Abstract
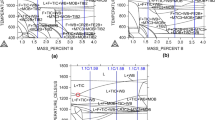
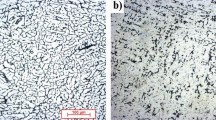
Commercially produced hot bands of continuous cast (CC) and direct chill (DC) cast AA 5052 aluminum alloy were cold rolled to different reductions from 10 pct through 90 pct. Evolution of deformation textures in the CC and DC materials was investigated by using three-dimensional orientation distribution functions (ODFs) that were determined by X-ray diffraction. The electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique was adopted to keep track of the evolution of grain boundaries of CC and DC materials during the early stages of cold rolling (≤40 pct thickness reduction). Results showed that the Cube cluster is found in annealed DC hot band. A much stronger Cube orientation is found in DC hot band than in CC hot band. The cold rolling texture evolutions for CC and DC materials follow the same path. The α and β fibers become well developed after 60 pct cold rolling in both CC and DC materials. The highest intensity along the β fiber (skeleton line) is located near the S orientation {123}〈634〉 in both materials. There exists a path by which the copper orientation (112)\([\overline {11} 1]\) develops at the expense of the Cube orientation (001)\([0\bar 10]\) with an increase in cold rolling reductions. Low-angle boundaries with misorientation angles between 1.5 and 5 deg are rapidly increased during the early stage of cold rolling. There is no evidence of the development of twin and twin-related boundaries in either CC or DC materials when the cold rolling reductions are less than 40 pct.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Wells, D.J. Lloyd, I.V. Samarasekera, J.K. Brimacombe, and E.B. Hawbolt: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29B, pp. 621–33.
B. Ren, Z. Li, C. Li, S. Ding, and J.G. Morris: in Advances in Hot Deformation Textures and Microstructures, J.J. Jonas, T.R. Bieler, and K.J. Bowman, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 207–21.
W.C. Liu, C.-S. Man, and J.G. Morris: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 807–14.
T. Sakai, S. Hamada, and Y. Saito: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 2569–73.
T. Sheppard and M.A. Zaidi: Met. Technol., 1982, vol. 9, pp. 368–74.
M.A. Zaidi and T. Sheppard: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 593–99.
L.G. Schulz: J. Appl. Phys., 1949, vol. 20, pp. 1033–36.
H.J. Bunge: Texture Analysis in Material Science, 1st ed., Butterworth and Co., London, 1982, pp. 1–41.
K. Pawlik: Phys. Status Solidi (b), 1986, vol. 134, pp. 477–83.
J. Pospiech and K. Lücke: Acta Metall., 1975, vol. 23, pp. 997–1007.
K. Lücke, J. Pospiech, J. Jura, and J. Hirsch: Z. Metallkd., 1986, vol. 77, pp. 312–21.
J.A. Venables and C.J. Harland: Phil. Mag., 1973, vol. 27, pp. 1193–200.
D.J. Dingley: Scanning Electron Microscopy, 1984, vol. 2, pp. 569–75.
B.L. Adams, S.I. Wright, and K. Kunze: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 819–31.
D.G. Brandon: Acta Metall., 1966, vol. 14, pp. 1479–84.
H. Grimmer, W. Bollmann, and D.H. Warrington: Acta Cryst., 1974, vol. 30, pp. 197–207.
M.L. Kronberg and F.H. Wilson: Trans. AIME, 1949, vol. 185, pp. 501–14.
W.T. Read and W. Shockley: Phys. Rev., 1950, vol. 78, pp. 275–89.
J.K. MacKenzie: Biometrica, 1958, vol. 45, pp. 229–40.
T.R. McNelley, D.L. Swisher, and M.T. Pérez-Prado: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 279–90.
T.R. McNelley, M.E. McMahon, and S.J. Hales: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 36, pp. 369–75.
M. Eddahbi, T.R. McNelley, and O.A. Ruano: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1093–102.
M.T. Pérez-Prado, G. González-Doncel, O.A. Ruano, and T.R. McNelley: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 2259–68.
O. Daaland and E. Nes: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 1389–411.
O. Daaland and E. Nes: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 1413–35.
H.E. Vatne, R. Shahani, and E. Nes: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4447–62.
K. Matsumoto, T. Shibayanagi, and Y. Umakoshi: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 439–51.
J. Hirsch, E. Nes, and K. Lücke: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 427–38.
J. Hirsch and K. Lücke: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 2863–82.
S. Panchanadeeswaran and D.P. Field: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 1683–92.
O. Engler: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 4827–40.
O. Engler: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 2743–53.
G. Wassermann: Z. Metallkd., 1963, vol. 54, pp. 61–5.
R.E. Smallman and C.S. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. A184, pp. 97–112.
C.S. Lee and B.J. Duggan: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 2691–9.
C.S. Lee, B.J. Duggan, and R.E. Smallman: Phil. Mag. Lett., 1993, vol. 68, pp. 185–90.
Y. Zhou, K.W. Neale, and L.S. Tóth: Text. Microstr., 1991, vol. 14–18, pp. 1055–60.
Y. Zhou, L.S. Tóth, and K.W. Neale: Acta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 3179–93.
G.D. Köhlhoff, B. Krentscher, and K. Lücke: Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Textures, C.M. Brakman, P. Jongenburger, and E.J. Mittemeijer, eds., Netherlands Society of Materials Science, Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 1984, pp. 95–100.
D.A. Hughes, Q. Liu, D.C. Chrzan, and N. Hansen: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 105–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Morris, J.G. Texture and grain-boundary evolutions of continuous cast and direct chill cast AA 5052 aluminum alloy during cold rolling. Metall Mater Trans A 34, 951–966 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0225-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0225-7