Abstract
Summary
Our purpose was to investigate the co-authorship network of Iranian researchers in the field of osteoporosis. We used 1328 documents retrieved from databases of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science in the analysis. The network had 183 authors in 13 clusters, low cohesion, and slow information flow between its members.
Purpose
This study aims to investigate the pattern and characteristics of cooperation between Iranian researchers in the field of osteoporosis through the co-authorship social network analysis.
Methods
All papers on osteoporosis with at least one Iranian author were retrieved from medical databases of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science from 2009 to 2019. After the removal of duplicates, the title and abstract of the papers were reviewed by two independent reviewers, and screening was performed according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The data were entered into the BibExecl software, and the different spelling forms in the author names were manually merged. The authors’ co-occurrence matrix was then developed and entered into the UCINET software and the cohesion indexes (density, diameter, and average distance) and centrality indexes (degree, betweenness, closeness, and eigenvector) for the co-authorship network were estimated. The institutions and countries of the authors of the entered papers were also used in the network analysis and their socio-graphs were drawn.
Results
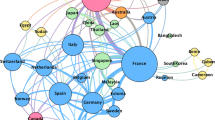
We used 1328 documents in the analysis. The co-authorship network was constructed only for authors with at least 5 papers. The network had 183 nodes (authors) in 13 clusters. Its density was 0.063 and its number of components was 2. The large component encompassed 95.6% and the small component 4.4% of authors. The average distance in the main component of the network was 3 and its diameter was 6. Larijani B was ranked first in the network in terms of degree, betweenness, closeness, and eigenvector centrality. In terms of the contribution of organizations in osteoporosis publications, Tehran University of Medical Sciences (with 35.5% of papers published in WoS database), Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (14.7%), and Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (9.3%) retained in the first to third place, respectively. In papers published on the WoS, most Iranian authors have collaborated with authors from the USA, Belgium, Canada, and the UK respectively.
Conclusion
The co-authorship network had low cohesion with slow information flow between its members. The collaboration with young researchers by the network’s active, efficient, and broker authors will lead to the maintenance and development of the network.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sözen T, Özışık L, Başaran NÇ (2017) An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol 4(1):46–56
Biglu MH, Ghavami M, Biglu S (2014) Authorship, institutional and citation metrics for publications on postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 25(4):1337–1343
Rajabi M, Ostovar A, Akbari Sari A, Sajjadi-Jazi SM, Fahimfar N, Larijani B et al (2020) Direct costs of osteoporotic fractures in Iran. [Unpublished manuscript]. In press
Cao L, Pauleen D, Wang WYC, Whitworth B (2011) Structural analysis in the Collaborative Research Network -- The Empirices of Chinese Meteorology Researchers. In: 2011 Fourth International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization, pp 15–19 April 2011
Sadoughi F, Valinejadi A, Shirazi MS, Khademi R (2016) Social network analysis of Iranian researchers on medical parasitology: a 41 year co-authorship survey. Iran J Parasitol 11(2):204–212
Ghafouri HB, Mohammadhassanzadeh H, Shokraneh F, Vakilian M, Farahmand S (2014) Social network analysis of Iranian researchers on emergency medicine: a sociogram analysis. Emerg Med J 31(8):619–624
Salamati P, Soheili F (2016) Social network analysis of Iranian researchers in the field of violence. Chin J Traumatol 19(5):264–270
Scott J (1988) Social network analysis. Sociology. 22(1):109–127
Askarishahi M, Ghasemi N, Fallahzade H, Ardekani MA, Afkhamiardekani A (2018) Comparing of decision tree with logistic regression model in evaluating osteoporosis. Tolooe Behdasht 17(1):14–23
Persson O, Danell R, Schneider JW (2009) How to use Bibexcel for various types of bibliometric analysis. Celebrating scholarly communication studies: a Festschrift for Olle Persson at his 60th Birthday. 5:9–24
Borgatti SP, Everett MG, Freeman LC (2002) Ucinet 6 for windows. software for social network analysis. Harvard MA: Analytic Technologies
Hansen DL, Shneiderman B, Smith MA, Himelboim I (2020) Chapter 3 - Social network analysis: measuring, mapping, and modeling collections of connections. In: Hansen DL, Shneiderman B, Smith MA, Himelboim I (eds) Analyzing Social Media Networks with NodeXL, 2nd edn. Morgan Kaufmann, pp 31–51
Sattarzadeh A, Galyani Moghaddam G, Momeni E (2016) The analysis of the structure of scientific collaboration networks in basic medical sciences in the science citation index from 1996 to 2013. Knowl Stud 2(6):1–20 [Persian]
Golbeck J (2013) Chapter 3 - Network structure and measures. In: Golbeck J (ed) Analyzing the Social Web. Morgan Kaufmann, Boston, pp 25–44
Perez C, Germon R (2016) Chapter 7 - Graph creation and analysis for linking actors: application to social data. In: Layton R, Watters PA (eds) Automating open source intelligence. Syngress, Boston, pp 103–129
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 84(2):523–538
Waltman L, Van Eck NJ, Noyons EC (2010) A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J Inf 4(4):629–635
Morlacchi P, Wilkinson I, Young L. A network analysis of the evolution of personal research networks among IMP researchers. 2005.
Billah SM, Gauch S (2015) Social network analysis for predicting emerging researchers. In: 2015 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K). IEEE
Hazeri A, Malekzade F, Aminian DS (2015) A study of scientific collaboration and co-authorship networks within knowledge management papers in the category of Library Science, Information Science in the Web of Science. Quart Knowl Inf Manag J 2(2):61–74 [Persian]
Mohammadian S, Vaziri E (2017) Analysis and visualization of scientific collaboration of Iran universities of medical sciences using social network analysis metrics based on Web of Science database. Payavard Salamat 11(1):43–56 [Persian]
Availability of data and material
All data used in this paper are available at Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus databases.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the Osteoporosis Research Center of Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences (grant no. 1398-2-103-916).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Search strategy preparation and searching the databases were performed by KKh, RA, NF, MS, FH, AO, and BL. Reviewing and screening of the papers were done by HY and SB. The analysis was performed by MJM and AA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KKh, MJM, and AO, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute, affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Science.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 1.12 mb)
Appendix. Search strategy
Appendix. Search strategy
Database | Search strategy | Execution date | No. of records |
|---|---|---|---|
PubMed | (“Osteoporosis” [Mesh] OR Osteop* [TIAB] OR “Bone Density” [Mesh] OR “Bone Density” [TIAB] OR “Bone Densities” [TIAB] OR “Bone Mineral” [TIAB] OR “Bone Loss” [TIAB] OR “Bone health” [TIAB] OR “Bone Quality” [TIAB] OR “Bone Marker” [TIAB] OR “Bone Markers” [TIAB] OR “Bone Mass” [TIAB] OR “Bone Turnover” [TIAB] OR “bone turn-over” [TIAB] OR “Bone Resorption” [TIAB] OR “Bone Formation” [TIAB] OROsteolysis [TIAB] OR ossification [TIAB] OR “osseous density” [TIAB] OR “skeletal mass” [TIAB] OR “Bone Diseases, Metabolic” [Mesh] OR (Bone [TIAB] AND Diseases [TIAB] AND Metabolic [TIAB]) OR “Bone Remodeling” [TIAB] OR “Bone Regeneration” [TIAB] OR “Densitometry” [Mesh] OR Densitometr* [TIAB] OR (Trabecular [TIAB] AND bone [TIAB] AND score [TIAB])OR “DXA” [TIAB] OR “DEXA Scan” [TIAB] OR “DEXA Scans” [TIAB] OR “Photon Absorptiometry” [TIAB] OR (Absorptiometry [TIAB] AND (“Dual-Energy” [TIAB] OR DPX [TIAB] OR “Dual X-Ray” [TIAB])) OR ((Densitometry [TIAB] OR Photodensitometry [TIAB]) AND X-Ray [TIAB])) AND IRAN[AD] | 12 Sep 2019 | 1584 |
Web of Science (Indexes: SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, BKCI-S, BKCI-SSH, ESCI, CCR-EXPANDED, IC.) | TS=(Osteop* OR (Bone NEAR/3 (Densit* OR Mineral OR Loss OR health* OR Quality OR Marker OR Mass OR Turnover OR turn-over OR Resorption OR Formation)) OR Osteolysis OR ossification OR (osseous NEAR/3 density) OR (skeletal NEAR/3 mass) OR (Bone NEAR/3 Diseases NEAR/3 Metabolic) OR “Bone Remodeling” OR “Bone Regeneration” OR Densitometr* OR (Trabecular NEAR/3 bone NEAR/3 score) OR “DXA” OR (DEXA NEAR/3 Scan) OR (Photon NEAR/3 Absorptiometry) OR (Absorptiometry NEAR/3 (“Dual-Energy” OR DPX OR “Dual X-Ray”)) OR ((Densitometry OR Photodensitometry) NEAR/3 X-Ray)) AND AD=(IRAN) | 12 Sep 2019 | 2452 |
Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (Osteop* OR (Bone W/3 (Densit* OR Mineral OR Loss OR health* OR Quality OR Marker OR Mass OR Turnover OR turn-over OR Resorption OR Formation)) OR Osteolysis OR ossification OR (osseous W/3 density) OR (skeletal W/3 mass) OR (Bone W/3 Diseases W/3 Metabolic) OR “Bone Remodeling” OR “Bone Regeneration” OR Densitometr* OR (Trabecular W/3 bone W/3 score ) OR “DXA” OR (DEXA W/3 Scan) OR (Photon W/3 Absorptiometry) OR (Absorptiometry W/3 (“Dual-Energy” OR DPX OR “Dual X-Ray”))OR ((Densitometry OR Photodensitometry) W/3 X-Ray)) AND AFFIL (IRAN) | 12 Sep 2019 | 2979 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalagi, K., Mansourzadeh, M.J., Aletaha, A. et al. Co-authorship network analysis of Iranian researchers on osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos 16, 74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-021-00914-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-021-00914-9