Abstract
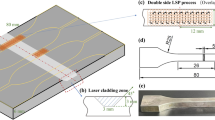
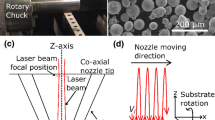
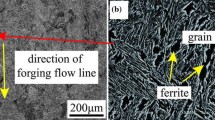
Laser cladding of gas-atomized M2 high-speed steel on the mild steel substrate was performed using scan rates of 1 to 10 mm/s, scan line spacings of 0.1 to 0.5 mm, and powder feed rates of 1 to 10 g/min, for a given laser power of 400 W. This article presents a detailed study of the microstructural evolution during laser cladding. The effect of scan rate, scan line spacing, and powder feed rate on cooling rate can be described in terms of the cladding-layer thickness, i.e., the thinner the layer, the higher the cooling rate. The degree of metastability in the laser-clad microstructure can be understood in terms of the lattice parameter of the bcc phase. The lattice parameter of the bcc phase increased with increasing layer thickness and reached a maximum value at a thickness of 0.3 mm. Correspondingly, the microstructure varied from a cellular or dendritic structure of δ ferrite and austenite to a mixture of martensite and retained austenite. However, further increasing the layer thickness led to a decrease of both the lattice parameters of the bcc phase and the proportion of retained austenite in the martensite. This was accompanied by an increase of the amount of carbide at the prior austenitic grain boundaries and a decrease of the carbon content in the martensite and retained austenite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Singh: J. Mater. Sci., 1994, vol. 29, pp. 5232–58.
Y.P. Hu, C.W. Chen, and K. Mukherjee: J. Mater. Sci., 1998, vol. 33, pp. 1287–92.
G. Hoyle: High Speed Steel, Butterworth & Co. Ltd., London, 1988, pp. 1–5.
R.H. Barkalow, R.W. Kraft, and J.I. Goldstein: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 919–26.
E.J. Galda and R.W. Kraft: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1727–33.
D.A. Porter and K.E. Easterling: Phase Transformation in Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed., Chapman & Hall, London, 1997, pp. 251–55.
F.A. Kirk: Powder Metall., 1981, vol. 24, pp. 70–74.
J.J. Rayment and B. Cantor: Met. Sci., 1978, vol. 12, pp. 156–63.
Young-Won Kim, P.R. Strutt, and H. Nowotny: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 881–86.
Leif Ahman: Metall. Trans., 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1829–35.
A. Tauqir, H. Nowotny, and P.R. Strutt: Metall. Trans., 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 3021–26.
C. Kim: J. Heat Treating, 1979, vol. 1, pp. 43–51.
F.R. Wilson and B.A. Harding: BCIRA J., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 318–31.
S.A. David and J.M. Vitek: Int. Mater. Rev., 1989, vol. 34, pp. 213–45.
H. Fredriksson: Met. Sci., 1976, vol. 10, pp. 77–86.
R.W.K. Honeycombe and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Steels, 2nd ed., Edward Arnold, London, 1995, pp. 89–96.
P.A. Molian and H.S. Rajasekhara: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1986, vol. 5, pp. 1292–94.
H. Fredriksson and J. Stjerndahl: Met. Sci., 1982, vol. 16, pp. 575–84.
P.R. Strutt, M. Tuli, M. Nowotny, and B.K. Har: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 36, pp. 217–22.
N. Suutala: Metall. Trans., 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 191–97.
S.J. Donachie and G.S. Ansell: Metall. Trans., 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1863–75.
R. Sare and R.W.K. Honeycombe: J. Mater. Sci., 1978, vol. 13, pp. 1991–2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, H.J., Chang, I.T.H. Microstructural evolution during laser cladding of M2 high-speed steel. Metall Mater Trans A 31, 2615–2625 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-0206-z
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-0206-z