Abstract
Objective
To investigate the potential mechanisms of electroacupuncture (EA) to prevent ischemic stroke.
Methods
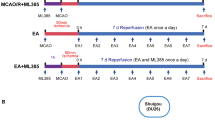
The method of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was employed to establish a rat model of ischemic stroke. Seventy-eight Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into the sham group, MCAO + EA control (EC) group, and MCAO + EA (EA) group according to a random number table (n=26 per group). EA was applied to the acupoints of Baihui (DU 20) and Shenting (DU 24) 5 min and 6 h, respectively after the onset of MCAO. Rats in the sham and EC groups received only light isoflurane anesthesia for 30 min after MCAO. The neuroprotective effects of EA were evaluated by rota-rod test, neurological deficit scores and infarct volumes. Additionally, Nissl staining and immunostaining were performed to examine brain damage, rod formation, cellular apoptosis, and neuronal loss induced by ischemia. The activities of caspase-3, and expression levels of cofilin and p-cofilin in mitochondria and cytoplasm after ischemic injury were determined by Western blot.
Results
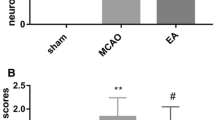
Compared with the EC group, EA significantly improved neuromotor function and cognitive ability after ischemic stroke (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Therapeutic use of EA also resulted in a significant decrease of cofilin rod formation and microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2) degradation in the cortical penumbra area compared with the EC rats (P<0.01). Furthermore, Western blot analysis showed that EA stimulation significantly inhibited mitochondrial translocation of cofilin and caspase-3 cleavage (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Additionally, brain damage (infarct volume and neuropathy), cellular apoptosis and neuronal loss induced by ischemia were remarkably suppressed by EA in the cortical penumbra of rats (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusion
EA treatment after ischemic stroke may attenuate ischemic brain injury and cellular apoptosis through the regulation of mitochondrial translocation of cofilin, a novel mechanism of EA therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019;139:e56–e528.
Zerna C, Thomalla G, Campbell BCV, Rha JH, Hill MD. Current practice and future directions in the diagnosis and acute treatment of ischaemic stroke. Lancet 2018;392:1247–1256.
Catanese L, Tarsia J, Fisher M. Acute ischemic stroke therapy overview. Circ Res 2017;120:541–558.
Liu AJ, Li JH, Li HQ, Fu DL, Lu L, Bian ZX, et al. Electroacupuncture for acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Chin Med 2015;43:1541–1566.
Zhan J, Pan R, Zhou M, Tan F, Huang Z, Dong J, et al. Electroacupuncture as an adjunctive therapy for motor dysfunction in acute stroke survivors: a systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ Open 2018;8:e017153.
Chen SQ, Cai DC, Chen JX, Yang H, Liu LS. Altered brain regional homogeneity following contralateral acupuncture at Quchi (LI 11) and Zusanli (ST 36) in ischemic stroke patients with left hemiplegia: an fMRI study. Chin J Integr Med 2020;26:20–25.
Long M, Wang Z, Zheng D, Chen J, Tao W, Wang L, et al. Electroacupuncture pretreatment elicits neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats associated with transient receptor potential vanilloid 1-mediated anti-oxidant stress and anti-inflammation. Inflammation 2019;42:1777–1787.
Jiang T, Wu M, Zhang Z, Yan C, Ma Z, He S, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuated cerebral ischemic injury and neuroinflammation through α 7nAChR-mediated inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in stroke rats. Mol Med 2019;25:22.
Jiang C, Yang S, Tao J, Huang J, Li Y, Ye H, et al. Clinical efficacy of acupuncture treatment in combination with RehaCom cognitive training for improving cognitive function in stroke: a 2 × 2 factorial design randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2016;17:1114–1122.
Liu W, Wu J, Huang J, Zhuo P, Lin Y, Wang L, et al. Electroacupuncture regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity via mir-134-mediated LIMK1 function in rats with ischemic stroke. Neural Plast 2017;2017:9545646.
Wang WW, Xie CL, Lu L, Zheng GQ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of Baihui (GV20)-based scalp acupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke. Sci Rep 2014;4:3981.
He J, Zhao C, Liu W, Huang J, Liang S, Chen L, et al. Neurochemical changes in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex associated with electroacupuncture for learning and memory impairment. Int J Mol Med 2018;41:709–716.
Xing Y, Wang MM, Feng YS, Dong F, Zhang F. Possible involvement of PTEN signaling pathway in the anti-apoptotic effect of electroacupuncture following ischemic stroke in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2018;38:1453–1463.
Chi L, Du K, Liu D, Bo Y, Li W. Electroacupuncture brain protection during ischemic stroke: a role for the parasympathetic nervous system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2018;38:479–491.
Posadas I, Perez-Martinez FC, Guerra J, Sanchez-Verdu P, Cena V. Cofilin activation mediates Bax translocation to mitochondria during excitotoxic neuronal death. J Neurochem 2012;120:515–527.
Chua BT, Volbracht C, Tan KO, Li R, Yu VC, Li P. Mitochondrial translocation of cofilin is an early step in apoptosis induction. Nat Cell Biol 2003;5:1083–1089.
Madineni A, Alhadidi Q, Shah ZA. Cofilin inhibition restores neuronal cell death in oxygen-glucose deprivation model of ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 2016;53:867–878.
Alhadidi Q, Bin Sayeed MS, Shah ZA. Cofilin as a promising therapeutic target for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 2016;7:33–41.
Chen B, Wang G, Li W, Liu W, Lin R, Tao J, et al. Memantine attenuates cell apoptosis by suppressing the calpain-caspase-3 pathway in an experimental model of ischemic stroke. Exp Cell Res 2017;351:163–172.
Zhou F, Guo J, Cheng J, Wu G, Xia Y. Electroacupuncture increased cerebral blood flow and reduced ischemic brain injury: dependence on stimulation intensity and frequency. J Appl Physiol 2011;111:1877–1887.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989;20:84–91.
Sun M, Zhao Y, Gu Y, Xu C. Inhibition of nNOS reduces ischemic cell death through down-regulating calpain and caspase-3 after experimental stroke. Neurochem Int 2009;54:339–346.
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 1999;22:391–397.
Liu L, Wang D, Wong KS, Wang Y. Stroke and stroke care in China: huge burden, significant workload, and a national priority. Stroke 2011;42:3651–3654.
Sun J, Shi J, Hou J, Guo C, Heng X, Qi G. Electroacupuncture protects rats from ischemic brain injury via coffilin in mice. J Cell Biochem 2020;121:43–48.
Zhou H, Yang C, Bai F, Ma Z, Wang J, Wang F, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates brain damage through targeting of neuronal calcium sensor 1 by miR-191a-5p after ischemic stroke. Rejuvenation Res 2017;20:492–505.
Wabnitz GH, Goursot C, Jahraus B, Kirchgessner H, Hellwig A, Klemke M, et al. Mitochondrial translocation of oxidized cofilin induces caspase-independent necrotic-like programmed cell death of T cells. Cell Death Dis 2010;1:e58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chen B and Qi DS conceived the idea and designed the experiments. Chen B, Lin WQ, Li ZF and Zhong XY performed the experiments and interpreted the experimental results. Zhao HJ, You XF, Wang J and Chen B participated in the study design and data analysis. Chen B, Qi DS and Lin WQ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the current version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81804175 and 81803883), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2019J01497), Foundation of Fujian Key Laboratory of Rehabilitation Technology (No. KF2019006), Special Research Project of National Clinical Research Base of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. JDZX2019040), and Educational Research Project for Young and Middle-Aged Teachers of Education Bureau of Fujian Province (No. JT180216)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Lin, Wq., Li, Zf. et al. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Ischemic Brain Injury and Cellular Apoptosis via Mitochondrial Translocation of Cofilin. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 705–712 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3335-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3335-4