Abstract
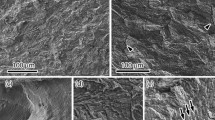
The objective of this study was to characterize hydrogen-assisted crack propagation in gas-tungsten arc (GTA) welds of the nitrogen-strengthened, austenitic stainless steel 21Cr-6Ni-9Mn (21-6-9), using fracture mechanics methods. The fracture initiation toughness and crack growth resistance curves were measured using fracture mechanics specimens that were thermally precharged with 230 wppm (1.3 at. pct) hydrogen. The fracture initiation toughness and slope of the crack growth resistance curve for the hydrogen-precharged weld were reduced by as much as 60 and 90 pct, respectively, relative to the noncharged weld. A physical model for hydrogen-assisted crack propagation in the welds was formulated from microscopy evidence and finite-element modeling. Hydrogen-assisted crack propagation proceeded by a sequence of microcrack formation at the weld ferrite, intense shear deformation in the ligaments separating microcracks, and then fracture of the ligaments. One salient role of hydrogen in the crack propagation process was promoting microcrack formation at austenite/ferrite interfaces and within the ferrite. In addition, hydrogen may have facilitated intense shear deformation in the ligaments separating microcracks. The intense shear deformation could be related to the development of a nonuniform distribution of hydrogen trapped at dislocations between microcracks, which in turn created a gradient in the local flow stress.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.R. Moody, S.L. Robinson, and W.M. Garrison: Res. Mech., 1990, vol. 30, pp. 143–206.
H.G. Nelson: in Treatise on Materials Science and Technology: Embrittlement of Engineering Alloys, C.L. Briant and S.K. Banerji, eds., Academic Press, New York, NY, 1983, vol. 25, pp. 275–359.
A.W. Thompson and I.M. Bernstein: in Advances in Corrosion Science and Technology, M.G. Fontana and R.W. Staehle, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1980, vol. 7, pp. 53–175.
G.R. Caskey: in Hydrogen Degradation of Ferrous Alloys, R.A. Oriani, J.P. Hirth, and M. Smialowski, eds., Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985, pp. 822–62.
J.A. Brooks and A.W. Thompson: Int. Mater. Rev., 1991, vol. 36, pp. 16–44.
J.A. Brooks and A.J. West: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 213–23.
J.A. Brooks, A.J. West, and A.W. Thompson: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 75–84.
M.I. Luppo, A. Hazarabedian, and J. Ovejero-Garcia: Corros. Sci., 1999, vol. 41, pp. 87–103.
M.J. Morgan, G.K. Chapman, M.H. Tosten, and S.L. West: Trends in Welding Research: Proc. 7th Int. Conf., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 2006, pp. 743–48.
A.M. Nasreldin, M.M.A. Gad, I.T. Hassan, M.M. Ghoneim, and A.A. El-Sayed: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 444–48.
C. Pan, Y.J. Su, W.Y. Chu, Z.B. Li, D.T. Liang, and L.J. Qiao: Corros. Sci., 2002, vol. 44, pp. 1983–93.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 1997, vol. 03.01, pp. 968–91.
C. SanMarchi, B.P. Somerday, and S.L. Robinson: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2007, vol. 32, pp. 100–16.
K.A. Nibur, B.P. Somerday, D.K. Balch, and C. SanMarchi: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 3795–3809.
D.J. Kotecki and T.A. Siewert: Weld. J., 1992, vol. 71, pp. 171s–178s.
C. SanMarchi, B.P. Somerday, J. Zelinski, X. Tang, and G.H. Schiroky: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 2763–75.
H.K. Birnbaum and P. Sofronis: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. A176, pp. 191–202.
M. Menard, J.M. Olive, A.-M. Brass, and I. Aubert: in Environment-Induced Cracking of Materials: Chemistry, Mechanics and Mechanisms, S.A. Shipilov, R.H. Jones, J.-M. Olive, and R.B. Rebak, eds., Elsevier, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2008, vol. 1, pp. 179–88.
K.A. Nibur, D.F. Bahr, and B.P. Somerday: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 2677–84.
I.M. Robertson: Eng. Fract. Mech., 2001, vol. 68, pp. 671–92.
C. SanMarchi, K.A. Nibur, D.K. Balch, and B.P. Somerday: J. Pressure Vessel Technol., 2008, vol. 130, art. no. 041401, 9 pp.
J.P. Hirth: in Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior, N.R. Moody and A.W. Thompson, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1990, pp. 677–85.
J.P. Hirth: in Hydrogen Effects in Materials, A.W. Thompson and N.R. Moody, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 507–22.
P. Sofronis and H.K. Birnbaum: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1995, vol. 43, pp. 49–90.
Y. Liang, P. Sofronis, and N. Aravas: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 2717–30.
P. Sofronis and R.M. McMeeking: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1989, vol. 37, pp. 317–50.
Y. Liang and P. Sofronis: Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2003, vol. 11, pp. 523–51.
H. Peisl: in Topics in Applied Physics: Hydrogen in Metals I, G. Alefeld and J. Volkl, eds., Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1978, vol. 28, pp. 53–74.
R.A. Oriani: Acta Metall., 1970, vol. 18, pp. 147–57.
R.B. McLellan: Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 1655–63.
J.K. Tien, A.W. Thompson, I.M. Bernstein, and R.J. Richards: Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 821–29.
J.J. Gilman: Micromechanics of Flow in Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1969.
P. Sofronis, Y. Liang, and N. Aravas: Eur. J. Mech., A/Solids, 2001, vol. 20, pp. 857–72.
Y. Liang, P. Sofronis, D.C. Ahn, R. Dodds, and D. Bammann: Mech. Mater., 2008, vol. 40, pp. 115–32.
J.R. Rice: Proc. 14th Int. Congr. on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, North-Holland Publishing, Delft, The Netherlands, 1977, pp. 207–20.
D.C. Ahn, P. Sofronis, and R.H. Dodds: Int. J. Fract., 2007, vol. 145, pp. 135–57.
J.P. Hirth and B. Carnahan: Acta Metall., 1978, vol. 26, pp. 1795–1803.
G.J. Thomas: in Hydrogen Effects in Metals, I.M. Bernstein and A.W. Thompson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 77–84.
Acknowledgments
Weld was fabricated by G. Gibbs and electron microscopy was conducted by J. Chames and R. Nishimoto. The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the United States Department of Energy (Contract No. DE AC04-94AL85000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 22, 2008.
C.H. CADDEN deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somerday, B., Dadfarnia, M., Balch, D. et al. Hydrogen-Assisted Crack Propagation in Austenitic Stainless Steel Fusion Welds. Metall Mater Trans A 40, 2350–2362 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9922-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9922-1