Abstract
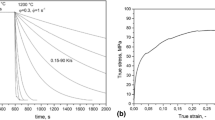
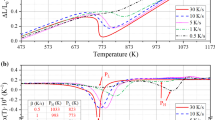
The correlation of the microstructure and mechanical properties of thermomechanically processed low-carbon steels containing B and Cu was investigated in this study. Eighteen kinds of steel specimens were fabricated by varying B and Cu contents and finish cooling temperatures (FCTs) after controlled rolling, and then tensile and Charpy impact tests were conducted on them. Continuous cooling transformation (CCT) diagrams of the B-free and B-added steel specimens under nondeformed and deformed conditions were constructed by a combination of deformation dilatometry and metallographic methods. The addition of a very small amount of B remarkably decreased the transformation start temperatures near a bainite start temperature (Bs) and thus expanded the formation region of low-temperature transformation phases such as degenerate upper bainite (DUB) and lower bainite (LB) to slower cooling rates. On the other hand, a deformation in the austenite region promoted the formation of quasipolygonal ferrite (QPF) and granular bainite (GB) with an increase in transformation start temperatures. The tensile test results indicated that tensile strength primarily increased with decreasing FCT, while the yield strength did not vary much, except in some specimens. The addition of B and Cu, however, increased the tensile and yield strengths simultaneously because of the significant microstructural change occasionally affected by the FCT. The Charpy impact test results indicated that the steel specimens predominantly composed of LB and lath martensite (LM) had lower upper-shelf energy (USE) than those consisting of GB or DUB, but had nearly equivalent or rather lower ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) in spite of the increased strength. According to the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analysis data, it was confirmed that LB and LM microstructures had a relatively smaller effective grain size than GB or DUB microstructures, which enhanced the tortuosity of cleavage crack propagation, thereby resulting in a decrease in DBTT.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
References
I. Tamura, H. Sekine, T. Tanaka, and C. Ouchi: Thermomechanical Processing of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels, Butterworth & Co. Ltd., London, UK, 1988.
T. Gladman: The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, The Institute of Materials, London, UK, 1997.
J.Y. Koo, M.J. Luton, N.V. Bangaru, R.A. Petkovic, D.P. Fairchild, C.W. Petersen, H. Asahi, T. Hara, Y. Terada, M. Sugiyama, H. Tamehiro, Y. Komizo, S. Okaguchi, M. Hamada, A. Yamamoto, and I. Takeuchi: Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng., 2004, vol. 14, pp. 2–10.
Y.N. Malinochka, G.Z. Koval’chuk, and V.N. Yarmosh: Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1982, vol. 24, pp. 760–65.
S.S. Ghasemi Banadkouki and D.P. Dunne: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 759–68.
A. Fatehi, A.M. Elwazri, J. Calvo, and S. Yue: Proc. Materials Science and Technology 2008, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2008, pp. 1562–70.
S.K. Banerji and J.E. Morral: Proc. Int. Symp. Boron in Steels, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979.
B.L. Bramfitt and J.G. Speer: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 817–29.
G. Krauss and S.W. Thompson: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 937–45.
T. Hayashi, F. Kawabata, and K. Amano: Proc. Materials Solution '97 on Accelerated Cooling/Direct Quenching Steels, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1997, pp. 93–99.
P. Cizek, B.P. Wynne, C.H.J. Davies, B.C. Muddle, and P.D. Hodgson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 1331–49.
B.C. Kim, S. Lee, N.J. Kim, and D.Y. Lee: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 139–49.
J.H. Chen, Y. Kikuta, T. Araki, M. Yoneda, and Y. Matsuda: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 1779–88.
Y.M. Kim, S.Y. Shin, H. Lee, B. Hwang, S. Lee, and N.J. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 1731–42.
J.C. Zhao and M.R. Notis: Acta Metall., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4203–18.
E. Hornbogen and R.C. Glenn: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1960, vol. 218, pp. 1064–70.
A. Youle and B. Ralph: Met. Sci., 1972, vol. 6, pp. 149–52.
S.R. Goodman, S.S. Brenner, and J.R. Low, Jr.: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 2363–69.
T.-H. Lee, Y.-O. Kim, and S.-J. Kim: Philos. Mag., 2007, vol. 87, pp. 209–24.
B. Hwang, Y.M. Kim, S. Lee, N.J. Kim, and S.S. Ahn: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 725–39.
B. Hwang, Y.G. Kim, S. Lee, Y.M. Kim, N.J. Kim, and J.Y. Yoo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 2107–14.
H. Kitahara, R. Ueji, N. Tsuji, and Y. Minamino: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1279–88.
S. Morito, X. Huang, T. Furuhara, T. Maki, and N. Hansen: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 5323–31.
T. Furuhara, S. Morito, and T. Maki: Proc. 1st Int. Symp. on Steel Science, ISIJ, Kyoto, Japan, 2007, pp. 51–56.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by a grant (Grant No. M2007010007) from the Fundamental R&D Program for Core Technology of Materials funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Gwacheon, Korea. The authors thank Professor Sunghak Lee, Dr. Sang Yong Shin, and Mr. Hyo Kyung Sung of Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH, Pohang, Korea) for their help with the Charpy impact test analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 3, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, B., Lee, C.G. & Lee, TH. Correlation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thermomechanically Processed Low-Carbon Steels Containing Boron and Copper. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 85–96 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0070-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0070-4