Abstract
Objective
To study the protective effect of anthocyanins extracted from Vaccinium Uliginosum (VU) on retinal 661W cells against microwave radiation induced retinal injury.
Methods
661W cells were divided into 6 groups, including control, model [661W cells radiated by microwave (30 mW/cm2, 1 h)] and VU groups [661W cells pretreated with anthocyanins extracted from VU (25, 50, 100 and 200 µg/mL, respectively) for 48 h, and radiated by microwave 30 mW/cm2, 1 h]. After treatment with different interventions, the cell apoptosis index (AI) was determined using Heochst staining; contents of malonaldehyde (MDA), glutataione (GSH), and activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) were measured. mRNA expressions of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase 1(HO-1) were detected by real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and the expression of HO-1 protein was examined by Western blot analysis. Nucleus and cytoplasm were separated and Nrf2 protein expression was further verified by Western blot analysis.
Results
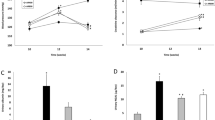
There was significant difference in AI among the groups (F=322.83, P<;0.05). Compared with the control group, AI was significantly higher in the model group and was lower in 4 VU-pretreated groups (P<;0.05). Linear regression analysis showed the decline of AI was in a dose-dependent manner with VU treatment (r=0.8419, P<;0.05). The MDA and GSH contents of 661W cells in VU-treated groups were significantly lower than the model group (P<;0.05). Compared with the model group, the SOD activity in the VU-treated groups (50, 100 and 200 µg/mL) was significantly higher (all P<;0.05). The Nrf2 and HO-1 mRNA expressions were slightly increased after irradiation, and obviously increased in 100 µg/mL VU-treated group. After irradiation, the relative expressions of HO-1 and Nrf2 proteins in nucleus were slightly increased (P<;0.05), and the changes in cytoplasm were not obvious, whereas it was significantly increased in both nucleus and cytoplasm in the VU treatment groups.
Conclusions
Anthocyanins extracted from VU could reduce apoptosis, stabilize cell membrane, and alleviate oxidant injury of mouse retinal photoreceptor 661W cells. The mechanism might be through activating Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway and inducing HO-1 transcription and translation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanjay S, Stefan D, Anna S, Katharina R, Marloes E, Benjamin S, et al. Radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure in everyday microenvironments in Europe: a systematic literature review. J Expos Sci Environm Epidemiol 2018;28:147–160.
Matus D, Pavol K, Eva M, Alexandra S, Beata G, Ekaterina N, et al. Microwaves from mobile phone induce reactive oxygen species but not DNA damage, preleukemic fusion genes and apoptosis in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Sci Rep 2019;9:16182–16197.
Stein Y, Udasin IG. Electromagnetic hypersensitivity (EHS, microwave syndrome)-review of mechanisms. Environ Res 2020;186:109445–10955.
Suetov AA, Alekperov SI. Acute ocular lesions after exposure to electromagnetic radiation of ultrahigh frequency (an experimental study). Vestn Oftalmol 2019;135:41–49.
Einat KP, Tamar H, Galia MR, Manuel M, Patricia LB, Niels K, et al. Activation of signaling cascades by weak extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017;43:1533–1546.
Hao YH, Zhang J, Wang H, Wang HY, Dong J, Xu XP, et al. HIF-1α regulates COXIV subunits, a potential mechanism of self-protective response to microwave induced mitochondrial damages in neurons. Sci Rep 2018;8:10403–10419.
Jo K, Bae GY, Cho K, Park SS, Suh HJ, Hong KB. An anthocyanin-enriched extract from Vaccinium uliginosum improves signs of skin aging in UVB-induced photodamage. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020;9:844–860.
Kim YH, Bang CY, Won EK, Kim JP, Choung SY. Antioxidant activities of Vaccinium uliginosum L. extract and its active components. J Med Food 2009;12:885–992.
Wang Y, Zhao L, Lu F, Yang X, Deng Q, Ji B, et al. Retinoprotective effects of bilberry anthocyanins via antioxidant, anti-Inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in a visible light-induced retinal degeneration model in pigmented rabbits. Molecules 2015;20:22395–22410.
Ooe E, Kuse Y, Yako T, Sogon T, Nakamura S, Hara H, et al. Bilberry extract and anthocyanins suppress unfolded protein response induced by exposure to blue LED light of cells in photoreceptor cell line. Mol Vis 2018;24:621–632.
Lennart H, Michael C, Tarmo K, Lena H. High radiofrequency radiation at Stockholm Old Town: an explosimeter study including the Royal Castle, Supreme Court, three major squares, and the Swedish Parliament. Mol Clin Oncol 2017;6:462–476.
Wei AM, Yang XS, Wang Y, He GL, Zhou Z, Zhang GB, et al. The injury effects of microwave exposure on visual performance and retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) in rats. Chin J Industr Hygiene Occupat Dis (Chin) 2012;30:172–177.
Brkljača Bottegaro N, Gotić J, Šuran J, Brozić D, Klobučar K, Bojanić K, et al. Effect of prolonged submaximal exercise on serum oxidative stress biomarkers (d-ROMs, MDA, BAP) and oxidative stress index in endurance horses. BMC Vet Res 2018;14:216–227.
Lee SG, Brownmiller CR, Lee SO, Kang HW. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of anthocyanins of Trifolium pratense (red clover) in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW-267.4 macrophages. Nutrients 2020;12:1089–1106.
Hernandez DF, Cervantes EL, Luna-Vital DA, Mojica L. Food-derived bioactive compounds with anti-aging potential for nutricosmetic and cosmeceutical products. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020;8:1–16.
Kutsyr O, Sánchez-Sáez X, Martínez-Gil N, de Juan E, Lax P, Maneu V, et al. Gradual increase in environmental light intensity induces oxidative stress and inflammation and accelerates retinal neurodegeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2020;61:1–19.
Yin L, Pi YL, Zhang MN. The effect of Vaccinium uliginosum on rabbit retinal structure and light-induced function damage. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:299–303.
Nutrient Data Laboratory Beltsville Human Nutrition Research Center Agricultural Research Service U.S. Department of Agriculture. USDA database for the proanthocyanidin content of selected foods release 2. 2015[EB/OL]. Available at: http://www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata/flav.
Narayanankutty A, Job JT, Narayanankutty V. Glutathione, an antioxidant tripeptide: dual roles in carcinogenesis and chemoprevention. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2019;20:907–917.
Gusti AMT, Qusti SY, Bahijri SM, Toraih EA, Bokhari S, Attallah SM, et al. Glutathione S-transferase (GSTT1 rs17856199) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS2 rs2297518) genotype combination as potential oxidative stress-related molecular markers for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2021;14:1385–1403.
Farooqui Z, Mohammad RS, Lokhandwala MF, Banday AA. Nrf2 inhibition induces oxidative stress, renal inflammation and hypertension in mice. Clin Exp Hypertens 2020;10:1–6.
Younis NS, Abduldaium MS, Mohamed ME. Protective effect of geraniol on oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity: role of the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020;9:977–987.
Chenet AL, Duarte AR, de Almeida FJS, Andrade CMB, de Oliveira MR. Carvacrol depends on heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and mitochondria-related protection in the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells line exposed to hydrogen peroxide. Neurochem Res 2019;44:884–896.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yin L contributed to the conception of the study; Yin L and Fan SJ conducted the experiment and wrote the manuscript; Zhang MN analyzed the data. All author read the paper and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, L., Fan, Sj. & Zhang, Mn. Protective Effects of Anthocyanins Extracted from Vaccinium Uliginosum on 661W Cells Against Microwave-Induced Retinal Damage. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 28, 620–626 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3527-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3527-y