Abstract
Objective
To explore the anti-inflammatory effects of ethyl lithospermate in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine-derived macrophages and zebrafish, and its underlying mechanisms.
Methods
3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assays were performed to investigate the toxicity of ethyl lithospermate at different concentrations (12.5–100 µ mol/L) in RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 12 h to establish an inflammation model in vitro, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) were assessed by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Western blot was used to ascertain the protein expressions of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65, phospho-STAT3 (p-STAT3, Tyr705), inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) α, and phospho-I κB α (p-IκB α, Ser32), and confocal imaging was used to identify the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and p-STAT3 (Tyr705). Additionally, the yolk sacs of zebrafish (3 days post fertilization) were injected with 2 nL LPS (0.5 mg/mL) to induce an inflammation model in vivo. Survival analysis, hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, observation of neutrophil migration, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were used to further study the anti-inflammatory effects of ethyl lithospermate and its probable mechanisms in vivo.
Results
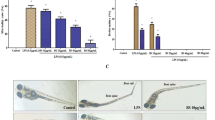
The non-toxic concentrations of ethyl lithospermate have been found to range from 12.5 to 100 µ mol/L. Ethyl lithospermate inhibited the release of IL-6 and TNF-α(P<0.05 or P<0.01), decreased IκBα degradation and phosphorylation (P<0.05) as well as the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and p-STAT3 (Tyr705) in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells (P<0.01). Ethyl lithospermate also decreased inflammatory cells infiltration and neutrophil migration while increasing the survival rate of LPS-stimulated zebrafish (P<0.05 or P<0.01). In addition, ethyl lithospermate also inhibited the mRNA expression levels of of IL-6, TNF-α, IκBα, STAT3, and NF-κB in LPS-stimulated zebrafish (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Ethyl lithospermate exerts anti-Inflammatory effected by inhibiting the NF-κB and STAT3 signal pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages and zebrafish.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Data will be made available on request.
References
Medzhitov R. The spectrum of inflammatory responses. Science 2021;374:1070–1075.
Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, Bi Y, Chen Q, Han X, et al. Research progress on the relationship between atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules 2018;8:80–91.
Khandia R, Munjal A. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 2020;119:199–245.
Henein MY, Vancheri S, Longo G, Vancheri F. The role of inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:12906.
Ozben T, Ozben S. Neuro-inflammation and antiinflammatory treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Biochem 2019;72:87–89.
Calsolaro V, Edison P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers Dement 2016;12:719–732.
Lambertsen KL, Finsen B, Clausen BH. Post-stroke inflammation-target or tool for therapy? Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:693–714.
Ren J, Fu L, Nile SH, Zhang J, Kai G. Salvia miltiorrhiza in treating cardiovascular diseases: a review on its pharmacological and clinical applications. Clin Ther 2019;10:753.
Arulselvan P, Fard MT, Tan WS, Gothai S, Fakurazi S, Norhaizan ME, et al. Role of antioxidants and natural products in inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016;2016:1–15.
Meim XD, Cao YF, Che YY, Li J, Shang ZP, Zhao WJ, et al. Danshen: a phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Front Pharmacol 2019;17:59–80.
Li ZM, Xu SW, Liu PQ. Salvia miltiorrhiza Burge (Danshen): a golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2018;39:802–824.
Ye T, Xiong D, Chen L, Li Y, Gong S, Zhang L, et al. Effect of Danshen on TLR2-triggered inflammation in macrophages. Phytomedicine 2020;70:153228.
Wang W, Li SS, Xu XF, Yang C, Niu XG, Yin SX, et al. Danshensu alleviates pseudo-typed SARS-CoV-2 induced mouse acute lung inflammation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022;43:771–780.
Min X, Zeng X, Zhao W, Han Z, Wang Y, Han Y, et al. Cryptotanshinone protects dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental ulcerative colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal inflammation. Phytother Res 2020;34:2639–2648.
Xia ZB, Yuan YJ, Zhang QH, Li H, Dai JL, Min JK. Salvianolic acid B suppresses inflammatory mediator levels by downregulating NF-kappa B in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Med Sci Monit 2018;24:2524–2532.
Xu L, Shen P, Bi Y, Chen J, Xiao Z, Zhang X, et al. Danshen Injection ameliorates STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in association with suppression of oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory factors and fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol 2016;38:385–394.
Ding B, Lin C, Liu Q, He Y, Ruganzu JB, Jin H, et al. Tanshinone II A attenuates neuroinflammation via inhibiting RAGE/NF-kappa B signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. J Neuroinflammation 2020;17:302.
Zhang Y, Feng X, Du M, Ding J, Liu P. Salvianolic acid B attenuates the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis by regulating MAPKs/NF-kappaB signaling pathways in LDLR-/- mice and RAW264.7 cells. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2022;36:3946320221079468.
Li NP, Liu JS, Liu JW, Tian HY, Zhou HL, Zheng YR, et al. Monoterpenoid indole alkaloids from the fruits of Gelsemium elegans and their anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorganic Chem 2021;107:104624.
He LJ, Liu JS, Luo D, Zheng YR, Zhang YB, Wang GC, et al. Quinolizidine alkaloids from Sophora tonkinensis and their anti-inflammatory activities. Fitoterapia 2019;139:104391.
Ryu SJ, Choi HS, Yoon KY, Lee OH, Kim KJ, Lee BY. Oleuropein suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cell and zebrafish. J Agric Food Chem 2015;63:2098–2105.
Zhou H, Cao H, Zheng Y, Lu Z, Chen Y, Liu D, et al. Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, attenuates acute inflammation in zebrafish and RAW 264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2020;249:112427.
Xie Y, Meijer AH, Schaaf MJM. Modeling inflammation in zebrafish for the development of anti-inflammatory drugs. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020;8:620984.
Zhang Y, Takagi N, Yuan B, Zhou Y, Si N, Wang H, et al. The protection of indolealkylamines from LPS-induced inflammation in zebrafish. J Ethnopharmacol 2019;243:112122.
Sulukan E, Ghosigharehagaji A, Baran A, Yildirim S, Bolat I, Ceyhun SB. A versatile toxicity evaluation of ethyl carbamate (urethane) on zebrafish embryos: morphological, physiological, histopathological, immunohistochemical, transcriptional and behavioral approaches. Toxicol Lett 2021;353:71–78.
Lu Z, Cao H, Liu D, Zheng Y, Tian C, Liu S, et al. Optimal combination of anti-inflammatory components from Chinese medicinal formula Liang-Ge-San. J Ethnopharmacol 2021;269:113747.
Wang X, Guo D, Li W, Zhang Q, Jiang Y, Wang Q, et al. Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) restricts MD2/TLR4-MyD88 complex formation and signalling in acute myocardial infarction-induced heart failure. J Cell Mol Med 2020;24:10677–10692.
Song Z, Feng J, Zhang Q, Deng S, Yu D, Zhang Y, et al. Tanshinone II A protects against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by regulating microglial activation and polarization via NF-κB pathway. Front Pharmacol 2021;12:641848.
Frangogiannis NG. The inflammatory response in myocardial injury, repair, and remodelling. Nat Rev Cardiol 2014;11:255–265.
Wolf D, Ley K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 2019;124:315–327.
Goswami SK, Ranjan P, Dutta RK, Verma SK. Management of inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Res 2021;173:105912.
Verma SK, Krishnamurthy P, Barefield D, Singh N, Gupta R, Lambers E, et al. Interleukin-10 treatment attenuates pressure overload-induced hypertrophic remodeling and improves heart function via signal transducers and activators of transcription 3-dependent inhibition of nuclear factor-κB. Circulation 2012;126:418–429.
Liberale L, Ministrini S, Carbone F, Camici GG, Montecucco F. Cytokines as therapeutic targets for cardio - and cerebrovascular diseases. Basic Res Cardiol 2021;116:23.
Frangogiannis NG. Regulation of the inflammatory response in cardiac repair. Circ Res 2012;110:159–173.
Lei W, Li X, Li L, Huang M, Cao Y, Sun X, et al. Compound Danshen Dripping Pill ameliorates post ischemic myocardial inflammation through synergistically regulating MAPK, PI3K/AKT and PPAR signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2021;281:114438.
Giridharan S, Srinivasan M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J Inflamm Res 2018;11:407–419.
Wu H, Liu H, Zhao X, Zheng Y, Liu B, Zhang L, et al. IKIP negatively regulates NF-κB activation and inflammation through inhibition of IKKα/β phosphorylation. J Immunol 2020;204:418–427.
Sun SC. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2017;17:545–558.
Liu H, Ma S, Xia H, Lou H, Zhu F, Sun L. Anti-inflammatory activities and potential mechanisms of phenolic acids isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza f. alba roots in THP-1 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 2018;222:201–207.
Yang J, Liao X, Agarwal MK, Barnes L, Auron PE, Stark GR. Unphosphorylated STAT3 accumulates in response to IL-6 and activates transcription by binding to NF kappa B. Genes Dev 2007;21:1396–1408.
Hoesel B, Schmid JA. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 2013;12:86.
MacRae CA, Peterson RT. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2015;14:721–731.
Liew PX, Kubes P. The neutrophil’s role during health and disease. Physiol Rev 2019;99:1223–1248.
Castanheira FVS, Kubes P. Neutrophils and NETs in modulating acute and chronic inflammation. Blood 2019;133:2178–2185.
Hidalgo A, Libby P, Soehnlein O, Aramburu IV, Papayannopoulos V, Silvestre Roig C. Neutrophil extracellular traps: from physiology to pathology. Cardiovasc Res 2022;118:2737–2753.
Mortaz E, Alipoor SD, Adcock IM, Mumby S, Koenderman L. Update on neutrophil function in severe inflammation. Front Immunol 2018;9:2171.
Zheng Y, Liu S, Fan C, Zeng H, Huang H, Tian C, et al. Holistic quality evaluation of Qingwen Baidu Decoction and its anti-inflammatory effects. J Ethnopharmacol 2020;263:113145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhou CH and Yang H performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Zhou CH and Zou LF analyzed data in this study. Liu DF and Zou LF assisted in many experiments. Yu LZ, Cao HH, and Deng LE contributed to the reagents. Wang ZW, Lu ZB and Liu JS designed the idea and supervised this study. All authors participated in this work and agreed to publish this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supported by Guangdong Province Universities and Colleges Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (No. GDHVPS2018) and Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by the China Association of Chinese Medicine (No. 2019-QNRC2-C14)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Ch., Yang, H., Zou, Lf. et al. Ethyl Lithospermate Reduces Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation through Inhibiting NF-κB and STAT3 Pathways in RAW 264.7 Cells and Zebrafish. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29, 1111–1120 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-023-3643-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-023-3643-y