Abstract
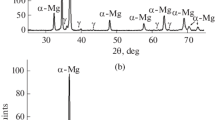
Amorphous magnesium-rich alloys Mg y X1-y (X=Ni or Cu and 0.82<y<0.89) have been produced by melt spinning. The crystallization kinetics of these alloys have been determined by in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) and isothermal and isochronal differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) combined with ex situ XRD. Microstructure analysis has been performed by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). Crystallization of the Mg-Cu alloys at high temperature takes place in two steps: primary crystallization of Mg, followed by simultaneous crystallization of the remaining amorphous phase to Mg and Mg2Cu. Crystallization of the Mg-Cu alloys at low temperatures takes place in one step: eutectic crystallization of Mg and Mg2Cu. Crystallization of the Mg-Ni alloys for a Mg content, y>0.85, takes place in two steps: primary crystallization of Mg and of a metastable phase (Mg∼5.5Ni, with Mg content y=0.85), followed by the decomposition of Mg∼5.5Ni. Crystallization of the Mg-Ni alloys for a Mg content y<0.85 predominantly takes place in one step: eutectic crystallization of Mg and Mg2Ni. Within the experimental window applied (i.e., 356 K<T<520 K and 0.82<y<0.89), composition dependence of the crystallization sequence in the Mg-Cu alloys and temperature dependence of the crystallization sequence in the Mg-Ni alloys has not been observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.T.W. Kempen, F. Sommer, and E.J. Mittemeijer: Max Planck Institute for Metals Research, Stuttgart, unpublished research, 2000.
A.T.W. Kempen, F. Sommer, and E.J. Mittemeijer: Max Planck Institute for Metals Research, Stuttgart, unpublished research, 2001.
F. Sommer, G. Bucher, and B. Predel: J. Phys. Coll., 1980, vol. 41, pp. 563–66.
G. Friedlmeier, M. Arakawa, T. Hirai, and E. Akiba: J. Alloys Compounds, 1999, vol. 292, pp. 107–17.
H. Feufel and F. Sommer: J. Alloys Compounds, 1995, vol. 224, pp. 42–54.
K. Micke and H. Ipser: Monatshefte Chemie, 1996, vol. 127, pp. 7–13.
V.I. Nizhenko, L.I. Floka, and G.P. Khilya: Russ. Metall., 1993, pp. 45–47.
K. Schubert and K. Anderko: Z. Metallkd., 1951, vol. 42, pp. 321–25.
P. Bagnoud and P. Feschotte: Z. Metallkd., 1978, vol. 69, pp. 114–20.
F. Gingl, P. Selvam, and K. Yvon: Acta Cryst., 1993, vol. B49, pp. 201–03.
U. Köster and U. Herold: in Glassy Metals I, Ionic Structure, Electronic Transport and Crystallization, H.-J. Günterodt and H. Beck, eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981, vol. 46, pp. 225–59.
W.A. Tiller: The Science of Crystallization, Macroscopic Phenomena and Defect Generation, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1991.
I. Telleria and J.M. Barandiaran: Thermochimica Acta, 1996, vols. 280–281, pp. 279–87.
W.H. Wang, Y.X. Zhuang, M.X. Pan, and Y.S. Yao: J. Appl. Phys., 2000, vol. 88, pp. 3914–18.
E.J. Mittemeijer: J. Mater. Sci., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 3977–87.
M. Avrami: J. Chem. Phys., 1939, vol. 7, pp. 1103–12.
M. Avrami: J. Chem. Phys., 1940, vol. 8, pp. 212–24.
M. Avrami: J. Chem. Phys., 1941, vol. 9, pp. 177–84.
J.W. Cahn: Acta Metall., 1956, vol. 4, pp. 449–59.
J.W. Christian: The Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1965.
O. Grong and O.R. Myhr: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 445–52.
W.A. Johnson and R.F. Mehl: Trans. Am. Inst. Min. (Metall.) Eng., 1939, vol. 135, pp. 416–41.
Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams 2, T.B. Massalski, ed., ASM, Materials Park, OH, 1990.
I. Bakonyi, F. Mehner, M. Rapp, A. Cziraki, H. Kronmüller, and R. Kirchheim: Z. Mettallkd., 1995, vol. 86, pp. 619–25.
W.H. Press, S.A. Teukolsky, W.T. Vetterling, and B.P. Flannery: Numerical Recipes in C, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1997.
International Centre of Diffraction Data (ICDD), PDF 35-0821, Pennsylvania, PA.
K. Yvon, W. Jeitschko, and E. Parthe: J. Appl. Cryst., 1977, vol. 10, pp. 73–74.
Atlas of Crystal Structure Types for Intermetallic Phases, J.L.C. Daams, P. Villars, and J.H.N.V. Vucht, eds., ASM, Materials Park OH, 1991.
G. Kreiner and H.F. Franzen: J. Alloys Compounds, 1995, vol. 221, pp. 15–36.
B. Chabot, K. Cenzual, and E. Parthe: Acta Cryst., 1980, vol. B36, pp. 2202–05.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kempen, A.T.W., Nitsche, H., Sommer, F. et al. Crystallization kinetics of amorphous magnesium-rich magnesium-copper and magnesium-nickel alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 33, 1041–1050 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0205-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0205-3