Abstract
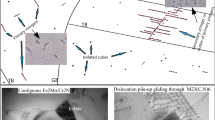
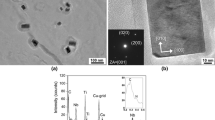
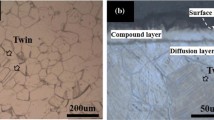
This article reports our efforts in characterization of an ultralow carbon 316LN-type stainless steel. The carbon content in the material is one-third that in a conventional 316LN, which further inhibits the formation of grain boundary carbides and therefore sensitizations. Our primary effort is focused on characterization of submicron size precipitates in the materials with the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique complemented by Auger electron spectroscopy (AES). Thermodynamic calculations suggested that several precipitates, such as M23C6, Chi, Sigma, and Cr2N, can form in a low carbon 316LN. In the steels heat treated at 973 K (700 °C) for 100 hours, a combination of EBSD and AES conclusively identified the grain boundary precipitates (≥100 nm) as Cr2N, which has a hexagonal closed-packed crystallographic structure. Increases of the nitrogen content promote formation of large size Cr2N precipitates. Therefore, prolonged heat treatment at relatively high temperatures of ultralow carbon 316LN steels may result in a sensitization.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
LECO is a trademark of LECO Corporation, St. Joseph, MI.
References
E.M. Mahla and N.A. Nielsen: Trans. ASM, 1951, vol. 43, pp. 290–322.
R. Stickler and A. Vinckier: Trans. ASM, 1961, vol. 54, pp. 362–80.
F.R. Beckitt and B.R. Clark: Acta Metall., 1967, vol. 15, pp. 113–29.
L.K. Singhal and J.W. Martin: Trans. AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 814–19.
C.D. Casa, V.B. Nileshwar, and D.A. Melford: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1969, vol. 207, pp. 1325–32.
G.F. Vander Voort: Metals Handbook, 10th ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1990, vol. 1, pp. 706–08.
W.O. Binder, C.M. Brown, and R. Franks: Trans. ASM, 1949, vol. 41, pp. 1301–70.
S.D. Washko and G. Aggen: Metals Handbook, 10th ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1990, vol. 1, pp. 841–907.
K. Han, Y. Xin, R.P. Walsh, S. Downey, and P.N. Kalu: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, vol. 516, pp. 169–79.
M. Shimada and S. Tone: Adv. Cryst. Eng. Mater., 1988, vol. 34, pp. 131–39.
R.P. Reed, R.P. Walsh, and C.N. McCown: Adv. Cryog. Eng. Mater., 1992, vol. 38, pp. 45–54.
K. Miyahara, D.-S. Bae, T. Kimura, and Y. Shimode: J. Nucl. Mater., 1995, vol. 226, pp. 92–103.
P. Shankar, H. Shaikh, S. Sivakumar, S. Venugopal, D. Sundararaman, and H.S. Khatak: J. Nucl. Mater., 1999, vol. 264, pp. 29–34.
N. Parvathavarthini and R.K. Dyal: J. Nucl. Mater., 2002, vol. 305, pp. 209–19.
H. Sahlaoui, K. Makhlouf, H. Sidhom, and J. Philibert: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 372, pp. 98–108.
L. Klimek and B. Piertrzyk: J. Alloys Compd., 2004, vol. 382, pp. 17–23.
J.A. Small and J.R. Michael: J. Microsc., 2001, vol. 201, pp. 59–69.
S.I. Wright and B.L. Adams: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 759–67.
S. Downey II, P.N. Kalu, and K. Han: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 480, pp. 96–100.
Y. Minami, H. Kimura, and Y. Ihara: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1986, vol. 2, pp. 795–806.
M.L. Saucedo-Munoz, Y. Watanabe, T. Shoji, and H. Takahashi: Cryogenics, 2000, vol. 40, pp. 693–700.
C.R. Sokei, I. Ferreira, R.C. Tokimatsu, and V.A. Ventrella: Acta Microsc., 2003, vol. 12, pp. 9–10.
T.-H. Lee, S.-J. Kim, E. Shin, and S. Takaki: Acta Crystallogr., 2006, vol. B62, pp. 979–86.
N. Hashimoto, E. Wakai, and J.P. Robertson: J. Nucl. Mater., 1999, vol. 273, pp. 95–101.
P. Shankar, P. Palanichamy, T. Jayakumar, B. Raj, and S. Ranganathan: Metall. Mater. Trans., 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2959–68.
P. Villars and L.D. Clavert: Pearson’s Handbook of Crystallographic Data for Intermetallic Phases, 2nd ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1991, pp. 2694–95.
TSL User Manual-OIM Analysis 5.2, Ametek Inc.
R.P. Walsh, L.T. Summers, and J.R. Miller: Proc. 16th CEC/ICMC Conf., T. Haruyama, T. Mitsui, and K. Yamafuji, eds., Kitakyushu, Japan, May 1996, Elsevier Science, New York, NY, 1996, pp. 1891–94.
J. Feng: Fus. Eng. Des., 2005, vol. 73 (2–4), pp. 357–73.
Acknowledgments
This work was performed at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, which is supported by NSF Cooperative Agreement No. DMR-0654118, by the State of Florida, and by the DOE. The Auger work was undertaken at ORNL, which is supported by the Assistant Secretary for Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Office of FreedomCAR and Vehicle Technologies, as part of the High Temperature Materials Laboratory User Program, ORNL, managed by UT–Battelle LLC for the United States Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725. Part of this work was supported by the US ITER Office. We thank Dr. H.M. Meyer III for performing the Auger studies; Mr. R.E. Goddard for maintenance of the SEM equipments; Mr. V.J. Toplosky for performing some experiments; and Mr. R.P. Walsh, Drs. J.R. Miller, and L.T. Summers for helpful discussions. The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent those of the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 16, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Downey, S., Han, K., Kalu, P. et al. A Study of Submicron Grain Boundary Precipitates in Ultralow Carbon 316LN Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 881–887 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0163-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0163-0