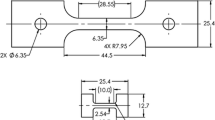
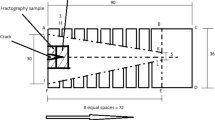
Abstract
Samples from two undermatched, multipass welds on 50.8-mm-thick HY-100 steel were tested using a novel microtensile test machine and the local material properties were investigated using a chemical analysis, metallography, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The microtensile test technique allowed samples from individual weld beads and weldmetal heat-affected zones to be tested in three orthogonal directions. Relationships between local microhardness and tensile properties were established. The filler metals for the two welds were MIL-70S and MIL-100S. The MIL-70S weld formed ferritic microstructures; the weld-metal heat-affected sites were predominantly polygonal ferrite, while the as-deposited regions were a mixture of lath and polygonal ferrite. This weld showed a large variation in properties from the central weld bead to the outer ones. The outermost site exhibited significant anisotropy in strength that was not revealed by microhardness measurements. The yield strength specification was 483 MPa, while the average at the center of the weld was 675 MPa and the outer sites had an average of 445 MPa. Elongation for the samples from the center was significantly lower as well, 5 pct as compared to 18 pct for the outer sites. The yield strength showed a strong correlation with the size of inclusions measured by TEM. Microprobe analysis found no dilution of the base metal alloying additions into the weld metal. The MIL-100S filler formed predominantly fine acicular ferrite throughout the weld. The strength was much more uniform; the yield strength specification was 690 MPa, while the center of the weld was 756 MPa and the outer sites had an average of 616 MPa. The inclusion size did not play an important role in the variation in mechanical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Sampath, D.A. Civis, and M.J. Kleinosky: Int. Symp. on Low-Carbon Steels for the 90’s, R. Asfahani and G. Tither, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 539–48.
S.K. Sampath, D.A. Civis, H. Dong, P.J. Konkol, and R.S. Green: Proc. High Performance Structural Steels, Cleveland, OH, Oct. 30–Nov. 1, 1995, ASM, Materials Park, OH, 1995, pp. 179–88.
J. Healy, J. Billingham, J.P. Chubb, R.L. Jones, and J. Galsworthy: Proc. Int. Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering—OMAE, ASME, New York, NY, 1993, vol. 3, part A, pp. 189–98.
T.J. Dawson and M. Yachnis: Welding J., 1977, vol. 56 (11), pp. 30–35.
J.W. Fisher and R.J. Dexter: Welding J., 1994, vol. 73 (1), pp. 35–43.
K. Satoh and M. Toyoda: Welding J., 1975, vol. 54 (9), pp. 311s-319s.
B.M. Patchett and D.G. Bellow: Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Welding and Energy Related Problems, 1983, pp. 269–78.
R.L. Tregoning: in Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics, R.S. Piascik, J.C. Newman, Jr., and N.E. Dowling, eds., 1997, ASTM, West Conshocken, PA, 1997, pp. 427–50.
R. Yee, L. Malik, and J. Morrison: Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics, J.H. Underwood, B.D. MacDonald, and M.R. Mitchell, eds., ASTM, West Conshocken, PA, 1997, pp. 450–68.
“Spoolarc 86 Electrode Tested in Accordance with AWS A5.18–93 for Electrodes of AWS/ASME Classification ER70S-6,” ESAB Welding and Cutting Products, Duluth, GA, 1996.
“Lincolnweld LA-100,” Lincoln Electric Company, Cleveland, OH, 1992.
F.B. Fletcher: “Average Chemistry and Mechanical Property Statistics for HY-100 Produced to MIL-S-16216K,” Lukens Steel, Metallurgical and Professional Services, personal communication, 1996.
R.E. Peterson: Stress Concentration Factors, Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY, 1974.
W.N. Sharpe, Jr.: Exp. Mech., 1968, vol. 8 (4), pp. 164–70.
W.N. Sharpe, Jr.: Opt. Eng., 1982, vol. 21, pp. 483–88.
W.N. Sharpe, Jr. and R.O. Fowler: in Small Specimen Test Techniques Applied to Nuclear Reactor Vessel Thermal Annealing and Plant Life Extension, William Corwin, Fahmy Haggag, and William Server, eds., ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1993.
D.A. LaVan: Ph.D. Dissertation, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, 1998, p. 322.
W.N. Sharpe, Jr., H. Zeng, Bin Yuan, and Shelby Wallace: Fracture ’94, 4th Nat. Conf. on Fracture, Johannesburg, South Africa, 1994.
B. Yuan and W.N. Sharper, Jr.: Fatigue ’96, Berlin, 6–10 May 1996, Berlin, Germany, 1996.
W.N. Sharpe, Jr., David A. LaVan, and Richard L. Edwards: Proc. 1997 Int. Conf. on Solid State Sensors and Actuators, IEEE, Chicago, IL, 1997, pp. 607–10.
W.N. Sharpe, Jr., D.A. LaVan, and A. McAleavey: Proc. 1997 ASME Congr., ASME, Dallas, TX, 1997.
M. Legros, K.J. Hemker, D.A. LaVan, W.N. Sharpe, Jr., M.N. Rittner, and J.R. Weertman: Proc. 1996 MRS Fall Symp.: Nanophase and Nanocomposite Materials II, MRS, Boston, MA, 1997, vol. 457, pp. 273–78.
M. Zupan, D. LaVan, and K.J. Hemker: Proc. MRS Fall Meeting: High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys VII, MRS, Boston, MA, 1997, vol. 460, pp. 171–76.
D.A. LaVan: Experimental Techniques, 1999, vol. 23 (3), pp. 31–34.
D.A. LaVan and W.N. Sharpe, Jr.: Exp. Mech., 1999, vol. 39 (3).
“Military Specification: Electrodes and Rods—Welding, Bare, Solid, or Alloyed Cored, Low Alloy Steel,” MIL-E-23765/2E(SH), Naval Sea Systems Command, Arlington, VA, 1994.
MIL-S-16216, “Steel Plate, Alloy, Structural, High Yield,” 1987, p 44.
K.H. Schwalbe: Eng. Fract. Mech., 1977, vol. 9, pp. 795–832.
A.G. Fox and D.G. Brothers: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 32 (7), pp. 1061–66.
R.W. Hertzburg: Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1989.
S.H. Goods and L.M. Brown: Acta Metallurgica, 1979, vol. 27 (1), pp. 1–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LaVan, D.A., Sharpe, W.N. Local properties of undermatched steel weld metal. Metall Mater Trans A 32, 913–922 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0348-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0348-7