Abstract
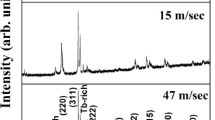
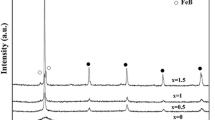
Melt-spun ribbons of (Fe0.65Co0.35)88Zr7B4Cu1 alloy have been prepared at different wheel speeds, namely, 47, 39, 34, and 17 m/s, and subsequently annealed at 773 K (500 °C) under controlled atmosphere. Structural and soft magnetic properties have been evaluated using X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, transmission electron microscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer. The structure of as-spun ribbons changes from fully amorphous to partially amorphous/nanocrystalline to fully nanocrystalline (bcc α-Fe(Co) + Fe2Zr) on decreasing the wheel speed. Annealing of amorphous ribbons leads to the precipitation of nanocrystalline bcc α-Fe(Co) phase. The Curie temperature (T c ) of the amorphous phase is found to increase with decreasing wheel speed possibly due to the effect of exchange field penetration of nanocrystals present in the amorphous matrix. The saturation magnetization (4πM s ) of as-spun ribbons having partially nanocrystalline bcc α-Fe(Co) phase is high as compared to the ribbons with completely amorphous phase, and it remains almost the same even after annealing. The lowest coercivity has been achieved in the ribbons that are fully amorphous, and the coercivity was found to increase with decreasing wheel speed.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronic Instruments Corp., Mahwah, NJ.
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
ADE is a trademark of Microsense, LLC, Boston, MA.
References
Y. Yoshizawa, S. Oguma, and K. Yamauchi: J. Appl. Phys., 1988, vol. 64, pp. 6044–46.
K. Suzuki, A. Makino, N. Kataoka, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1991, vol. 32, pp. 93–102.
M.E. McHenry, M.A. Willard, and D.E. Laughlin: Prog. Mater. Sci., 1999, vol. 44, pp. 291–433.
B.D. Cullity and C.D. Graham: Introduction to Magnetic Materials, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2009, pp. 466–67.
M.A. Willard, M.Q. Huang, D.E. Laughlin, M.E. McHenry, J.O. Cross, V.G. Harris, and Franchetti: J. Appl. Phys., 1999, vol. 85, pp. 4421–23.
M.A. Willard, D.E. Laughlin, M.E. McHenry, D. Thomas, K. Sickafus, J.O. Cross, and V.G. Harris: J. Appl. Phys., 1998, vol. 84, pp. 6773–77.
M.E. McHenry and D.E. Laughlin: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 223–38.
M.A. Willard, D.E. Laughlin, and M.E. McHenry: J. Appl. Phys., 2000, vol. 87, pp. 7091–96.
M. Müller, H. Grahl, N. Mattern, U. Kühn, and B. Schnell: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1996, vol. 160, pp. 284–86.
F. Johnson, C.Y. Um, M.E. McHenry, and H. Garmestani: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2008, vol. 297, pp. 93–98.
F. Shahri and A. Beitollahi: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2007, vol. 354, pp. 1487–93.
Y.Q. Wu, T. Bitoh, K. Hono, A. Makino, and A. Inoue: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 4069–77.
D. Arvindha Babu, B. Majumdar, R. Sarkar, D. Akhtar, and V. Chandrasekaran: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 41, pp. 195002–195008.
B. Majumdar and D. Akhtar: Bull. Mater. Sci., 2005, vol. 28, pp. 395–99.
B. Majumdar, S. Bysak, and D. Akhtar: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007, vol. 309, pp. 300–06.
F.E. Luborsky: Amorphous Metallic Alloys, Monographs in Materials, Butterworth & Co. Publishers Ltd., London, 1983, pp. 8–11.
D. Arias and J.P. Abriata: Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1988, vol. 9 (5), pp. 597–604.
A. Hernando and I. Navarro: Phys. Rev. B, 1995, vol. 51, pp. 3281–84.
J.S. Garitaonandia, D.S. Schmool, and J.M. Barandiran: Phys. Rev. B, 1998, vol. 58, pp. 12147–58.
R. Alben, J.J. Becker, and M.C. Chi: J. Appl. Phys., 1978, vol. 47, pp. 1653–58.
G. Herzer: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1991, vol. A133, pp. 1–5.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO), New Delhi, India. The authors thank Dr. A.K. Singh, DMRL, Hyderabad, India, and Dr. Kiran, MIDHANI, Hyderabad, India, for their help with XRD and coercivity measurements. It is a pleasure to thank Dr. G. Malakondaiah, Director, DMRL, Hyderabad, India, for continued support and permission to publish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 22, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arvindha Babu, D., Srivastava, A., Majumdar, B. et al. Influence of Melt-Spinning Parameters on the Structure and Soft Magnetic Properties of (Fe0.65Co0.35)88Zr7B4Cu1 Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 1313–1320 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0159-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0159-9