Abstract
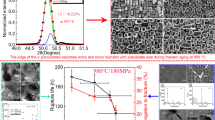
The high-temperature creep deformation and fracture behavior of a directionally solidified Ni-base superalloy DZ951 have been investigated over a wide stress range of 110 to 880 MPa at high temperatures (700 °C to 1000 °C). In this article, the detailed creep deformation and fracture mechanism have been studied. The results show that the creep curves exhibit strong temperature dependence. From transmission election microscopy (TEM) observations, it is suggested that the deformation mechanism is temperature dependent and mainly consists of three dislocation-controlling mechanisms: stacking faults and dislocation-pair shearing, dislocation bowing, and dislocation climbing. It is found that the fracture mode of DZ951 alloy changes from cleavagelike fracture at low temperature to ductile fracture at high temperature. At 700 °C, the creep cracks mainly initiate at the surface and propagate along the cleavagelike facets. With increasing temperature, cracks can initiate at the surface, carbide/matrix interface, and cast pore. The growth of microcrack has a direction perpendicular to the stress direction. The creep-rupture data follow the Monkman–Grant relationship in different temperature regions.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan.
PHILIPS is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
References
F.L. VerSynder and R.W. Guard: Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 32, pp. 485–93.
F.L. VerSynder and M.E. Shank: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1970, vol. 6, pp. 213–47.
M. McLean: Directionally Solidified Materials for High Temperature Service, TMS, London, 1983, pp. 180–89.
D.N. Duhl: in Superalloys II, C.T. Sims, N.S. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel, eds., John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY, 1987, pp. 189–92.
F.R.N. Nabarro and H.L. de Villiers: The Physics of Creep, Taylor and Francis, London, 1995, pp. 83–97.
L.R. Liu, T. Jin, N.R. Zhao, Z.H. Wang, X.F. Sun, H.R. Guan, and Z.Q. Hu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 361, pp. 191–97.
L.R. Liu, T. Jin, N.R. Zhao, Z.H. Wang, X.F. Sun, H.R. Guan, and Z.Q. Hu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 385, pp. 105–12.
Q.Z. Chen, C.N. Jones, and D.M. Knowles: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 385, pp. 402–18.
X.B. Liu, B. Kang, W. Carpenter, and E. Barbero: J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 1967–73.
U. Krupp, R. Orosz, H.J. Christ, U. Buschmann, and W. Wiechert: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2004, vols. 461–464, pp. 37–43.
A. Jacques and P. Bastie: Phil. Mag., 2003, vol. 83, pp. 3005–27.
R.C. Reed, N. Matan, D.C. Cox, M.A. Rist, and C.M.F. Rae: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 3367–81.
M. Kolbe, K. Neuking, and G. Eggeler: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, vol. 234, pp. 877–79.
M. Kolbe, A. Dlouhy, and G. Eggeler: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 246, pp. 133–42.
V. Sass and M. Feller-Kniepmeier: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 245, pp. 19–28.
S. Nategh and S.A. Sajjadi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 339, pp. 103–08.
A.C. Picasso, A.J. Marzocca, and I. Alvarez: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, vol. 234, pp. 1099–1102.
R. Srinicasan, G.F. Eggeler, and M.J. Mills: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 4867–78.
T. Tong, S. Dalby, J. Byrne, M.B. Henderson, and M.C. Hardy: Int. J. Fatigue, 2001, vol. 23, pp. 897–902.
M. Okazaki and Y. Yamazaki: Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, vol. 21, pp. 79–86.
Z.K. Chu, J.J. Yu, X.F. Sun, N.R. Zhao, H.R. Guan, and Z.Q. Hu: Trans. Nonferrous Metall. Soc. China, 2006, vol. 16, pp. 1949–52.
P.C. Xia, J.J. Yu, X.F. Sun, H.R. Guan, and Z.Q. Hu: J. Alloys Compd., 2006, vol. 443, pp. 125–31.
J.H. Gittus: Creep Viscoelasticity and Creep Fracture in Solids, Applied Science, London, 1975, pp. 473–79.
S.A. Sajjadi and S. Nategh: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vol. 307, pp. 158–64.
L.Z. He, Q. Zheng, X. F. Sun, H.R. Guan, Z.Q. Hu, A.K. Tieu, C. Lu, and H.T. Zhu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 2385–91.
F.C. Monkman and N.J. Grant: Proc. ASTM, 1956, vol. 56, pp. 593–620.
A.K. Koul, R. Castillo, and K. Willett: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, vol. 66, pp. 213–26.
S.A. Sajjadi, S. Nategh, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 325, pp. 484–89.
G.L. Erickson, K. Harris, and R.E. Schwer: TMS-AIME Meeting, Houston, TX, Mar. 1985, pp. 1–10.
T. Link and M. Feller-Kniepmeier: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 99–105.
B.H. Kear, J.M. Oblak, and A.F. Giamei: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2477–86.
P.R. Bhowal, E.F. Wright, and E.L. Raymond: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1709–17.
B.A. Lerch and V. Gerold: Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 1709–16.
B.A. Lerch and V. Gerold: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 2135–41.
S.G. Tian, J.H. Zhang, H.C. Yang, Y.B. Xu, and Z.Q. Hu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vol. 262, pp. 271–78.
T.M. Pollock and A.S. Argon: Acta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 42, pp. 1–30.
T.P. Gabb, S.L. Draper, D.R. Hull, R.A. Mackay, and M.V. Nathal: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1989, vol. 118, pp. 59–69.
J.T. Guo, D. Ranucci, E. Picco, and P.M. Strocchi: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 2329–35.
J.T. Guo, C. Yuan, H.C. Yang, V. Lupinc, and M. Maldini: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1103–10.
R.S. Mishra, S.P. Singh, A.M. Sriramamurthy, and M.C. Pandey: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1995, vol. 11, pp. 341–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 30, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Z., Yu, J., Sun, X. et al. High-Temperature Creep Deformation and Fracture Behavior of a Directionally Solidified Ni-Base Superalloy DZ951. Metall Mater Trans A 40, 2927–2937 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0001-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0001-4