Abstract
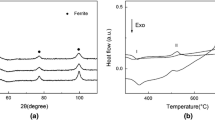
In the present study, the mechanical properties of Fe processed via severe plastic deformation (equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP)) at room temperature were investigated for the first time. The grain size of annealed Fe, with an initial grain size of about 200 µm, was reduced drastically during ECAP. After eight passes, the grain size reaches 200 to 400 nm, as documented by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The value of microhardness during pressing increases 3 times over that of the starting material after the first pass and increases slightly during subsequent pressing for higher-purity Fe. Examination of the value of microhardness after eight passes as a function of post-ECAP annealing temperature shows a transition from recovery to recrystallization, an observation that resembles the behavior reported for heavily deformed metals and alloys. The tensile and compression behaviors were examined. In tension, a drop in the engineering stress-engineering strain curve beyond maximum load was observed both in the annealed Fe and the ECAP Fe. This drop is related to the neck deformation. The fracture surface, examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), shows vein patterns, which is different from the dimples found on the fracture surface of annealed Fe. In compression, an initial strain-hardening region followed by a no-strain-hardening region was observed in the ECAP Fe. The yield strength in tension of the ECAP Fe was observed to be higher than that in compression. The strengthening mechanisms and softening behavior are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.E. Fougere, J.R. Weertman, and R.W. Siegel: NanoStruct. Mater., 1995, vol. 5, pp. 127–34.
T.R. Malow and C.C. Koch: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 2285–95.
T.R. Malow and C.C. Koch: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 6459–73.
S. Takaki, K. Kawasaki, and Y. Kimura: in Ultrafine Grained Materials, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Semiatin, C. Suryanarayana, N.N. Thadhani, and T.C. Lowe, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 247–55.
D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma: in Ultrafine Grained Materials, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Semiatin, C. Suryanarayana, N.N. Thadhani, and T.C. Lowe, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 309–18.
Y. Sakai, M. Ohtaguchi, Y. Kimura, and K. Tsuzaki: in Ultrafine Grained Materials, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Semiatin, C. Suryanarayana, N.N. Thadhani, and T.C. Lowe, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 361–70.
R.Z. Valiev, Y.V. Ivanisenko, E.F. Rauch, and B. Baudelet: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4705–12.
D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma: Scripta Mater., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 73–78.
K.T. Park, Y.S. Kim, J.G. Lee, and D.H. Shin: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. A293, pp. 165–72.
N. Tsuji, Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, and S. Tanigawa: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 40, pp. 795–800.
K. Nakashima, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 1589–99.
M. Furukawa, Y. Iwahashi, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, vol. A257, pp. 328–32.
K. Oh-ishi, Z. Horita, M. Furukawa, M. Nemoto, and T.G. Langdon: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 2011–13.
M.A. Meyers and K.K. Chawla: Mechanical Metallurgy Principles and Applications, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1984.
B.Q. Han and D.C. Dunand: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. A277, pp. 297–304.
B.D. Cullity: Elements of X-ray Diffraction, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Inc., Reading, MA, 1978.
H.P. Klug and L. Alexander: X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1974, p. 661.
A.K. Sinha: Ferrous Physical Metallurgy, Butterworth and Co., London, 1989, p. 98.
F. Scholz, J.H. Driver, and E. Woldt: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 40, pp. 949–54.
P. Cotterill and P.R. Mould: Recrystallization and Grain Growth in Metals, Surrey University Press, London, 1976, p. 55.
A.A. Nazarov, A.E. Romanov, and R.Z. Valiev: Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 1033–40.
G. Langford and M. Cohen: Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 623–38.
V.M. Segal: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1995, vol. A197, pp. 157–64.
T.H. Courtney: Mechanical Behavior of Materials, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New York, NY, 2000.
E. Schafler, M. Zehetbauer, A. Borbely, and T. Ungar: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1997, vols. A234–A236, pp. 445–48.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby: Deformation-Mechanism Maps: The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1982, p. 32.
N. Hansen: Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 2167–90.
Y. Bergstrom and H. Hallen: Met. Sci., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 341–47.
W.B. Morrison and R.L. Miller: in Ultrafine-Grain Metals, J.J. Burke and J. Weiss, eds., Syracuse University Press, Syracuse, NY, 1970, pp. 182–211.
T.G. Nieh, J. Wadsworth, C.T. Liu, G.E. Ice, and K.S. Chung: Mater. Trans., 2001, vol. 42, pp. 613–18.
A. Inoue, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, and K. Kurosaka: J. Mater. Res., 2001, vol. 16, pp. 2836–44.
T. Mukai, T.G. Nieh, Y. Kawamura, A. Inoue, and K. Higashi: Scripta Mater., 2002, vol. 46, pp. 43–47.
J.E. Carsley, W.W. Milligan, S.A. Hackey, and E.C. Aifantis: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 2479–81.
J.E. Carsley, A. Fisher, W.W. Milligan, and E.C. Aifantis: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 2261–71.
S. Kinoshita, P.J. Wray, and G.T. Horne: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1965, vol. 233, pp. 1902–04.
B.J. Brindley and J.T. Barnby: Acta Metall., 1966, vol. 14, pp. 1765–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, B.Q., Mohamed, F.A. & Lavernia, E.J. Mechanical properties of iron processed by severe plastic deformation. Metall Mater Trans A 34, 71–83 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0209-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0209-7