Abstract
Objective
To screen the active components from Fuzheng Huayu Recipe (FZHY) and redesign a new recipe composed of the active components, and validate the effect of active components formulation from FZHY against liver fibrosis.
Methods
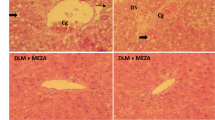
Thirty-two components from FZHY were evaluated for their activities against liver fibrosis respectively, with 6 kinds of cell models in vitro, including oxidative stressed hepatocyte in L-02, hypoxia injured/proliferative hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells in SK-HEP-1 and human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (HHSEC), and activated hepatic stellate cell in LX-2. The comprehensive activity of each component against liver fibrosis was scored according to the role of original herbs in FZHY and cell functions in fibrogenesis. Totally 7 active components were selected and combined with equal proportion to form a novel active components formulation (ACF). The efficacy of ACF on liver fibrosis were evaluated on activation of LX-2 and proliferation of HHSEC in vitro and in liver fibrosis model mice induced by dimethylnitrosamine (DMN). Totally 72 mice were divided into 6 groups using a random number table, including normal, high-dose ACF control (20 µ mol/L × 7 components/kg body weight), model, low-, medium-, high-dose ACF groups (5, 10, 20 µ mol/L × 7 components/kg body weight, respectively). Hematoxylin eosin and Sirius red stainings were used to observe inflammation and fibrosis change of liver tissue; scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were utilized to observe the effect of ACF on ultrastructure of hepatic sinusoids.
Results
Fifteen components from FZHY showed higher scores for their activity on against liver fibrosis. Among them, 7 components including tanshinone II A, salvianolic acid B, cordycepin, amygdalin, quercetin, protopanaxatriol, and schizandrin B were recombined with equal proportions to form ACF. ACF at 1,2, 4 µ mol/L showed strong inhibitory effects on activation of LX-2 and proliferation of HHSEC in vitro (all P<0.01). Compared with the model group, ACF attenuated liver collagen deposition, improved sinusoidal capillarization in a dose-dependent manner (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
ACF exerts a satisfactory effect against experimental liver fibrosis and attenuates sinusoidal capillarization, which warrant a further research and development for herbal components formulation on liver fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mercedes F, David S, Jordi B, Isabelle C, Massimo P, Jaume B. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol 2009;50:604–620.
DeLeve LD. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2015;61:1740–1746.
Thabut D, Shah V. Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease: new targets for the treatment of portal hypertension?. J Hepatol 2010;53:976–980.
Friedman Scott L. Hepatic fibrosis: emerging therapies. Dig Dis 2015;33:504–507.
Lee Youngmin A, Wallace Michael C, Friedman Scott L. Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: a translational success story. Gut 2015;64:830–841.
Liu P, Hu YY, Liu C, Xu LM, Liu CH, Sun KW, et al. Multicenter clinical study on Fuzhenghuayu Capsule against liver fibrosis due to chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:2892–2899.
Hassanein T, Box TD, Tong MJ, Pozza R, Rossaro L, Glenn JS, et al. A phase II, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter study to assess the antifibrotic activity of Fuzheng Huayu in chronic hepatitis C patients with hepatic fibrosis. Hepatol Int 2014;8:S308–S309.
Liu CH, Hu YY, Xu LM, Liu C, Liu P. Effect of Fuzheng Huayu Formula and its actions against liver fibrosis. Chin Med 2009;4:38–53.
Liu HL, Lv J, Zhao ZM, Xiong AM, Tan Y, Glenn Jeffrey S, et al. Fuzhenghuayu Decoction ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by attenuating experimental sinusoidal capillarization and liver angiogenesis. Sci Rep 2019;9:18719.
Zhao ZM, Liu HL, Sun X, Guo T, Shen L, Tao YY, et al. Levistilide A inhibits angiogenesis in liver fibrosis via vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway. Exp Bio Med 2017;242:974–985.
Lv J, Tan Y, Zhao ZM, Huang K, Shen L, Tao YY, et al. Fuzheng Huayu components formula exerted anti-liver fibrosis through inhibiting angiogenesis. World Chin Med (Chin) 2015;10:186–191.
Jamall IS, Finelli VN, Que Hee SS. A simple method to determine nanogram levels of 4-hydroxyproline in biological tissues. Anal Biochem 1981;112:70–75.
Friedman Scott L. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;7:425–436.
Liu CH, Zhao ZM, Lv J. Advances in the understanding and treatment of liver fibrosis in traditional Chinese medicine. J Clin Hepatol (Chin) 2019;35:728–733.
Cui XW, Zhang GJ. Component Chinese medicine and Chinese medicine modernization. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2009;20:1290–1291.
Zhang BL, Wang YY. Basic research on key scientific issues of TCM prescription-modern Chinese medicine was developed by the combination of components. Chin J Nat Med (Chin) 2005;3:258–261.
Huang K, Zhao ZM, Liu HL, Sun X, Lv J, Tao YY, et al. Evaluation of cryptotanshinone inhibition of angiogenesis in human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica (Chin) 2016;51:1257–1262.
Zhu CW, Lv J, Zhao ZM, Tao YY, Liu CH. Effect of schisantherin A inhibit liver sinusoid endothelial cell function and action against liver fibrosis relating to angiogenesis. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2016;41:279–284.
Guo T, Liu ZL, Zhao Q, Zhao ZM, Liu CH. A combination of astragaloside I, levistilide A and calycosin exerts anti-liver fibrosis effects in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2018;39:1483–1492.
Xu MM, Wang XH, Zou Y, Zhong XS. Key role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver fibrosis. Biosci Trends 2017;11:163–168.
Greuter T, Shah VH. Hepatic sinusoids in liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis: new pathophysiological insights. J Gastroenterol 2016;51:511–519.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liu CH designed the project; Tan Y, Sun X and Liu HL performed the experiments; Sun X, Lyu J and Zhao ZM analyzed the data; Sun X and Lyu J drafted the manuscript; Liu CH critically revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supported by the Major Projects of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2014ZX10005001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81603467, 81730109) and the Third Batch of Open Projects of Shanghai Innovation Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine Health Service (No. ZYJKFW201811013)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Tan, Y., Lyu, J. et al. Active Components Formulation Developed from Fuzheng Huayu Recipe for Anti-Liver Fibrosis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 28, 538–544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3293-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3293-x