Abstract
Objective
To interpret the pharmacology of quercetin in treatment of atherosclerosis (AS).
Methods
Fourteen apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE−/−) mice were divided into 2 groups by a random number table: an AS model (ApoE−/−) group and a quercetin treatment group (7 in each). Seven age-matched C57 mice were used as controls (n=7). Quercetin [20 mg/(kg·d)] was administered to the quercetin group intragastrically for 8 weeks for pharmacodynamic evaluation. Besides morphological observation, the distribution of CD11b, F4/80, sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) and P21 was assayed by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence to evaluate macrophage infiltration and tissue senescence. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MSC/MS) was performed to study the pharmacology of quercetin against AS. Then, simultaneous administration of an apelin receptor antagonist (ML221) with quercetin was conducted to verify the possible targets of quercetin. Key proteins in apelin signaling pathway, such as angiotensin domain type 1 receptor-associated proteins (APJ), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), tissue plasminogen activator (TPA), uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) and angiotensin II receptor 1 (AT1R), were assayed by Western blot.
Results
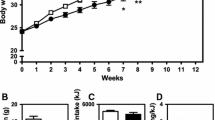
Quercetin administration decreased lipid deposition in arterial lumen and improved the morphology of ApoE−/− aortas in vivo. Quercetin decreased the densities of CD11b, F4/80 and P21 in the aorta and increased the level of serum apelin and the densities of APJ and Sirt1 in the aorta in ApoE−/− mice (all P<0.05). Plasma metabolite profiling identified 118 differential metabolites and showed that quercetin affected mainly glycerophospholipids and fatty acyls. Bioinformatics analysis suggested that the apelin signaling pathway was one of the main pathways. Quercetin treatment increased the protein expressions of APJ, AMPK, PGC-1α, TPA and UCP1, while decreased the AT1R level (all P<0.05). After the apelin pathway was blocked by ML221, the effect of quercetin was abated significantly, confirming that quercetin attenuated AS by modulating the apelin signaling pathway (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
Quercetin alleviated AS lesions by up-regulation the apelin signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rikitake Y. The apelin/APJ system in the regulation of vascular tone: friend or foe? J Biochem 2021;169:383–386.
Yang R, Fang W, Liang J, Lin C, Wu S, Yan S, et al. Apelin/APJ axis improves angiotensin II-induced endothelial cell senescence through AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Arch Med Sci 2018;14:725–734.
Li M, Fang H, Hu J. Apelin-13 ameliorates metabolic and cardiovascular disorders in a rat model of type 2 diabetes with a high-fat diet. Mol Med Rep 2018;18:5784–5790.
Nagano K, Kwon C, Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Kim JD, Kishikawa N, et al. Cooperative action of APJ and α1A-adrenergic receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells induces vasoconstriction. J Biochem 2019;166: 383–392.
Song J, Tang J, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Zhong J. Targeting the elabela/apelin-apelin receptor axis as a novel therapeutic approach for hypertension. Chin Med J 2022;135:1019–1026.
Liu W, Yan J, Pan W, Tang M. Apelin/Elabela-APJ: a novel therapeutic target in the cardiovascular system. Ann Transl Med 2020;8:243.
Luo G, Xiang L, Xiao L. Quercetin alleviates atherosclerosis by suppressing oxidized LDL-induced senescence in plaque macrophage via inhibiting the p38MAPK/p16 pathway. J Nutr Biochem 2023;116:109314.
Zhou W, Wang F, Qian X, Luo S, Wang Z, Gao X, et al. Quercetin protects endothelial function from inflammation induced by localized disturbed flow by inhibiting NRP2-VEGFC complex. Int Immunopharmacol 2023;116:109842.
Ren K, Jiang T, Zhao GJ. Quercetin induces the selective uptake of HDL-cholesterol via promoting SR-BI expression and the activation of the PPARγ/LXRα pathway. Food Funct 2018;9:624–635.
Jiang Y, Jiang L, Wang Y, Ma D, Li X. Quercetin attenuates atherosclerosis via modulating oxidized LDL-induced endothelial cellular senescence. Front Pharmacol 2020;11:512.
Ren K, Jiang T, Zhao GJ. Quercetin induces the selective uptake of HDL-cholesterol via promoting SR-BI expression and the activation of the PPARγ/LXRα pathway. Food Funct 2018;9:624–635.
Patel RV, Mistry BM, Shinde SK, Syed R, Singh V, Shin HS. Therapeutic potential of quercetin as a cardiovascular agent. Eur J Med Chem 2018;155:889–904.
Kawai Y, Nishikawa T, Shiba Y, Saito S, Murota K, Shibata N, et al. Macrophage as a target of quercetin glucuronides in human atherosclerotic arteries: implication in the anti-atherosclerotic mechanism of dietary flavonoids. J Biol Chem 2008;283:9424–9434.
Xiao L, Liu L, Guo X, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou F, et al. Quercetin attenuates high fat diet-induced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice: a critical role of NADPH oxidase. Food Chem Toxicol 2017;105:22–33.
Zhou Q, Chen L, Tang M, Guo Y, Li L. Apelin/APJ system: a novel promising target for anti-aging intervention. Clin Chin Acta 2018;487:233–240.
Chen T, Wu B, Lin R. Association of apelin and apelin receptor with the risk of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Oncotarget 2017;8:57345.
Chun HJ, Ali ZA, Kojima Y, Kundu RK, Sheikh AY, Agrawal R, et al. Apelin signaling antagonizes Ang II effects in mouse models of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 2008;118:3343–3354.
Bertrand C, Valet P, Castan-Laurell I. Apelin and energy metabolism. Front Physiol 2015;6:115.
Bertrand C, Pradère J, Geoffre N, Deleruyelle S, Masri B, Personnaz J, et al. Chronic apelin treatment improves hepatic lipid metabolism in obese and insulin-resistant mice by an indirect mechanism. Endocrine 2018;60:112–121.
Hirose A, Terauchi M, Osaka Y, Akiyoshi M, Kato K, Miyasaka N. Effect of soy lecithin on fatigue and menopausal symptoms in middle-aged women: a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr J 2018;17:4.
Stegemann C, Pechlaner R, Willeit P, Langley SR, Mangino M, Mayr U, et al. Lipidomics profiling and risk of cardiovascular disease in the prospective population-based bruneck study. Circulation 2014;129:1821–1831.
van der Veen JN, Kennelly JP, Wan S, Vance JE, Vance DE, Jacobs RL. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2017;1859:1558–1572.
Zhu Y, Feng Y, Shen L, Xu D, Wang B, Ruan K, et al. Effect of metformin on the urinary metabolites of diet-induced-obese mice studied by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-TOF/MS). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2013;925:110–116.
Rai R, Ghosh AK, Eren M, Mackie AR, Levine DC, Kim SY, et al. Downregulation of the apelinergic axis accelerates aging, whereas its systemic restoration improves the mammalian healthspan. Cell Rep 2017;21:1471–1480.
Maeda M, Tsuboi T, Hayashi T. An inhibitor of activated blood coagulation factor x shows anti-endothelial senescence and anti-atherosclerotic effects. J Vasc Res 2019;56:181–190.
Craige SM, Kröller-Schön S, Li C, Kant S, Cai S, Chen K, et al. PGC-1α dictates endothelial function through regulation of eNOS expression. Sci Rep 2016;6:38210.
Jung TW, Park HS, Choi GH, Kim D, Lee T. β-Aminoisobutyric acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammation and insulin resistance in adipocytes through AMPK-mediated pathway. J Biomed Sci 2018;25:27.
Barroso WA, Victorino VJ, Jeremias IC, Petroni RC, Ariga S, Salles TA, et al. High-fat diet inhibits PGC-1α suppressive effect on NF-κB signaling in hepatocytes. Eur J Nutr 2018;57:1891–1900.
Han F, Zhang Y, Shao M, Mu Q, Jiao X, Hou N, et al. C1q/TNF-related protein 9 improves the anti-contractile effects of perivascular adipose tissue via the AMPK-eNOS pathway in diet-induced obese mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2018;45:50–57.
Cheng L, Wang J, Dai H, Duan Y, An Y, Shi L, et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue: a novel therapeutic strategy for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adipocyte 2021;10:48–65.
Gaspar RC, Pauli JR, Shulman GI, Muñoz VR. An update on brown adipose tissue biology: a discussion of recent findings. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2021;320:E488–E495.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liu LQ performed zoology experiment, and drafted the manuscript. Zhang P performed zoology experiments and animal care. Qi YZ and Li H collected samples and analyzed data. Jang YH revised the manuscript. Yang CH designed the experiments. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supported by Shandong Province ‘Taishan Scholar’ Construction Project Funds (No. 2018-35)
Electronic supplementary material
Appendix 1
TOP 30 Differential Metabolites in Plasma Non-targeted Metabonomics by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography/tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) (n = 7, Que vs Model)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Lq., Zhang, P., Qi, Yz. et al. Quercetin Attenuates Atherosclerosis via Modulating Apelin Signaling Pathway Based on Plasma Metabolomics. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29, 1121–1132 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-023-3645-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-023-3645-9