.
S. Ankem, D. Banerjee, D.J. McNeish, J.C. Williams, and S.R. Seagle: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 2015–25.
M. Peters and C. Leyens: Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003, pp. 153–82.
R.R. Boyer and R. Bajoraitis: in Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1980’s, R.R. Boyer and H.W. Rosenberg, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 295–305.
Y. Kawabe and S. Muneki: in Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1990’s, D. Eylon, R.R. Boyer, and D.A. Koss, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 187–97.
M. Niiomi, B. Gong, T. Kobayashi, Y. Ohyabu, and O. Toriyama: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 1141–51.
R.H. Van Stone, J.R. Low Jr., and J.L. Shannon, Jr.: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 539–47.
R.H. Van Stone and T.B. Cox: ASTM STP 600, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1976, pp. 5–29.
A.L. Pilchak and J.C. Williams: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 22–25.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for financially supporting this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 3, 2010
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, P., El-Chaikh, A. & Christ, HJ. Effect of Duplex Aging on the Initiation and Propagation of Fatigue Cracks in the Solute-rich Metastable β Titanium Alloy Ti 38-644. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 2652–2667 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0662-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0662-7