Abstract
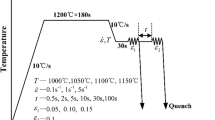
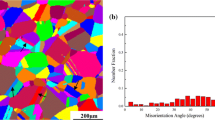
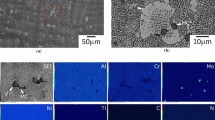
Deformation and microstructure evolution in Co-33Ni-20Cr-10Mo superalloy during hot deformation are studied by carrying out compression tests between 950 °C and 1200 °C with an increment of 50 °C at strain rates of 0.1, 1, 10, and 30 s−1. The flow curves obtained for the aforementioned strain rates in this temperature range show that this alloy has high work-hardening characteristics; this is due to the strong dislocation-solute interactions associated with dynamic strain aging (DSA). Microstructures deformed at temperatures up to 1050 °C consist of numerous deformation twins and highly dense dislocations, which are attributed to the high activation energy for deformation and the relatively low strain-rate sensitivity m in the temperature range of 950 °C to 1200 °C. Dynamic recrystallization (DRX), which is dependent on the strain rate, occurs at T = 1000 °C, 1050 °C, 1100 °C, 1150 °C, and 1200 °C.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
References
J.P. Immarigeon, K. Rajan, and W. Wallace: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 339–45.
A. Chiba, X.G. Li, and M.S. Kim: Philos. Mag., 1999, vol. 79, pp. 1533–54.
M.A. Meyers, O. Vohringer, and V.A. Lubarda: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 4025–39.
R.E. Reed Hill, J.P. Hirth, and H.C. Rogers: Deformation Twinning, Gordon and Breach, New York, 1964, p. 7.
P. Mullner, C. Solenthaler, and M.O. Speidel: Acta Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 1727–32.
G. Gottstein, H. Mecking, and D. Zabardjadi: Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Strength of Metals and Alloys, Nancy, France, 1976, pp. 1126–34.
R. Raj: Trans. AIME, 1981, vol. 12, pp. 1089–97.
C.E. Campbell, W.J. Boettinger, and U.R. Kattner: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 775–92.
H.J. McQueen and N.D. Ryan: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, vol. 322, pp. 43–63.
M.C. Somani, K. Muraleedharan, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, and V. Singh: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, vol. 245, pp. 88–99.
S.C. Medeiros, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, W.G. Frazier, and R. Srinivasan: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. 293, pp. 198–207.
A.A. Guimares and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1655–66.
A. Kelly and R.B. Nicholson: Progr. Mater. Sci., 1967, vol. 10, p. 984.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, 2nd ed., McGraw Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1976, pp. 138.
H. Monajati, M. Jahazi, S. Yue, and A.K. Taheri: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 895–905.
R. Ebrahimi, A. Najafizadeh, and R. Shateri: Proc. 81st Steel Symp., Iranian Institute for Iron and Steel, Isphahan, Iran, 2003, pp. 230–37.
A. Van Den Beukel and U.F. Kocks: Acta Mater., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 1027–34.
F. Montheillet and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 3346–48.
T. Chunfeng, P. Feng, Q. Xuanhui, D. Baihua, W. Tianjian, and H. Xinbo: Rare Met., 2008, vol. 27, pp. 292–98.
X. Yourong, C. Liangshen, J. Lei, and W. Deying: Proc. 2nd Int. Conf., Intelligent Processing and Manufacturing of Materials, IPMM, Honolulu, 1999, vol. 2, pp. 805–10.
M.J. Weis, M.C. Mataya, S.W. Thompson, and D.K. Matlock: in Superalloy 71- Metallurgy and Applications, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989, p. 135.
C.I. Garcia, G.D. Wang, D.E. Camus, E.A. Loria, and A.J. DeArdo: in Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, E.A. Loria, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1994, p. 293.
L.X. Zhou and T.N. Baker: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. A177, pp. 1–9.
W. Chen and M.C. Chaturvedi: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. A183, pp. 81–89.
S.C. Medeiros, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, W.G. Frazier, and R. Srinivasan: Scripta Mater., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 17–23.
D.W. Livesey and C.M. Sellars: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 136–44.
G. Shen, S.L. Semiatin, and R. Shivpuri: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 1795–1803.
T. Sakai and M. Ohashi: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1990, vol. 6, pp. 1251–57.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Cooperation of Innovative Technology and Advanced Research in Evolutional Area, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 29, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kartika, I., Matsumoto, H. & Chiba, A. Deformation and Microstructure Evolution in Co-Ni-Cr-Mo Superalloy during Hot Working. Metall Mater Trans A 40, 1457–1468 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9829-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9829-x