Abstract
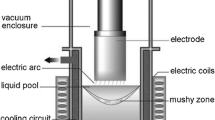
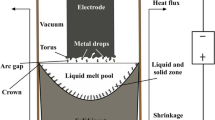
White spot is the term for a particulate dispersion lean in niobium found in vacuum arc remelted (VAR) ingots of niobium containing nickel-based superalloys, such as INCONEL718, that can be detrimental to the mechanical properties. While spot can result from exogenous fragments that fall into the VAR melt pool and remain incompletely melted. In this study, white spot formed when dendrite clusters fall-in from the shrinkage pipe of vacuum induction melted (VIM) electrodes is considered by simulations. The motion and dissolution of the dendrite cluster particles were simulated in the framework of a macroscopic heat and fluid flow model of the VAR process. Two scales of heat and mass transfer are considered within the cluster: interdendritic solute diffusion within particles and the thermal interaction between the particle and the bulk convective melt. The dissolution behavior of dendrite cluster fall-in was investigated for a range of initial particle conditions including solid fraction, Nb content, drop height, and initial temperature. The operational window where the exogenous particles completely dissolve was determined as a function of cluster size, density, and location. It was found that particles smaller than 3 mm are completely dissolved under all conditions simulated in this study. All factors studied demonstrated significant influence on particle dissolution. Particles with a solid fraction less than 0.5, a Nb content greater than 4 pct, or an initial temperature greater than 1400 K are likely to be dissolved immediately after entering the melt pool. Drop height and initial density had the greatest effect on particle dissolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Chen, W.H. Yang, K.-M. Chang, S.K. Mannan, and J.J. deBarbadillo: Proc. 1999 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe, NM, A. Mitchell, L. Ridgway, and M. Baldwin, eds., AVS, 1999, pp. 122–27.
P. Auburtin and A. Mitchell: Proc. 1999 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe, NM, A. Mitchell, L. Ridgway, and M. Baldwin, eds., AVS, 1999, pp. 18–34.
L.A. Jackman, G.E. Maurer, and S. Widge: Adv. Mater. Processes, 1993, vol. 5, pp. 18–25.
B.K. Damkroger, J.B. Kelley, M.E. Schlienger, J.A. Van Den Avyle, R.L. Williamson, and F.J. Zanner: in Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1994, pp. 125–35.
A. Mitchell: Proceedings of the 1986 Vacuum Metallurgical Conf. on Special Metals Melting and Processing, ISS, AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1989, pp. 55–61.
X. Xu, W. Zhang, P.D. Lee, and M. McLean: Proc. Mod. of Casting, Welding and Adv. Sol. Proc. IX, P.R. Sahm, P.N. Hansen, and J.G. Conley, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 574–81.
A. Jardy, S. Hans, and D. Ablitzer: Modeling of Casting, Welding and Advanced Solidification Processes VII, M. Cross and J. Campbell, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1995, pp. 205–12.
L.A. Bertram, J.A. Brooks, and D.G. Evans: Proc. 1999 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe, NM, A. Mitchell, ed., AVS, 1999, pp. 156–67.
P. Auburtin and A. Mitchell: Proc. 1997 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe, NM, A. Mitchell, ed., AVS, 1997, pp. 18–34.
W. Zhang, P.D. Lee, and M. McLean: Intermetallics and Superalloys: EUROMAT 99—Vol. 10, D.G. Morris, S. Naka, and P. Caron, eds., Wiley-VCH, New York, NY, 2000, pp. 123–28.
W. Zhang, P.D. Lee, M. McLean, and R.J. Siddall: Conf. 9th Int. Symp. on Superalloys, Seven Springs, PA, Sept. 17–21, 2000, T.M. Pollock, R.D. Kissinger, R.R. Bowman, K.A. Green, M. McLean, S.L. Olson, and J.J. Schirra, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 29–37.
P.D. Lee, R.M. Lothian, L.J. Hobbs, and M. McLean: Superalloys 1996, R.D. Kissinger, D.J. Deye, D.L. Anton, A.D. Cetel, M.V. Nathal, T.M. Pollock, and D.A. Woodford, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 435–42.
I. Kim, S. Elghobashi, and W.A. Sirignano: J. Fluid Mech., 1998, vol. 367, pp. 221–53.
R. Clift, J.R. Grace, and M.E. Weber: Bubbles, Drops and Particles, Academic Press, New York, NY, 1978, pp. 117–20.
C. Mo and A.S. Sangani: Phys. Fluids, 1994, vol. 6, pp. 1637–52.
D.R. Poirier: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1987, vol. 18B, pp. 245–55.
B.A. Grimes, J.J. Meyers, and A.I. Liapis: J. Chromatogr. A, 2000, vol. 890, pp. 61–72.
W.E. Ranz and W.R. Marshall, Jr.: Chem. Eng. Progr., 1952, vol. 48, pp. 173–80.
Y. Sahai and G.R. St. Pierre: Advances in Transport Processes in Metallurgical Systems, Elsevier Science, New York, NY, 1992, p. 15.
T.K. Sherwood and C.R. Wilke: Mass Transfer, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1975, p. 151.
N.P. Cheremisinoff: Handbook of Heat and Mass Transfer: Mass Transfer and Reactor Design, GulfPub. Co., Houston, TX, 1986, p. 67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Lee, P.D. & McLean, M. Numerical simulation of dendrite white spot formation during vacuum arc remelting of INCONEL718. Metall Mater Trans A 33, 443–454 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0105-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0105-6