Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tibetan medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills (RZPs) in the treatment of patients with motor and sensory dysfunction after stroke.
Methods
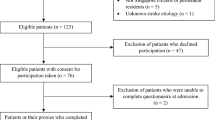
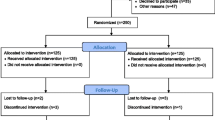
A total of 120 convalescent stroke patients hospitalized in the Rehabilitation Department of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine from June 2017 to December 2019 were enrolled in this trial. Patients were assigned to control (60 cases) and research (60 cases) groups by computer random assignment. All patients received internal treatment and modern rehabilitation training. On this basis, the research group was given oral RZPs for 4 weeks, while the control group was given oral placebo. The primary outcome was motor function of the affected side evaluated by simplified Fugl-Meyer Motion Assessment Scale (FMA-M). The secondary outcomes included sensory function, activity of daily living (ADL), quality of life, balance function, and pain, which were assessed by Fugl-Meyer Sensory Assessment Scale (FMA-S), Modified Barthel Index (MBI), Special Scale of the Quality of Life (SS-QOL), Berg Balance Scale (BBS), and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), respectively. All of the assessments were performed before treatment, and 4 and 8 weeks after treatment. Vital signs, liver and kidney functions, routine blood test, blood coagulation profile, and routine urinalysis of patients were monitored.
Results
After 4-week treatment, the FMA-M, BBS and FMA-S scores in the research group significantly increased compared with the control group (P<0.05). At 8-week follow-up, the BBS and MBI scores in the research group were higher than the control group (P<0.05). There was no statistical difference between the 2 groups in the SS-QOL and VAS scores at 4 and 8 weeks (P>0.05). Moreover, after treatment, there was no significant difference in vital signs, liver and kidney functions, blood coagulation function, blood routine and urinalysis between the 2 groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion
RZPs improved limb motor, balance, and sensory functions of stroke patients during recovery period with good safety. (Trial registration No. NCT04029701)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia J. Status of hand function rehabilitation after stroke. Geriatr Med Health Care (Chin) 2015;21:129–131.
Chen Z, Liu YG, He X, Li JT, Chen W, Li XH, et al. Research progress of stroke rehabilitation based on data mining technology. Chin J Rehabil Med (Chin) 2019;34:229–233.
Zhang SH, Wang YL, Zhang CX, Zhang CP, Xiao P, Li QF, et al. Effect of interactive dynamic scalp acupuncture on post-stroke cognitive function, depression, and anxiety: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Chin J Integr Med 2022;28:106–115.
Chen SQ, Cai DC, Chen JX, Yang H, Liu LS. Altered brain regional homogeneity following contralateral acupuncture at Quchi (LI 11) and Zusanli (ST 36) in ischemic stroke patients with left hemiplegia: an fMRI study. Chin J Integr Med 2020;26:20–25.
Fan JJ, Li X, Sun HH, Li QE, Wu HC, Ren XQ. Excavation of the connotation of white meridians disease based on Tibetan medical theory and analysis of the composition and usage of Baimai Ointment. China J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2022;47:1409–1414.
Zheng LJ, Ren XQ, Wang MQ, Mao M, Gao JQ, Zhou ZY, et al. Exploring the rule of the diagnosis and treatment of stroke based on the Tibetan medical theory of white meridian. Modern Tradit Chin Med Mater Med World Sci Technol (Chin) 2017;19:370–374.
Luo YM, Ren XQ, Song HR, Xi DJ, Tao XH. Research progress of Tibetan medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills in the past 20 years. Chin J Ethn Med (Chin) 2017;23:69–72.
Duo J, Hu QW. Clinical observation of 219 cases of white meridian (neuropathic pain) treated by Ruyi Zhenbao Pills. Inner Mongol J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;28:17–18.
Wang HM, Sun H. Observation on clinical efficacy of Ruyi Zhenbao Pills combined with Valaciclovir Tablets on herpes zoster. Shanxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2013;29:28–29.
Zhai SM. Clinical observation on Tibetan medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Pharm Chin Minor (Chin) 2015;21:23.
Liu RY, Wu WJ, Tan R, Xie B, Zhong ZD, He JP, et al. Intervention effect of Tibetan patent medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills in acute ischemic stroke in rats. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2015;40:556–559.
Xie B, Liu RY, He JP, Tan R. Study on preventing efficacy of combined using of three classical Tibetan prescriptions in focal cerebral ischemia injury of rats. Modern Tradit Chin Med Mater Med World Sci Technol (Chin) 2014;16:1846–1849.
Duojieladan, Hong M, Chen QH, Liu YJ, Han M, Sun W. Toxicological study on Tibetan medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills. Food Drug (Chin) 2014;16:413–416.
Chinese Neurology Association, Chinese Neurosurgery Association. Key points of diagnosis of various cerebrovascular diseases (1995). Chin J Neurol (Chin) 1996;29:60–61.
Li LQ, Li CM, Zhao HL, Huang Y, Wei W. Meta-analysis of clinical studies of edaravone combined with Xueshuantong in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. J Cardiovasc Cerebrovasc Dis Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 2015;13:1598–1604.
Rao ML. Abstract of guidelines for the prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases in China. J Stroke Neurolog Dis (Chin) 2005;22:484–487.
Zhang T. Guidelines for the rehabilitation of stroke in China. Chin J Front Med (Electr Version, Chin) 2012;4:55–76.
Sanford J, Moreland J, Swanson LR, Stratford PW, Gowland C. Reliability of the Fugl-Meyer assessment for testing motor performance in patients following stroke. Phys Ther 1993;73:447–454.
Wang YL, ed. Neurological rehabilitation evaluation method. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House;2015:503–504.
Giang P, Williams A, Argyros L. Automated extraction of the Barthel Index from clinical texts. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2013;2013:486–495.
Zhao Y, Pan YH. Quality of life scale for stroke patients. Chin J Clin (Chin) 2013;7:10212–10214.
Jin DM, Yan TB, Zeng HH. A study on the validity and reliability of the Berg Balance Scale. Chin J Rehabil Med (Chin) 2003;18:24–26.
Huskisson EC, Jone J, Scott PJ. Application of visual analogue scales to the measurement of functional capacity. Rheumatol Rehabil 1976;15:185–187.
Gu LJ, Zhang JJ. Effect of Ruyi Zhenbao Tablets on the improvement of sequelae of cerebral ischemia in rats. Chin J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2013;31:1288–1230.
Pharmacopoeia Committee of the Ministry of Health, People’s Republic of China. People’s Republic of China Health Ministry of Medicine Standards—Tibetan medicine (volume 1). Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Publishing House;1995:123–124.
Xu ZG, Bao XH, Tian QJ. A review of research on Ruyi Zhenbao Pills (Tablets). Chin Folk Ther (Chin) 2020;28:106–109.
Wang HP, Ma ZY, Li L. Research status of the incidence and treatment of white meridian disease in Tibetan medicine. Chin Ethn Folk Med (Chin) 2012;21:9–10.
Liu XY, Wang LE, Fu JL. Clinical observation of Ruyi Zhenbao Pills in treating post-stroke sequelae. Shandong Med J (Chin) 2010;50:88.
Huang LX. Clinical trial of Ruyi Zhenbao Pill in the treatment of motor and sensory dysfunction after stroke [Dissertation]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine;2018.
Wang XM. Clinical observation of Tibetan medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills combined with rehabilitation training in treating hemiplegic shoulder pain. Chin J Ethn Med (Chin) 2013;19:11–13.
Liu RY, Wu WJ, Tan R, Xie B, Zhong ZD, He JP, et al. Intervention effect of Tibetan medicine Ruyi Zhenbao Pills on the subacute stage of ischemic stroke in rats. Chin J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2015;40:556–559.
Zhang X, Fan LN, Tan R, Li JC, He LL, Gu J. A preliminary comparative study on the rules of cardiovascular medication of three classic Tibetan medicine prescriptions. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2014;25:747–748.
Zhu XY, Wang HY, Li HP, Wang HP, Lan XH, Song RS, et al. Ruyi Zhenbao Pill’s protective and regeneration-promoting effects on zebrafish nerve injury. Drug Evaluat Res (Chin) 2017;40:307–313.
Acknowledgement
We sincerely thank for the consent of all patients and their families. We also thank for the help of blinding from Methodological Team in Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ling SS and Pan RH designed this study and wrote the draft. Chen HX conceived this study and revised the manuscript. Zhan LC helped with the operation training, including drugs distribution and assessment test. Li M was responsible for cases inclusion and randomization. Yang ZJ and Zhan LC helped with the data analysis. Yang HD and Ling SS registered and submitted this trial to ClinicalTrials.gov. All authors have read and approved the final version of this paper.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest of publication or others.
Supported by SHEN Bao-fan Academic Experience Inheritance Studio of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, Ss., Pan, Rh., Zhan, Lc. et al. Ruyi Zhenbao Pills for Patients with Motor and Sensory Dysfunction after Stroke: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 28, 872–878 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-3577-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-3577-9